1 min read
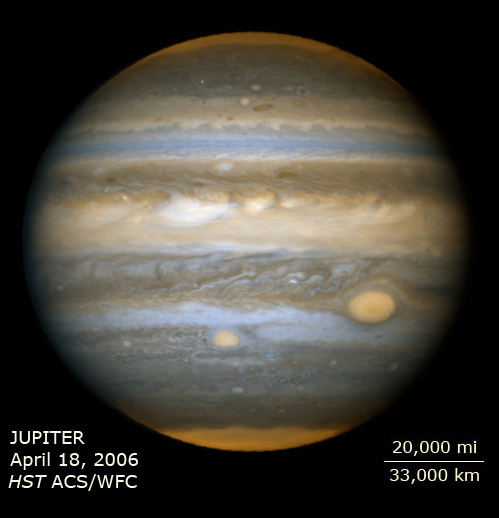
Jupiter’s New Red Spot – HST ACS/WFC: April 16, 2006

About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The semi-major axis of Jupiter's orbit about the sun is 5.2 Astronomical Units (778 million km or 483 million miles).
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The planet has a diameter of roughly 88,789 miles (142,984 km) at the equator.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposals: 10783: A. Simon-Miller (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center), G. Orton (Jet Propulsion Laboratory), and N. Chanover (New Mexico State University) 10782: I. de Pater, M. Wong, P. Marcus, X. Asay-Davis (University of California - Berkeley), and C. Go, (Astronomical League of the Philippines). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.April 16, 2006
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.330nm, 435nm, 475nm, 502nm, 550nm, 656nm, 658nm, 892nm
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Jupiter, Red Spot Jr.
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateMay 4, 2006
- Science ReleaseHubble Snaps Baby Pictures of Jupiter’s “Red Spot Jr.”
- Credit

Red-orange: F892N (near-IR strong methane band) Blue-cyan: F502N (continuum/cyan light)

Related Images & Videos

Hubble Snaps Baby Pictures of Jupiter's "Red Spot Jr."
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope is giving astronomers their most detailed view yet of a second red spot emerging on Jupiter. For the first time in history, astronomers have witnessed the birth of a new red spot on the giant planet, which is located half a billion miles away. The...

Jupiter's New Red Spot - HST ACS/HRC: April 8, 2006
Image of the partial disk of Jupiter from ACS/HRC on April 8, 2006 at 02:33UT. This contrast-enhanced image was taken in blue (F435W) and red (F656N) light. The group involved with the observation was led by Amy Simon-Miller (NASA GoddardSpace Flight Center), Glenn Orton (Jet...

Jupiter's New Red Spot - HST ACS/HRC: April 25, 2006
Deprojected map image of the Red Spot region of Jupiter from ACS/HRC at 00:41 UT on April 25, 2006. Each pixel spans 0°.05 in latitude and longitude, with the top of the image lying just along the equator. Three filters are shown here in red (F658N), green (F502N), and blue...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov