1 min read
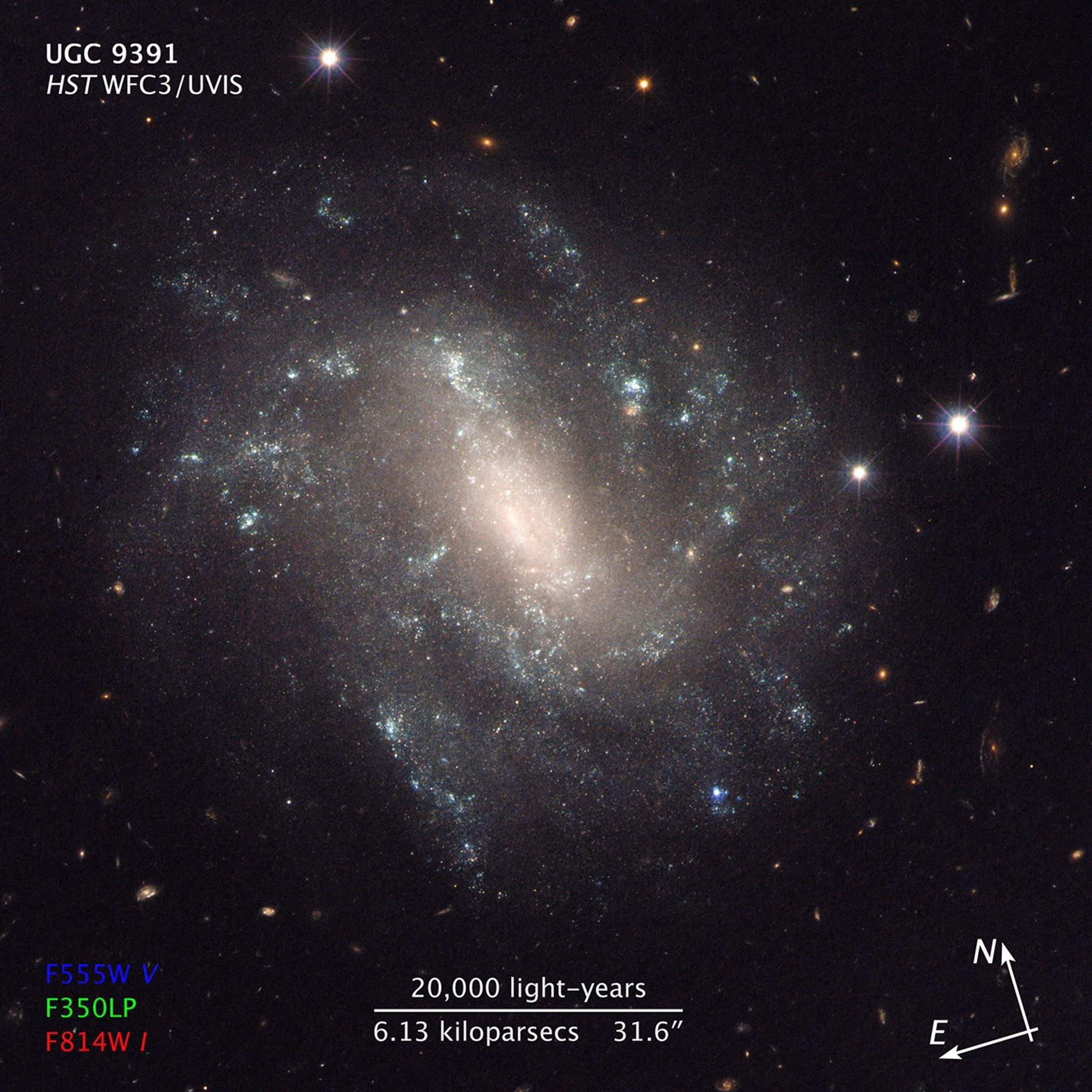
Galaxy UGC 9391

This Hubble Space Telescope image shows one of the galaxies in the survey to refine the measurement for how fast the universe expands with time, called the Hubble constant.
