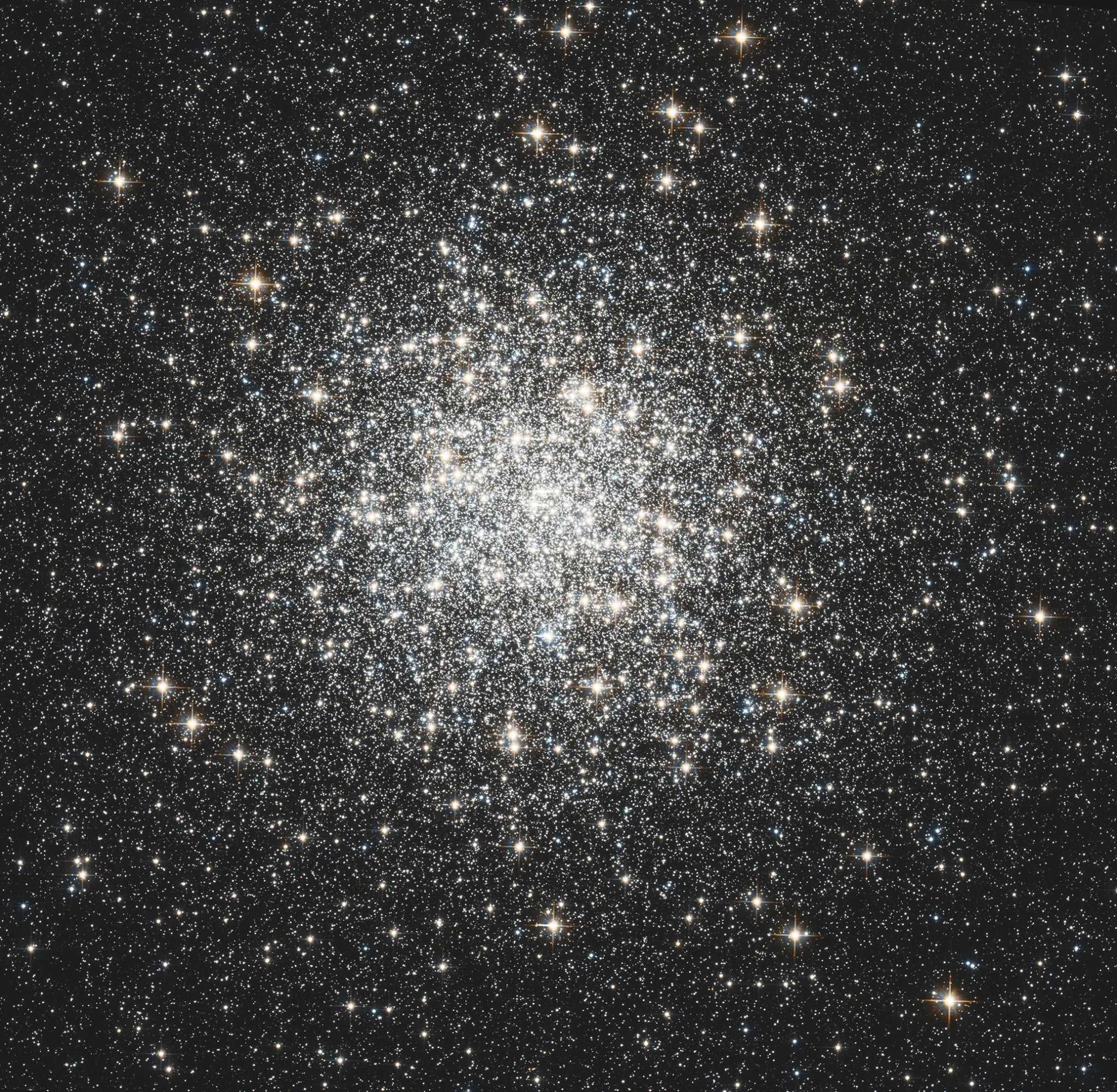
Messier 3
Messier 3 holds more than 500,000 stars.
Distance
34,000 light-years
Apparent Magnitude
6.2
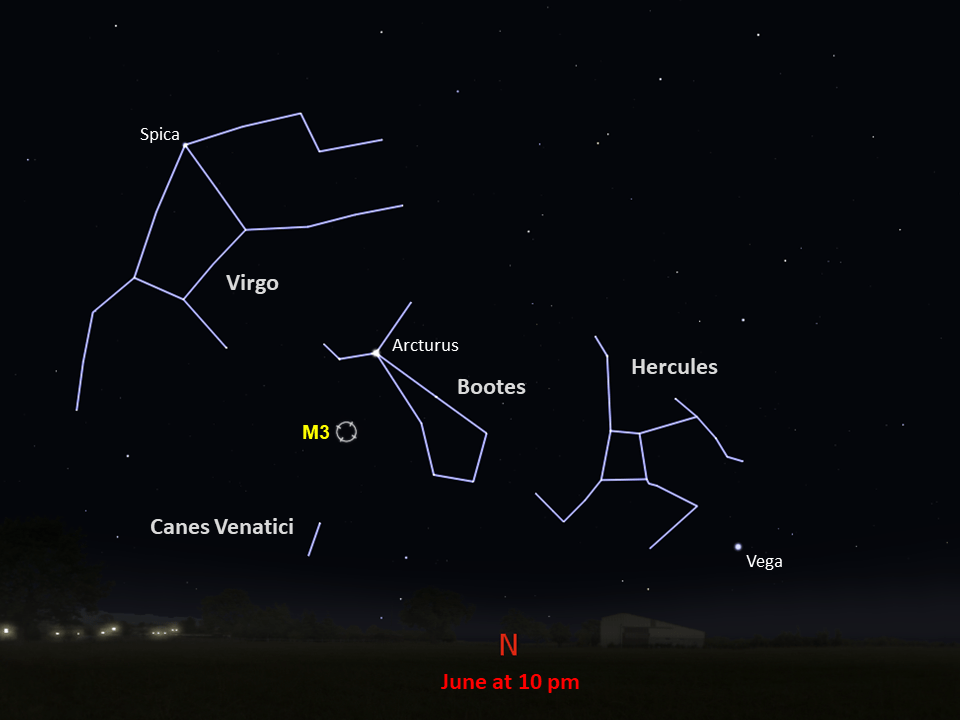
constellation
Canes Venatici
object type
Globular Cluster
The globular cluster M3 was the first object in the Messier catalog to be discovered by Charles Messier himself. Messier spotted the cluster in 1764, mistaking it for a nebula without any stars. This misunderstanding of M3’s nature was corrected in 1784 when William Herschel was able to resolve the cluster’s individual stars. Today it is known to contain over 500,000 stars.
M3 is notable for containing more variable stars than any other known cluster. The brightness of a variable star fluctuates with time. For some variable stars, their period relates to their intrinsic luminosity, so astronomers can use those stars’ brightness fluctuations to estimate their distances. This makes them extremely useful for measuring distances to deep-sky objects. M3 contains at least 274 variable stars.
The cluster is located 34,000 light-years from Earth in the constellation Canes Venatici. It has an apparent magnitude of 6.2 and can be spotted using a pair of binoculars. The best time to observe M3 is during June.
For more information about Hubble's observations of M3, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
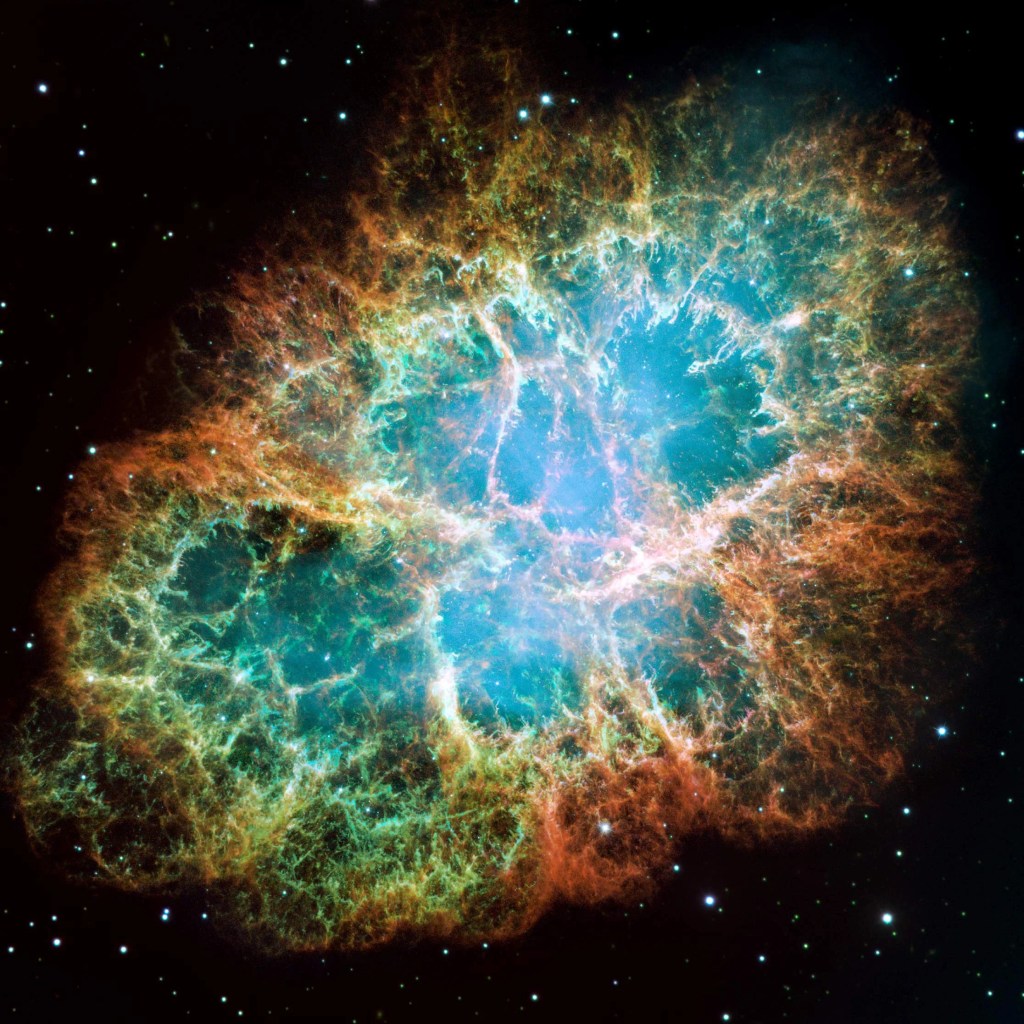

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.