1 min read
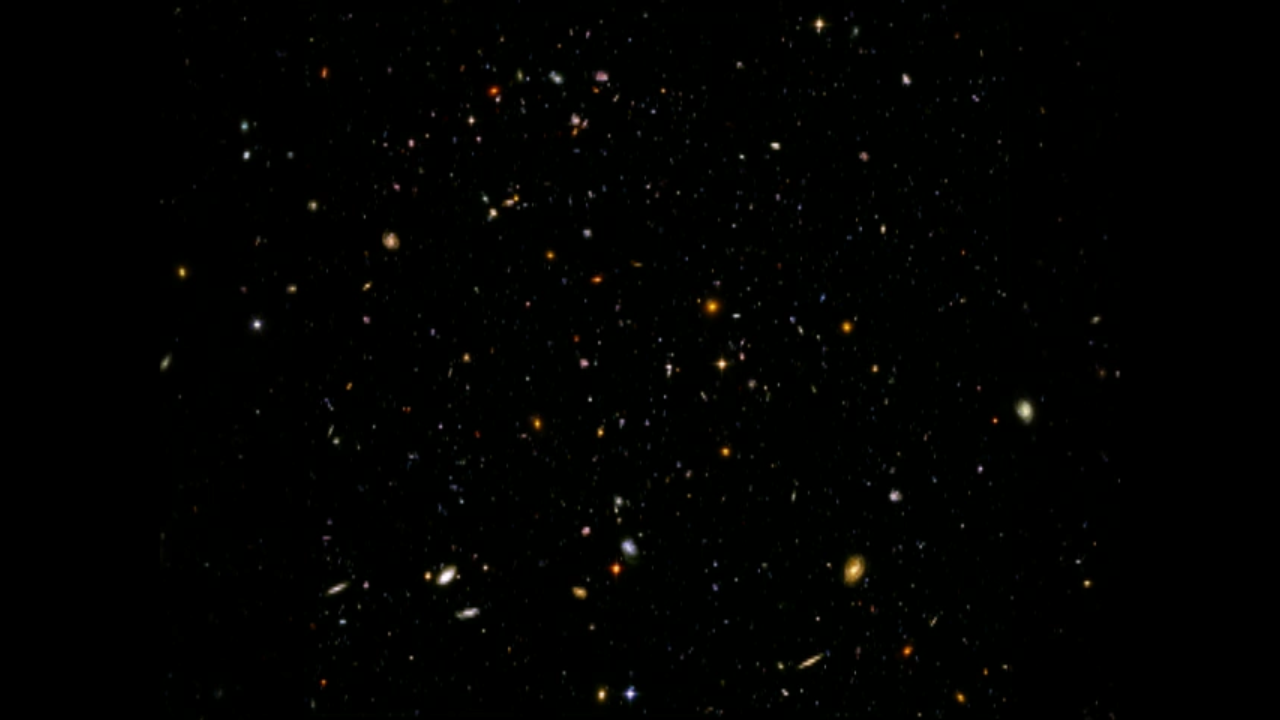
Farthest Objects Ever Seen Pinpointed in the Hubble Ultra Deep Field
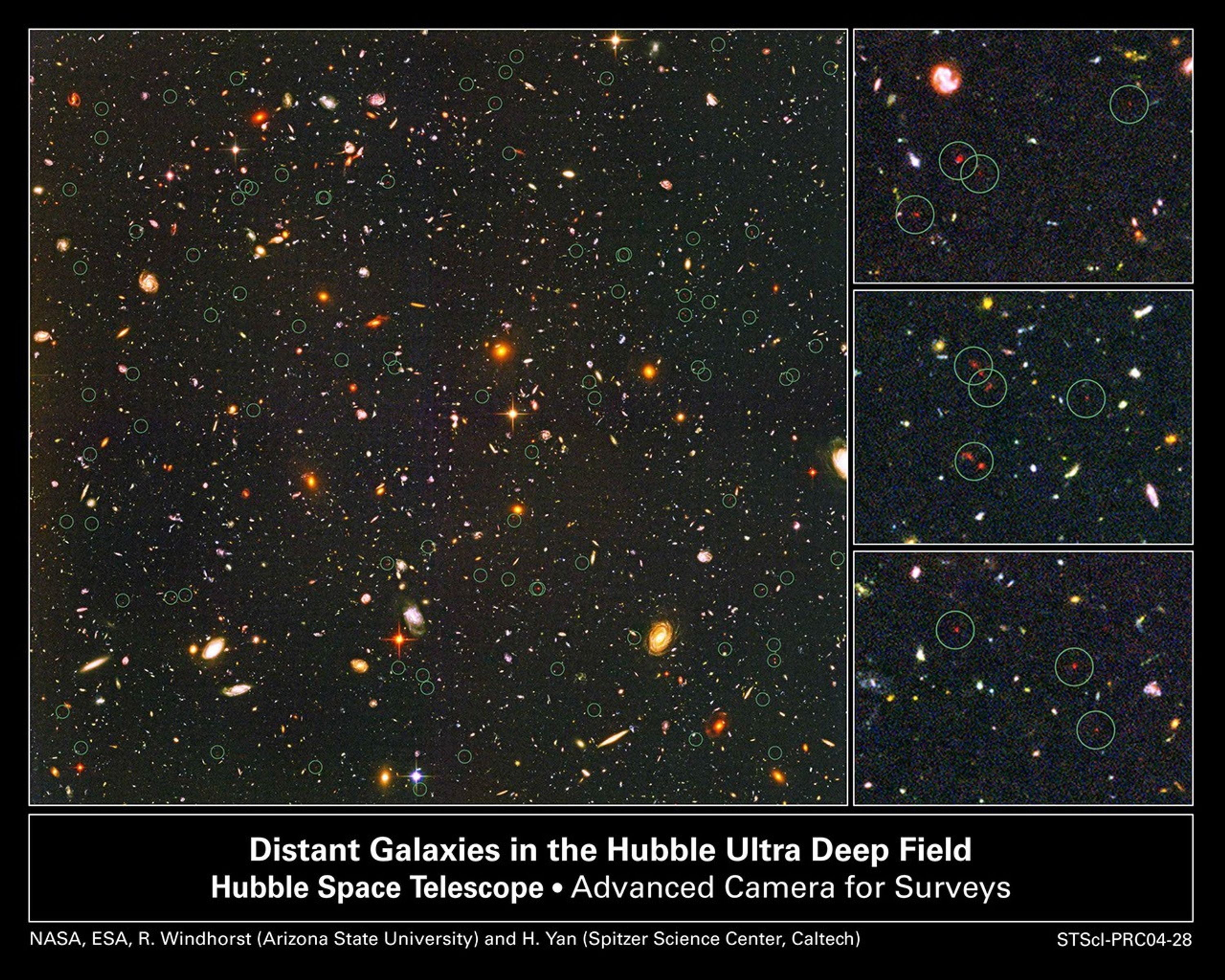
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.03h 32m 39.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-27° 48' 0.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Fornax
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The image is 3 arcminutes square.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from the following proposal: 9978:: HUDF Team (STScI). The science teams are: — A.J. Bunker (Univ.of Exeter U.K./ Inst. of Astrophysics, Univ. of Cambridge, U.K.), E.R. Stanway (Inst. of Astrophysics, Univ. of Cambridge, U.K.), R.S. Ellis (California Inst. of Tech.), and R.G. McMahon (Inst. of Astrophysics, Univ. of Cambridge, U.K.) — M. Stiavelli, S. M. Fall, and N. Panagia (STScI) — H. Yan (Spitzer Science Center, California Inst. of Tech.) and R.A. Windhorst (Arizona State Univ.) — R.J. Bouwens and G.D. Illingworth (Univ. of California, Santa Cruz), R.I. Thompson (Steward Obs./Univ. of Arizona), J.P. Blakeslee (Johns Hopkins Univ.), M.E. Dickinson (National Optical Astronomy Obs.), T.J. Broadhurst (The Hebrew Univ., Israel), D.J. Eisenstein and X. Fan (Steward Obs./Univ. of Arizona), M. Franx (Leiden Observatory, Netherlands), G. Meurer (Johns Hopkins Univ.), and P. van Dokkum (Yale Univ.) — S. Malhotra, J.E. Rhoads, N. Pirzkal and C. Xu (STScI) - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.September 24, 2003 - January 16, 2004, Exposure Time: 11.3 days
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F606W (V), F775W (i), F850LP (z)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.HUDF, Hubble Ultra Deep Field
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Optical Survey
- Release DateSeptember 23, 2004
- Science ReleaseHubble Approaches the Final Frontier: The Dawn of Galaxies
- Credit

Blue: F435W (B) Green: F606W (V), F775W (i) Red: F850LP (z)

Related Images & Videos

STScI Science Writers' Workshop (Webcast)
Space Telescope Science Institute hosted a workshop for science writers regarding early science results from the Hubble Ultra Deep Field. Five research teams analyzing the Ultra Deep Field presented their findings during a live webcast from 9am - 12pm (EDT) on September 23, 2004.

Hubble Ultra Deep Field 3-D Fly-Thru
A flight through the Hubble Ultra Deep Field, the most distant visible-light view of the universe. The redshifts of 5,333 galaxies were converted to distances to assemble a 3-D model of the data. This scientific visualization flies through the data to showcase its true 3-D...
3-D Illustration: Cosmological Reionization Process
"The end of the dark ages": A 3-D illustration of the "Cosmological Re-ionization" process, which occurred shortly after the birth of the universe. The first stars formed and were able to re-heat hydrogen gas, turning it into transparent plasma. The first stars, grouped in...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov


