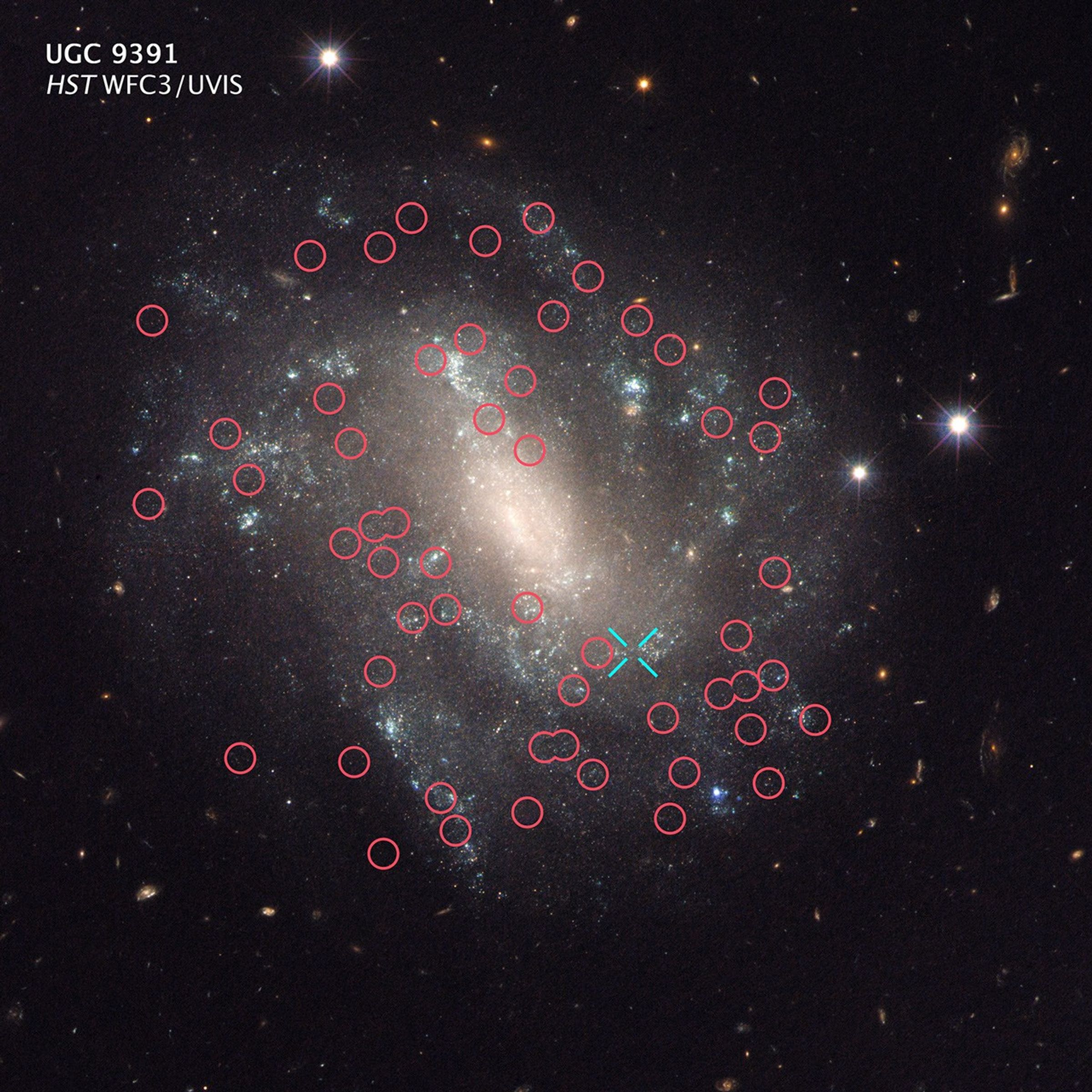
The galaxy, UGC 9391, contains two types of stars that astronomers use to calculate accurate distances to galaxies, a key measurement in determining the Hubble constant. The red circles mark the locations of Cepheid variable stars. These stars pulsate at rates that correspond to their true brightness, which can be compared with their apparent brightness as seen from Earth to accurately determine their distance.
The blue "X" at bottom right denotes the location of supernova 2003du, a special class of exploding star called a Type Ia supernova. These supernovae are another commonly used cosmic yardstick. They flare with the same brightness and are brilliant enough to be seen from relatively longer distances. Astronomers calibrate the supernovae with the Cepheids in galaxies such as UGC 9391 so that they can accurately calculate the distances to faraway exploding stars. UGC 9391 resides 130 million light-years from Earth.
The observations for this composite image were taken between 2012 and 2013 by Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.14h 34m 37.02s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.59° 20' 16.11"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Draco
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.130 million light-years (40 million parsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.Data were provided by the HST proposal 12880: A. Riess (JHU/STScI), L. Macri (Texas A&M University), A. Filippenko (University of California, Berkeley), S. Jha (Rutgers), S. Casertano (STScI), P. Nugent (Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory), and M. Ganeshalingam (University of California, Berkeley). The science team comprises: A. Riess (JHU/STScI), L. Macri and S. Hoffmann (Texas A&M University), D. Scolnic (JHU/University of Chicago), S. Casertano (STScI), A. Filippenko (University of California, Berkeley), B. Tucker (University of California, Berkeley/Mount Stromlo Observatory), M. Reid (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), D. Jones (JHU), J. Silverman (University of Texas, Austin), R. Chornock (Ohio University, Athens), P. Challis (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics), W. Yuan (Texas A&M University), and R. Foley (University of Illinois, Urbana-Champaign). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.December 2012 - March 2013
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F350LP, F555W (V), and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.UGC 9391
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Barred spiral galaxy
- Release DateJune 2, 2016
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Finds Universe Is Expanding Faster Than Expected
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3/UVIS instrument. Several filters were used to sample various wavelengths. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F555W (V), Green: F350LP Red: F814W (I)

Related Images & Videos
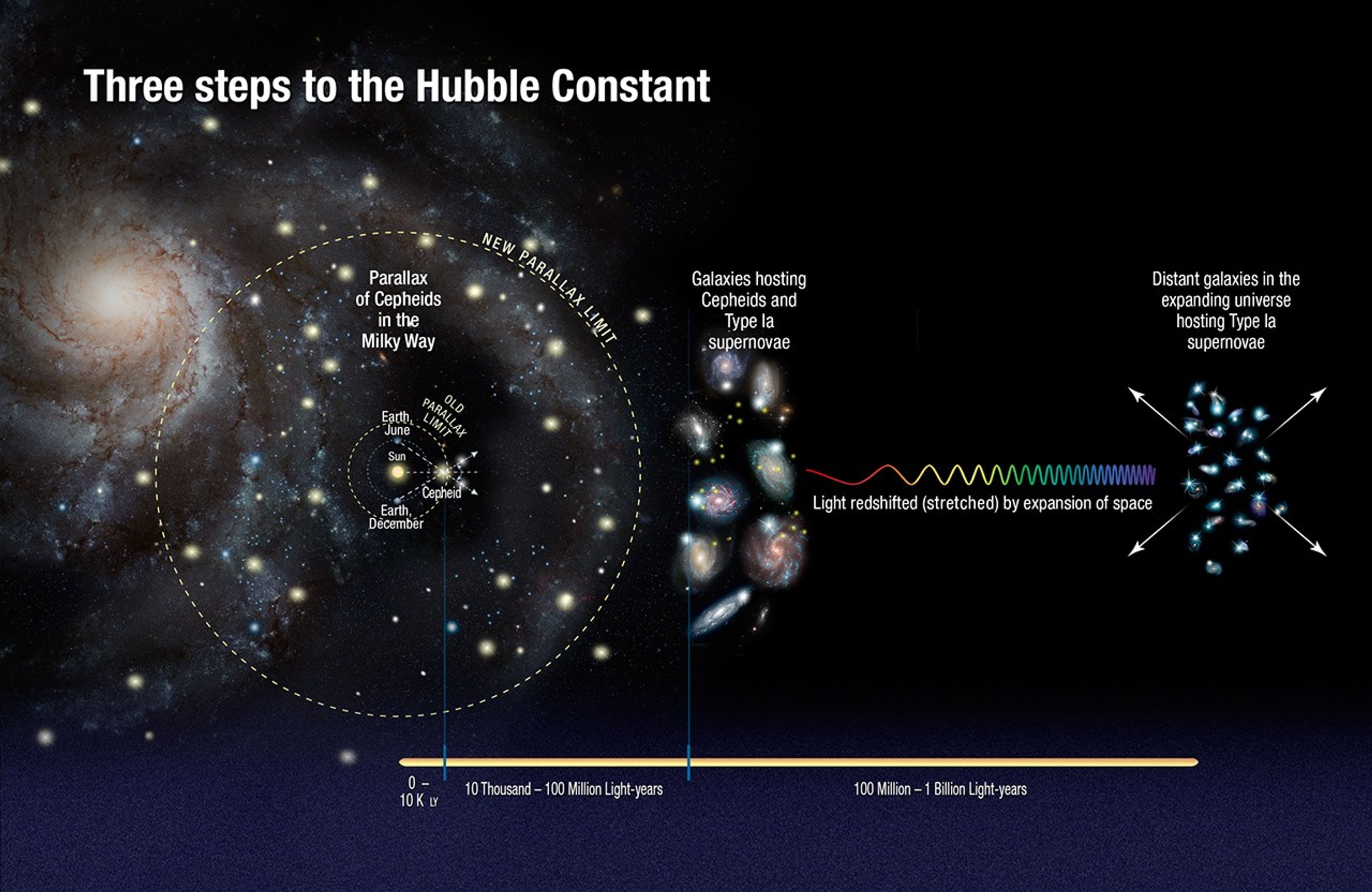
Three Steps to Hubble Constant (Artist's Illustration)
This illustration shows the three steps astronomers used to measure the universe's expansion rate to an unprecedented accuracy, reducing the total uncertainty to 2.4 percent. Astronomers made the measurements by streamlining and strengthening the construction of the cosmic...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov
















-1.jpg?w=1024)












