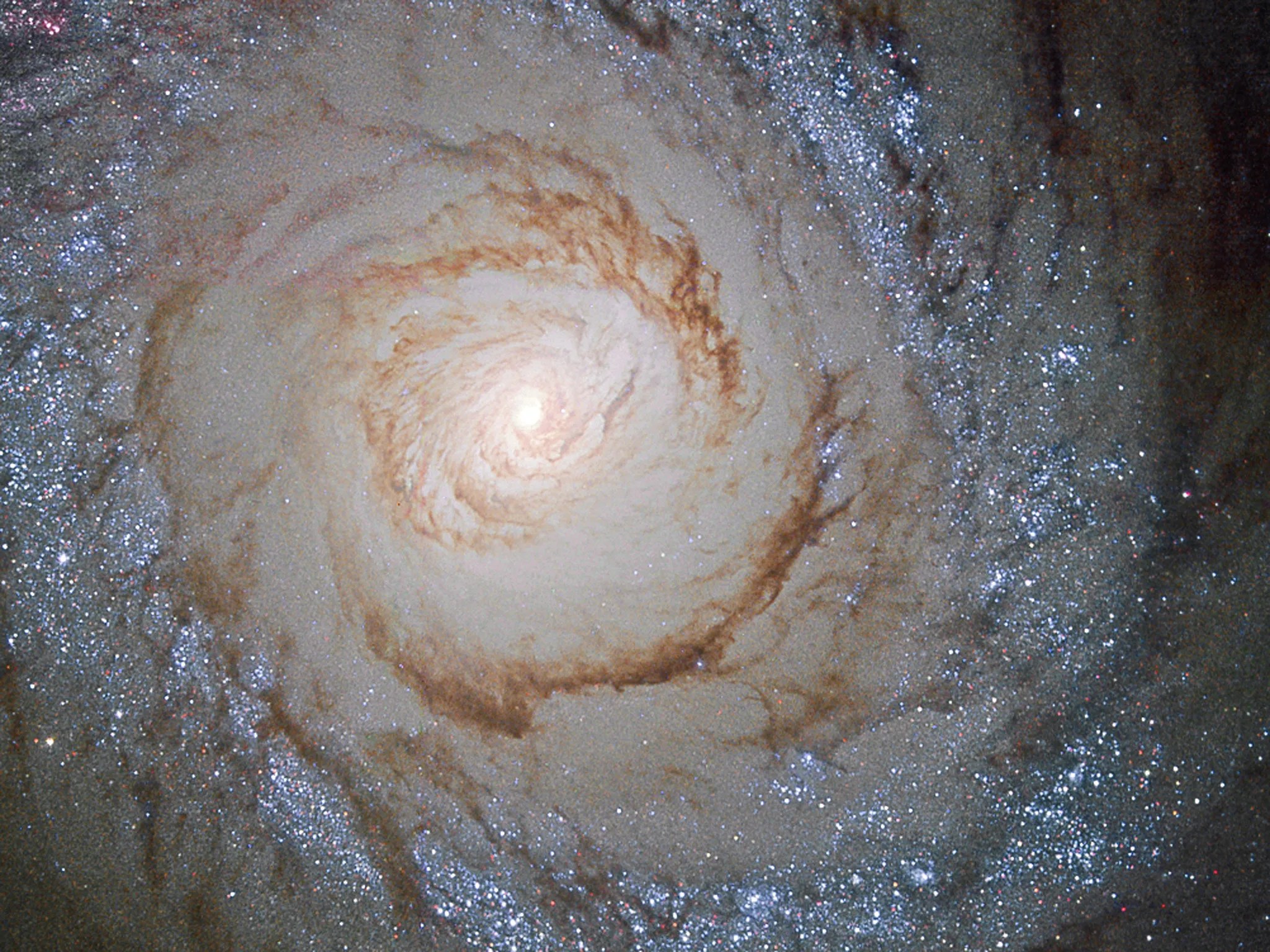
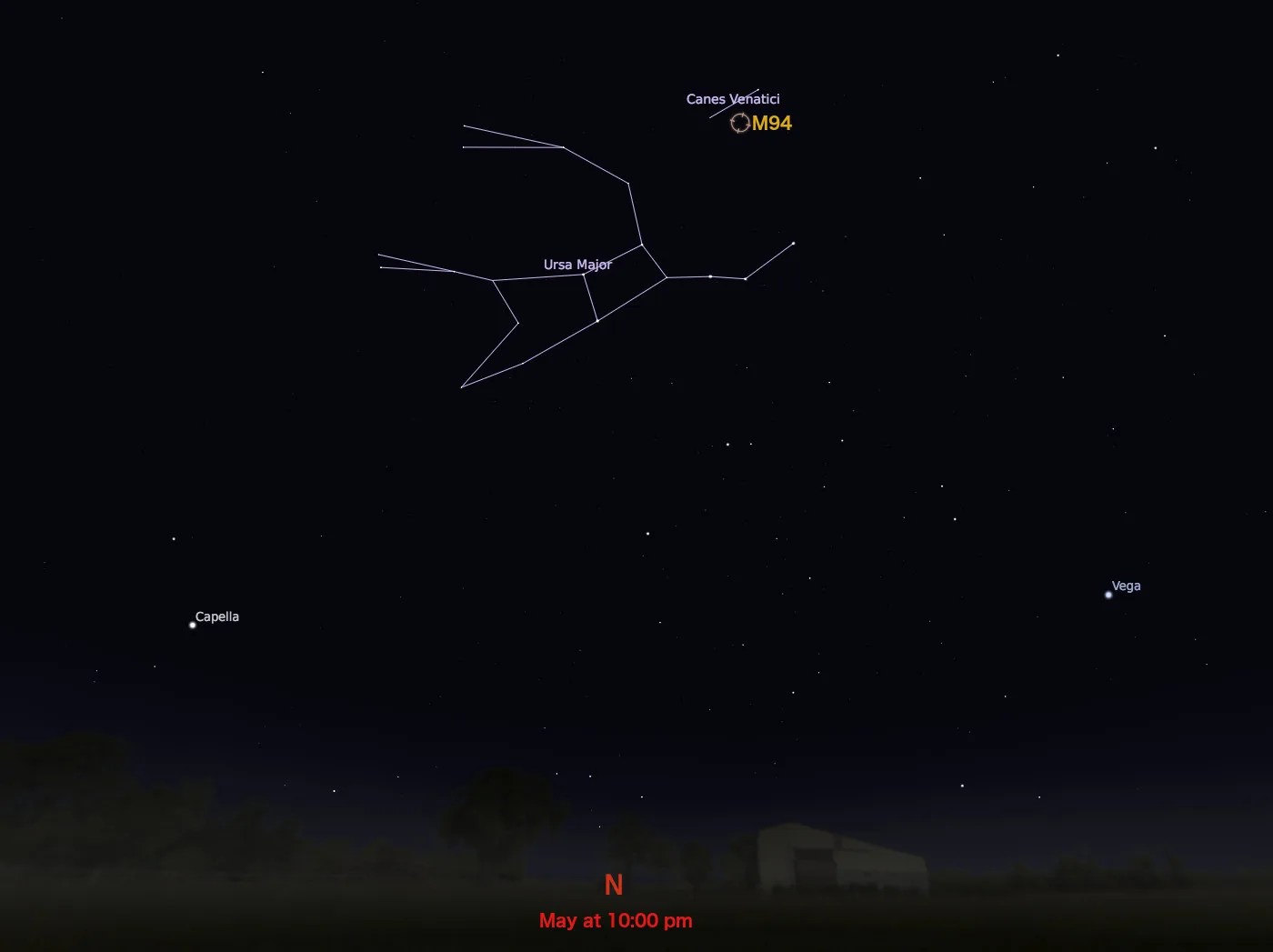
Messier 94
This colorful spiral has two recently discovered faint arms outside of its core region that extend far out into space.
Distance
16 million light-years
Apparent Magnitude
9.0
constellation
Canes Venatici
object type
Spiral Galaxy
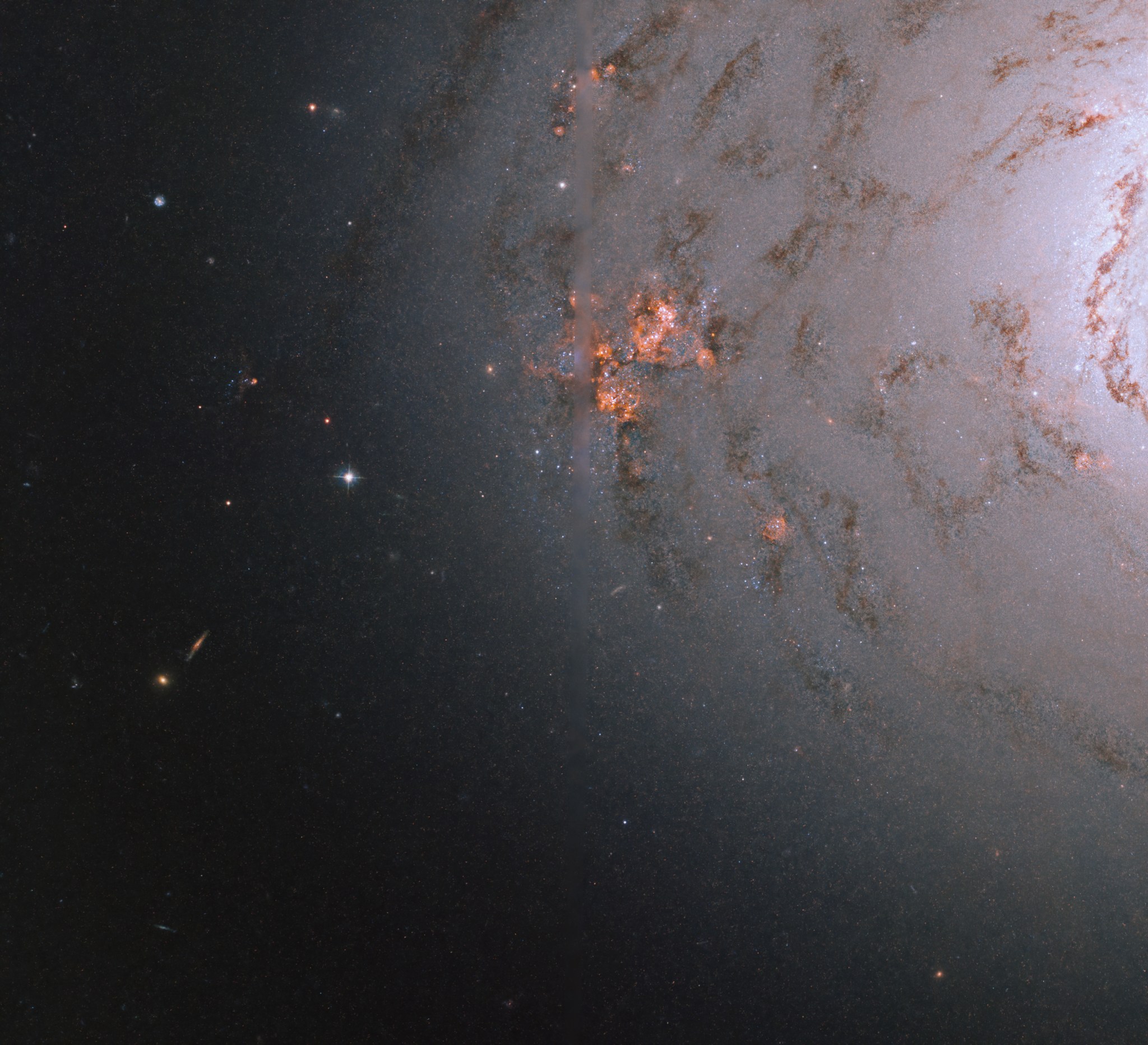
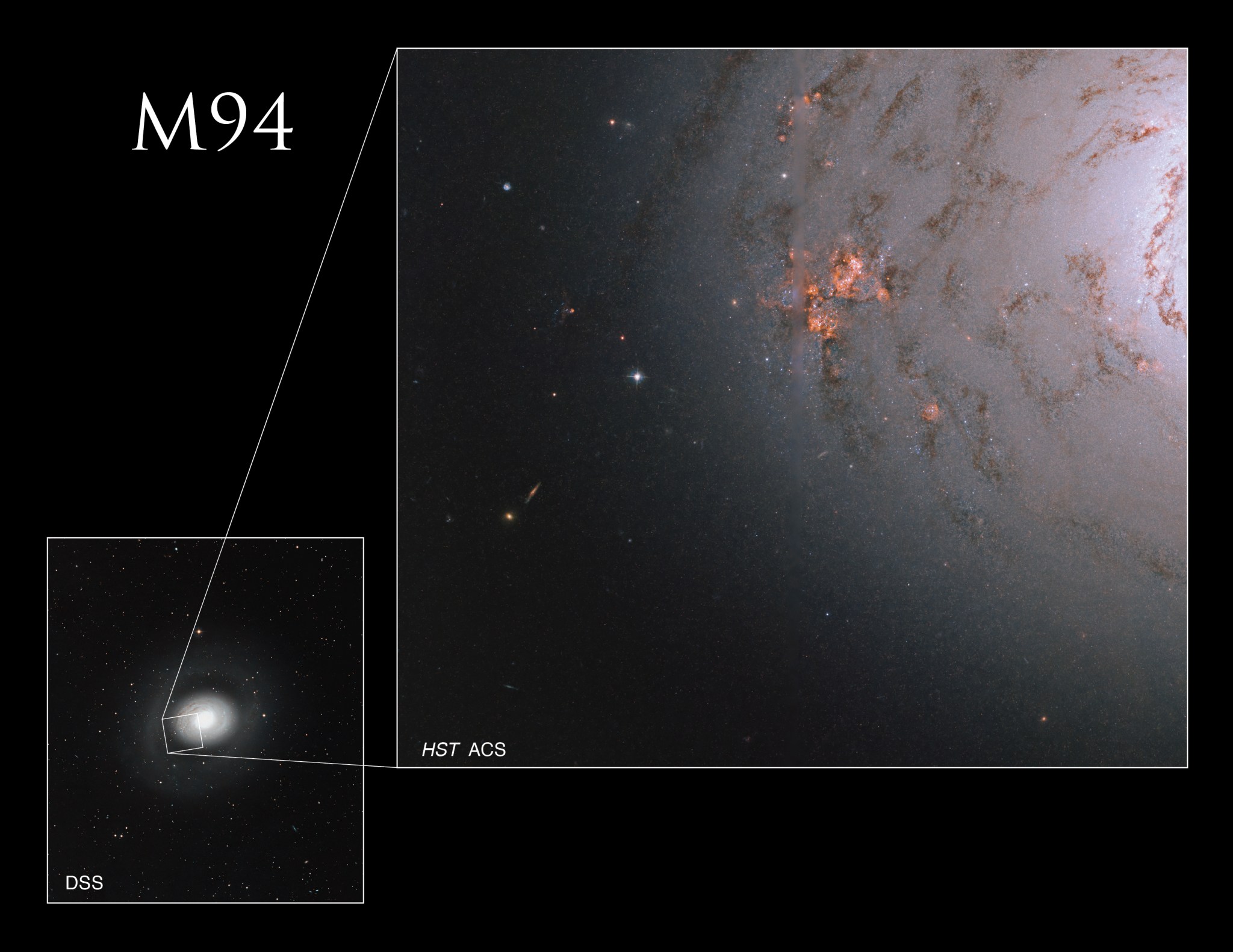
M94 is a spiral galaxy located 16 million light-years away in the constellation Canes Venatici. It was discovered in 1781 by Pierre Méchain, a French astronomer for whom an asteroid was named in 2002. Also cataloged as NGC 4736, the galaxy has an apparent magnitude of 9 and can be spotted through a small telescope. The best time of year to observe M94 is during May.
The Hubble image above of M94’s core is composed of observations taken at visible and infrared wavelengths. New stars are forming at a high rate within the bright ring. This region is known as a starburst ring. The cause of this peculiarly shaped star-forming region is likely a pressure wave traveling outward from the galactic center, compressing the gas and dust in the outer regions. The compression of material means the gas starts to collapse into denser clouds. Inside these dense clouds, gravity pulls the gas and dust together until the temperature and pressure are high enough for stars to be born.
Although M94 was initially believed to be roughly 30,000 light-years in diameter, two faint spiral arms (not visible in this image) were recently discovered outside of its core region that extend far out into space. This discovery has effectively tripled the galaxy’s known diameter. M94 is also notable for its deficiency of dark matter relative to other galaxies. Astronomers do not know why it lacks the normal amount of dark matter, but the galaxy has been the subject of extensive study as a result.
For more information about Hubble’s observations of M94, see:
Explore Hubble's Messier Catalog
The following pages contain some of Hubble’s best images of Messier objects.

Overview The Messier catalog, begun by astronomer Charles Messier in the 18th Century and revised over the years, includes some…
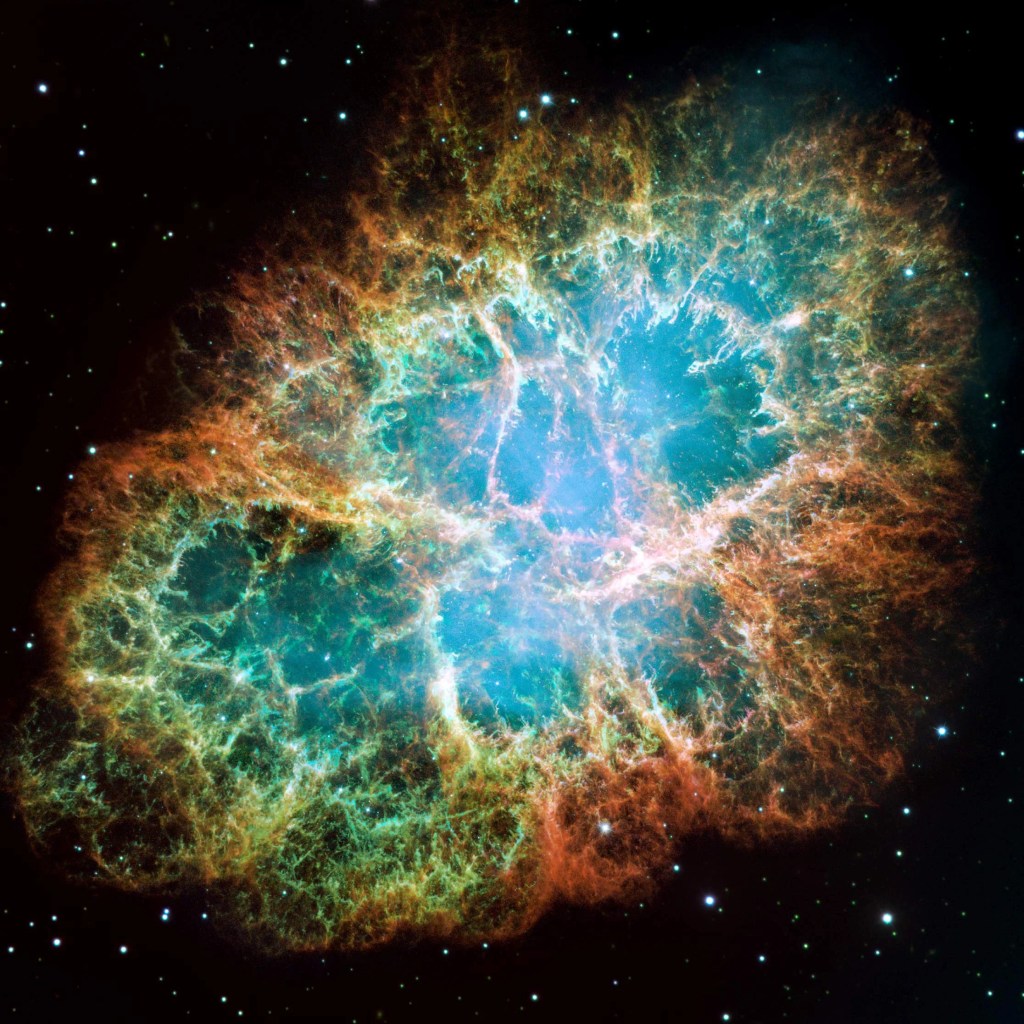

Better known as the Crab Nebula, Charles Messier originally mistook Messier 1 for Halley’s Comet, which inspired him to create…

Hubble's image of Messier 2 is comprised of visible and infrared wavelengths of light.