1 min read
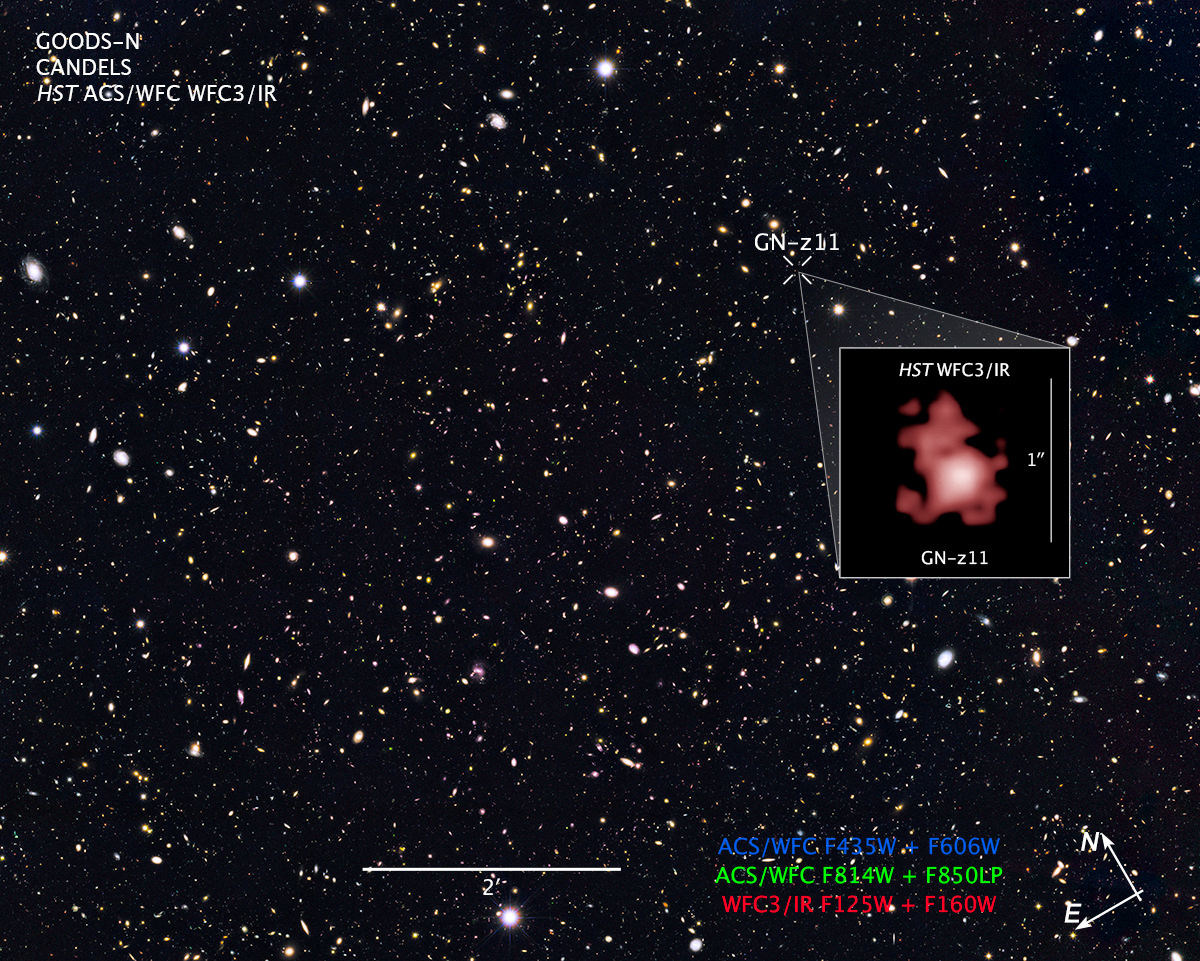
Compass and Scale Image for GOODS-N and GN-z11
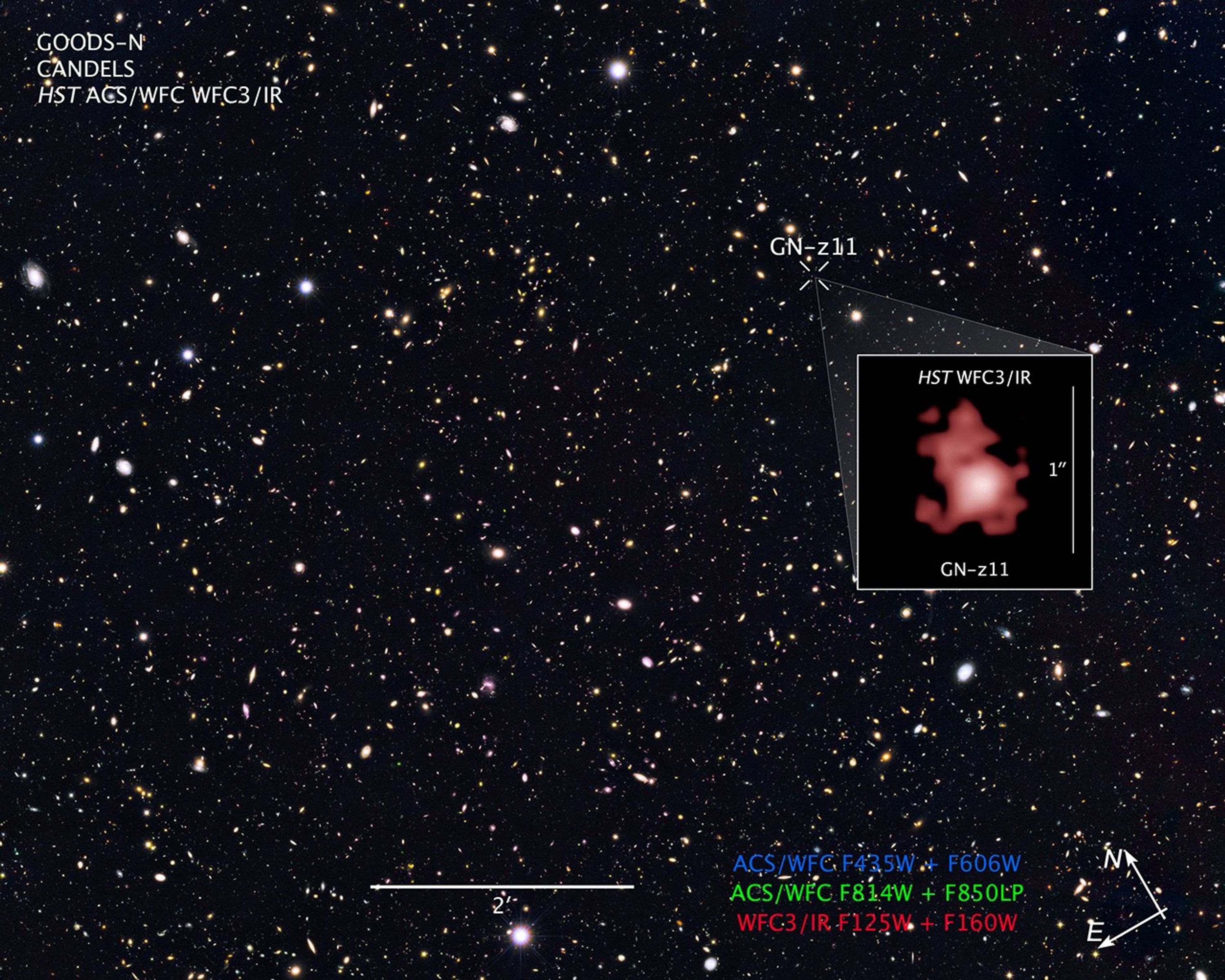

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h 36m 54.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.62° 14' 15.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Major
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Recent data were obtained from the HST proposal 13871, PI: P. Oesch (Yale University), G. Illingworth (University of California, Santa Cruz), I. Labbé (Leiden University), G. Brammer (STScI), R. Bouwens and M. Franx (Leiden University), P. van Dokkum (Yale University), D. Magee (UCO/Lick Observatory/University of California, Santa Cruz), I. Momcheva (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), R. Smit (Durham University), M. Ashby, G. Fazio, J. Huang, and S. Willner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), V. Gonzalez (University of California, Riverside), R. Skelton (South African Astronomical Observatory), M. Trenti (University of Melbourne), and L. Spitler (Macquarie University/Australian Astronomical Observatory). The science team includes: P. Oesch (Yale University), G. Brammer (STScI), P. van Dokkum (Yale University), G. Illingworth (University of California, Santa Cruz), R. Bouwens, I. Labbé, and M. Franx (Leiden University), I. Momcheva, M. Ashby, and G. Fazio (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), V. Gonzalez (University of California, Riverside), B. Holden and D. Magee (UCO/Lick Observatory/University of California, Santa Cruz), R. Skelton (South African Astronomical Observatory), R. Smit (Durham University), L. Spitler (Macquarie University/Australian Astronomical Observatory), M. Trenti (University of Melbourne), and S. Willner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC, and HST>WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 11, 2015, and April 3, 2015
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.Main CANDELS/GOODS-N Field: HST>ACS/WFC: F435W (B), F606W (V), F814W (I), and F850LP (z), and HST> WFC3/IR: F105W (Y), F125W (J), and F160W (H) Grism Data (February 11, 2015, and April 3, 2015): HST>WFC3/IR: G141
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.GOODS North Survey, and GN-z11 (inset image)
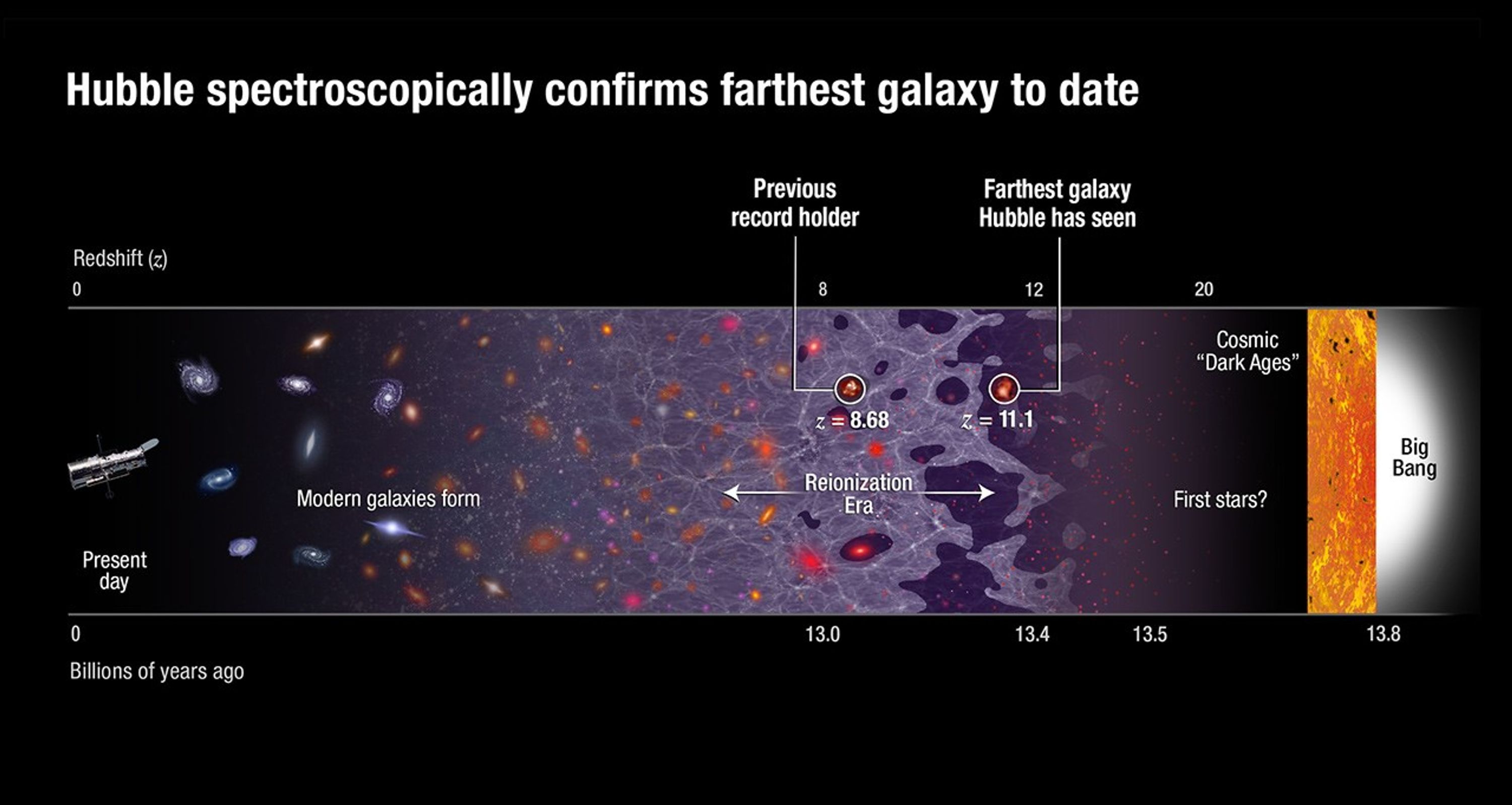
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Farthest Galaxy Candidate from CANDELS/GOODS-N Field
- Release DateMarch 3, 2016
- Science ReleaseHubble Team Breaks Cosmic Distance Record
- Credit

The main GOODS-N composite includes exposures acquired by the ACS and WFC3 instruments on the Hubble Space Telescope. Several filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F435W (B) + F606W (V) Green: F814W (I) + F850LP (z) Red: F125W (J) + F160W (H)
Related Images & Videos
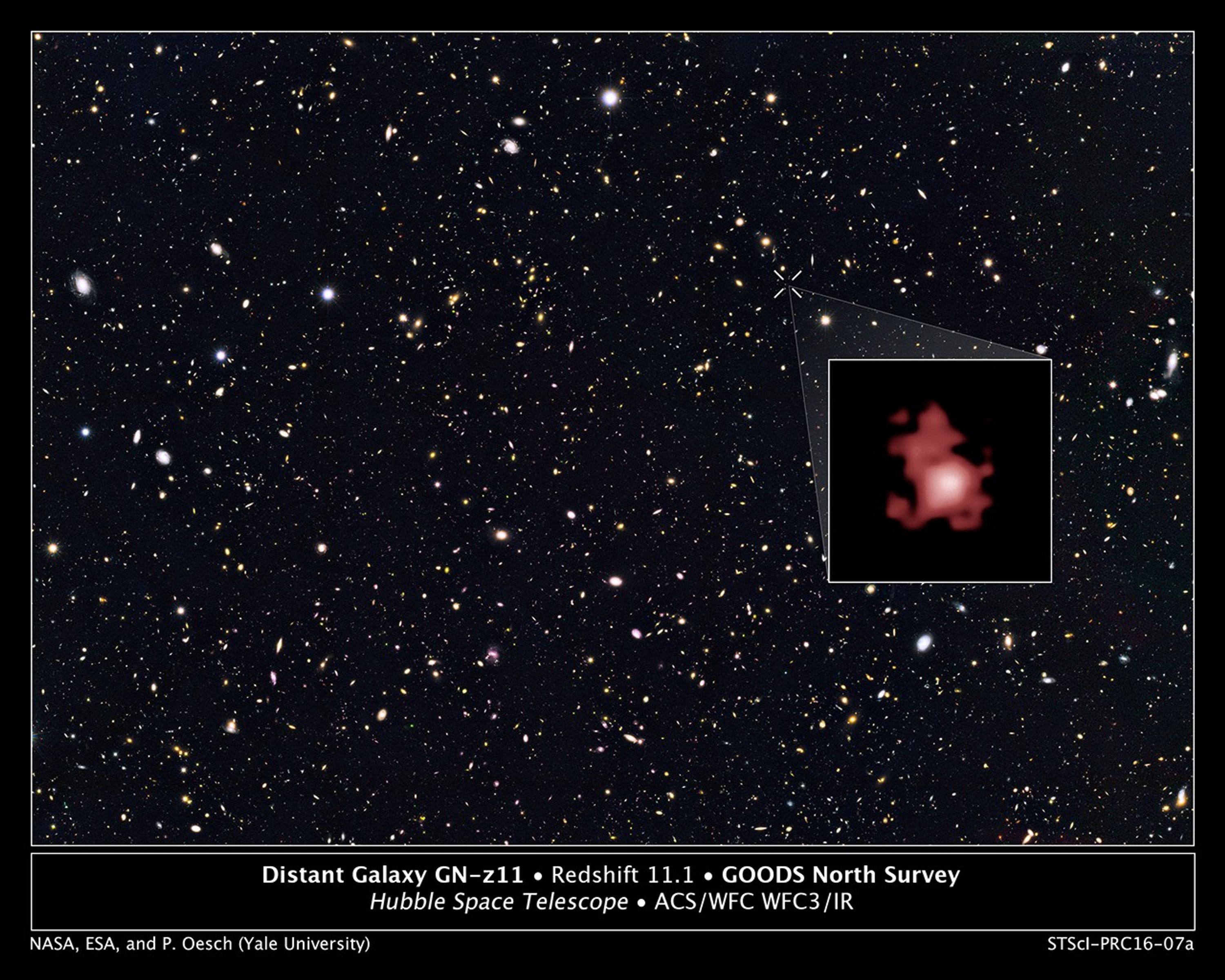

Distant Galaxy GN-z11 in GOODS North Survey
Hubble Space Telescope astronomers, studying the northern hemisphere field from the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS), have measured the distance to the farthest galaxy ever seen. The survey field contains tens of thousands of galaxies stretching far back into...
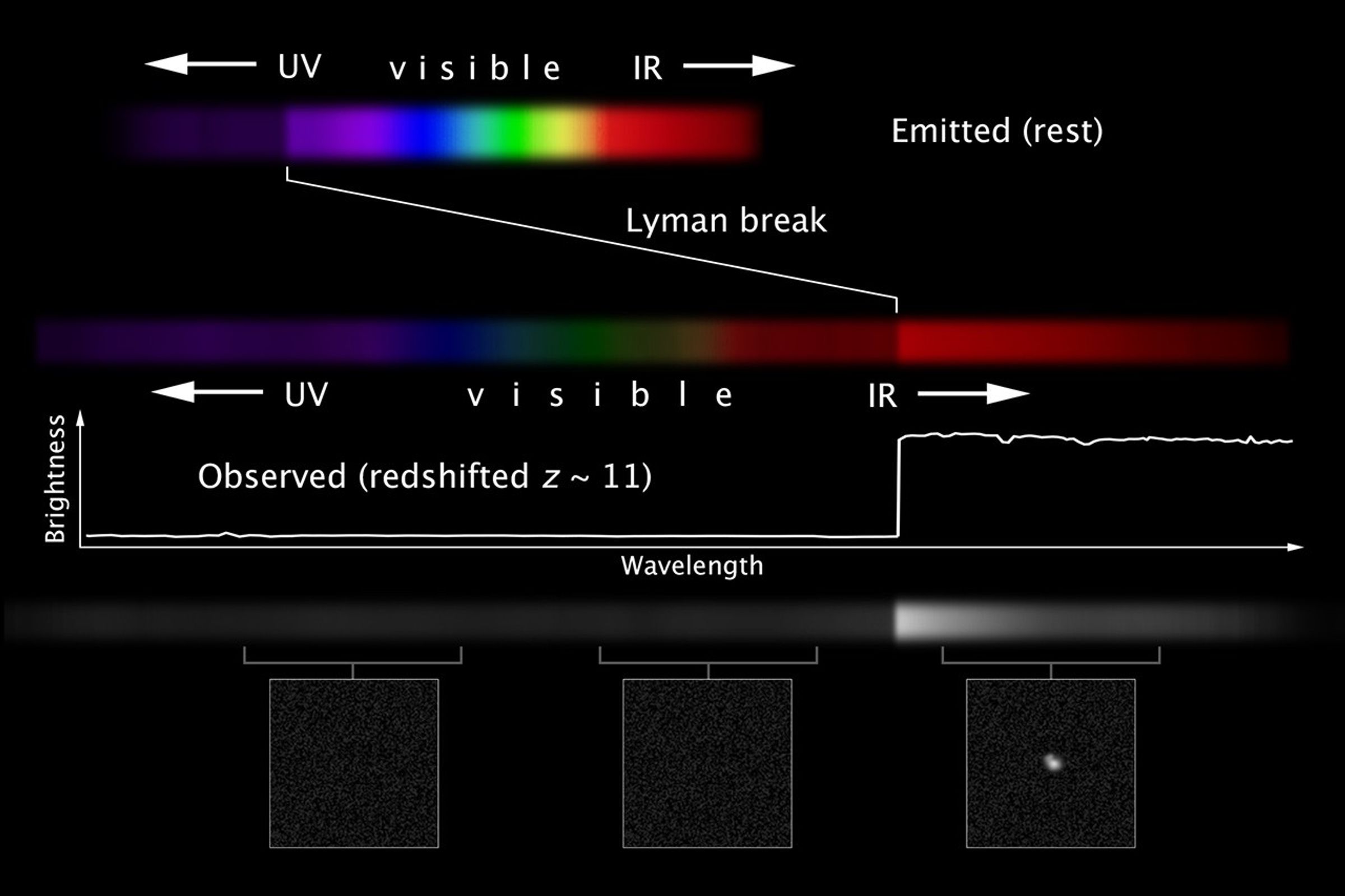
Redshift and Measuring Distance to Remote Galaxies
Galaxies emit light across the entire electromagnetic spectrum. Star-forming galaxies have areas of intense activity, but the light in the ultraviolet can be blocked by clouds surrounding the star-formation region. This causes a significant and identifiable drop in the light...
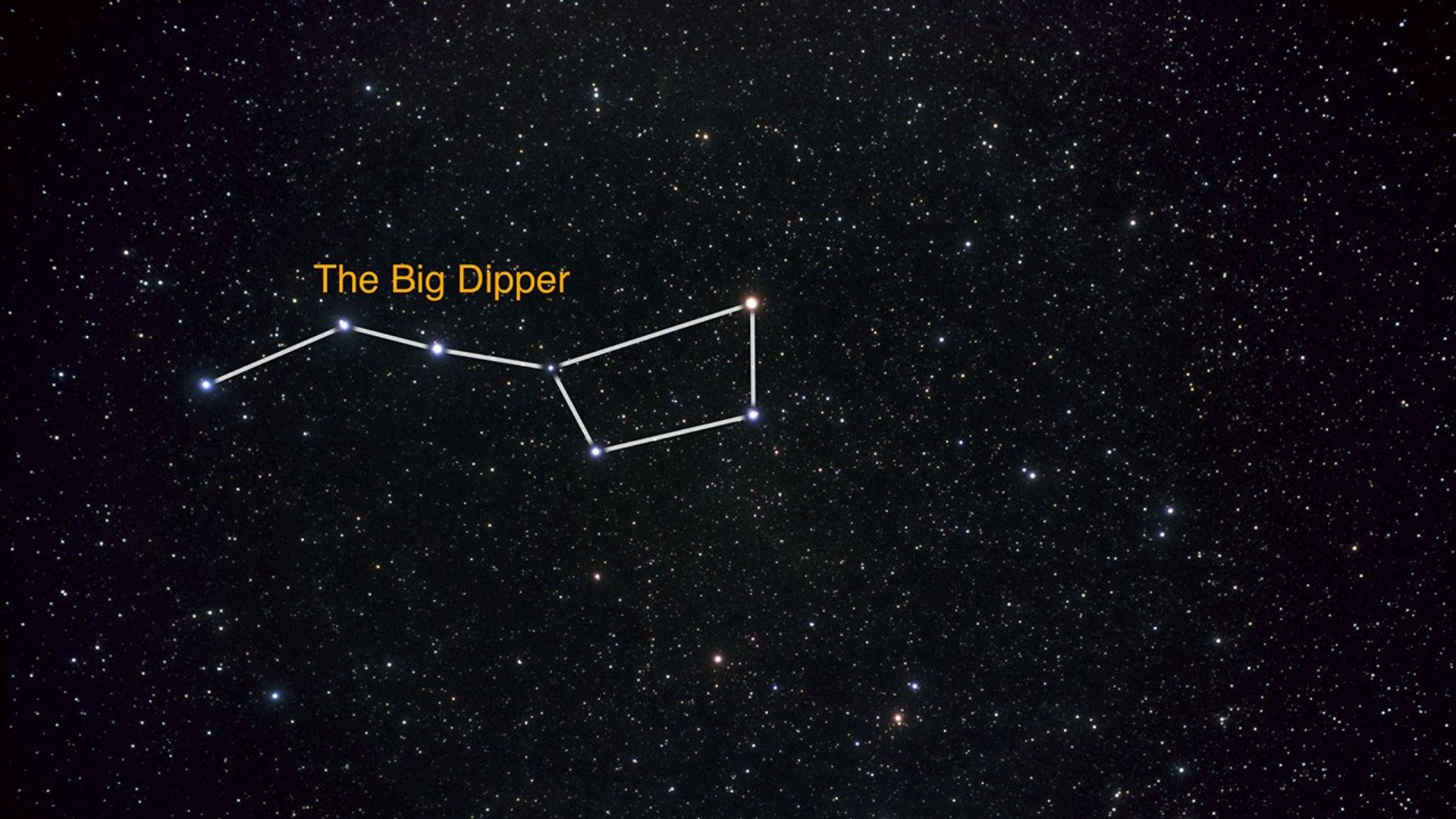
Zoom into GOODS North Survey and Distant Galaxy GN-z11
This animation shows the location of galaxy GN-z11, which is the farthest galaxy ever seen. The video begins by locating the Big Dipper, then showing the constellation Ursa Major. It then zooms into the GOODS North field of galaxies, and ends with a Hubble image of the young...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov