1 min read
Hubble Ultra Deep Field

The galaxy, named HUDF-JD2, was pinpointed among approximately 10,000 others in a small area of sky called the Hubble Ultra Deep Field (HUDF). This is the deepest image of the universe ever made at optical and near-infrared wavelengths.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03h 32m 39.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27° 48' 0.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Fornax
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is 3 arc minutes square
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from the following proposal: 9978: S. Beckwith, S. Malhotra, M. Giavalisco, N. Panagia, J. Rhoads, M. Stiavelli, R. Somerville, S. Casertano, B. Margon, C. Blades, J. Caldwell, and M. Clampin (STScI), M. Corbin (CSC), M. Dickinson, H. Ferguson, and A. Fruchter (STScI), R. Hook (STScI/ECF), S. Jogee, A. Koekemoer, R. Lucas, M. Sosey and L. Bergeron (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.September 24, 2003 - January 16, 200,4 Exposure Time: 11.3 days
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F606W (V), F775W (I), F850LP (z)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Hubble Ultra Deep Field; HUDF
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Deep Field Survey
- Release DateSeptember 27, 2005
- Science ReleaseSpitzer and Hubble Team Up to Find “Big Baby” Galaxies in the Newborn Universe
- Credit

Color Info
Color InfoA brief description of the methods used to convert telescope data into the color image being presented.
Blue: F435W (B) Green: F606W (V) + F775W (I) Red: F850LP (z)

Compass and Scale
Compass and ScaleAn astronomical image with a scale that shows how large an object is on the sky, a compass that shows how the object is oriented on the sky, and the filters with which the image was made.
Related Images & Videos
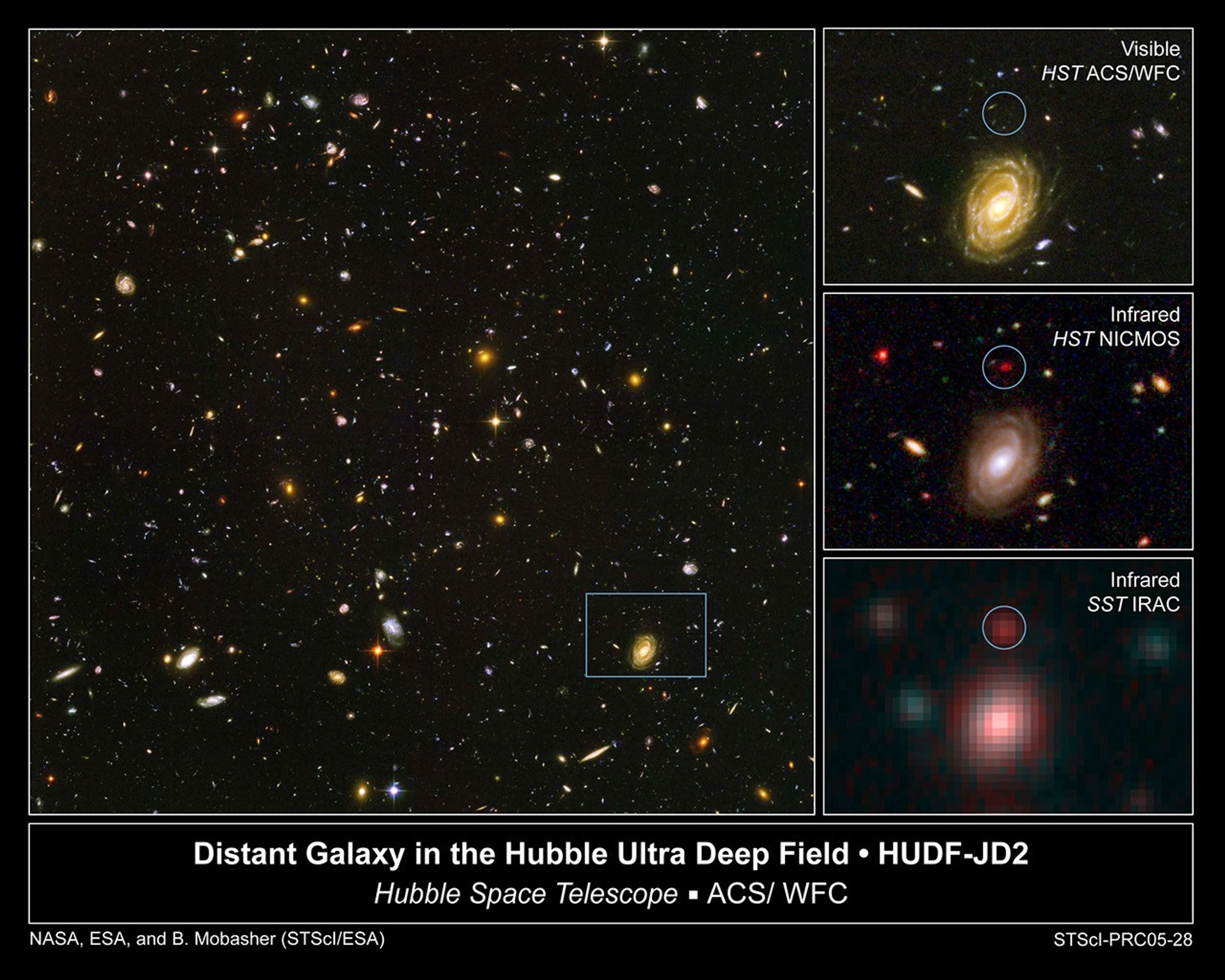

Galaxy HUDF-JD2 in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
This image demonstrates how data from two of NASA's Great Observatories, the Spitzer and Hubble Space Telescopes, are used to identify one of the most distant galaxies ever seen. This galaxy is unusually massive for its youthful age of 800 million years. (After the Big Bang, the...

Galaxy HUDF-JD2 – Infrared
The Spitzer Infrared Array Camera (IRAC), easily detected the galaxy at longer infrared wavelengths. Spitzer's IRAC is sensitive to the light from older, redder stars which should make up most of the mass in a galaxy. The brightness of the infrared galaxy suggests that it is...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov