1 min read
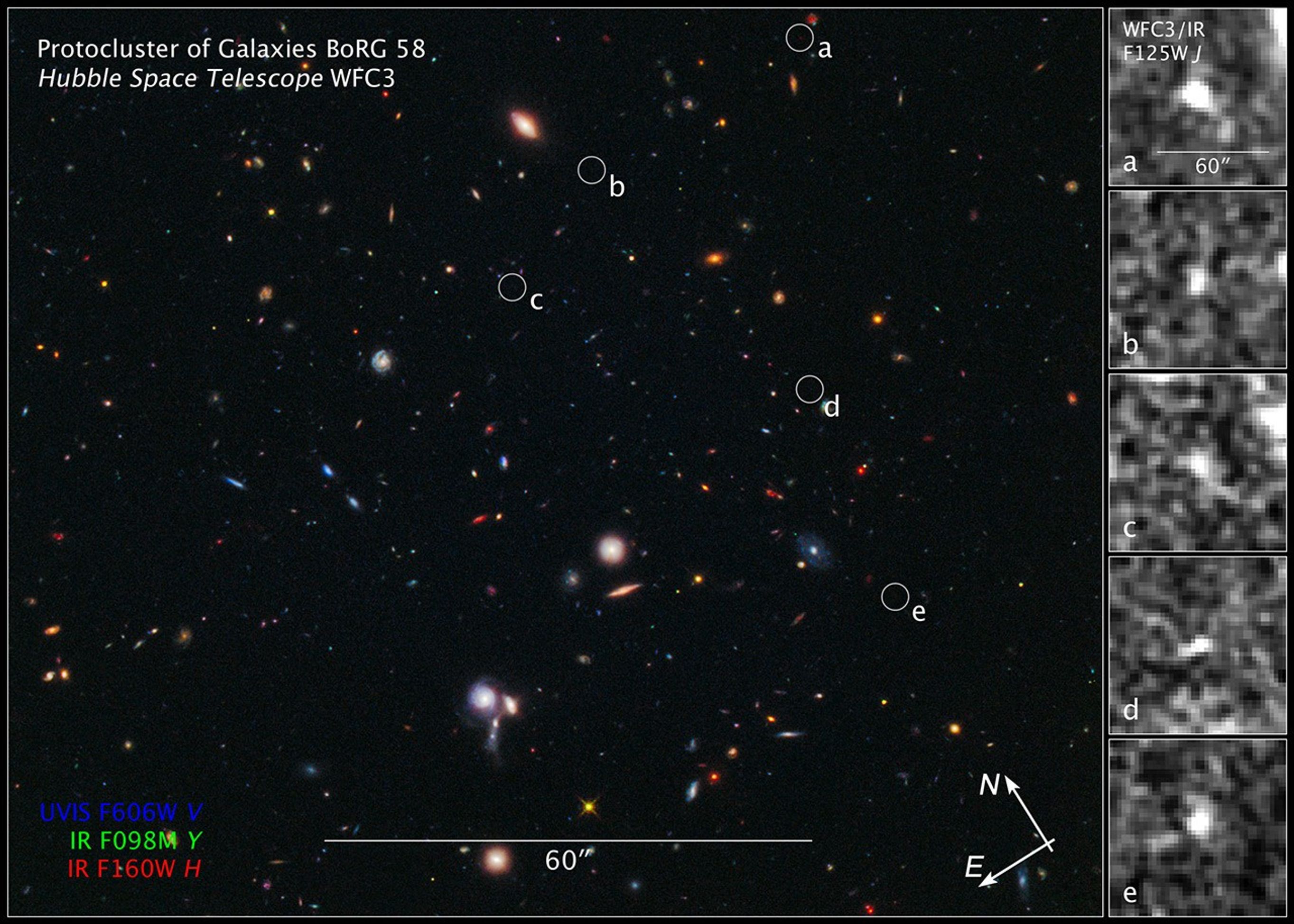
Hubble BoRG 58 Survey Field

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.14h 36m 55.1s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.50° 43' 9.79"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Boötes
About the Data
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS and HST>WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.July 28, 2010, Exposure Time: 2.6 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.WFC3/UVIS: F606W (V), WFC3/IR: F098M (blue grism), and F160W (H)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Galaxies from the Brightest of Reionizing Galaxies (BoRG) Survey, BoRG 58
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Survey Field
- Release DateJanuary 10, 2012
- Science ReleaseHubble Pinpoints Farthest Protocluster of Galaxies Ever Seen
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3 instrument on HST. Several filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: F606W (V) Green: F098M (blue grism) Red: F160W (H)
Related Images & Videos
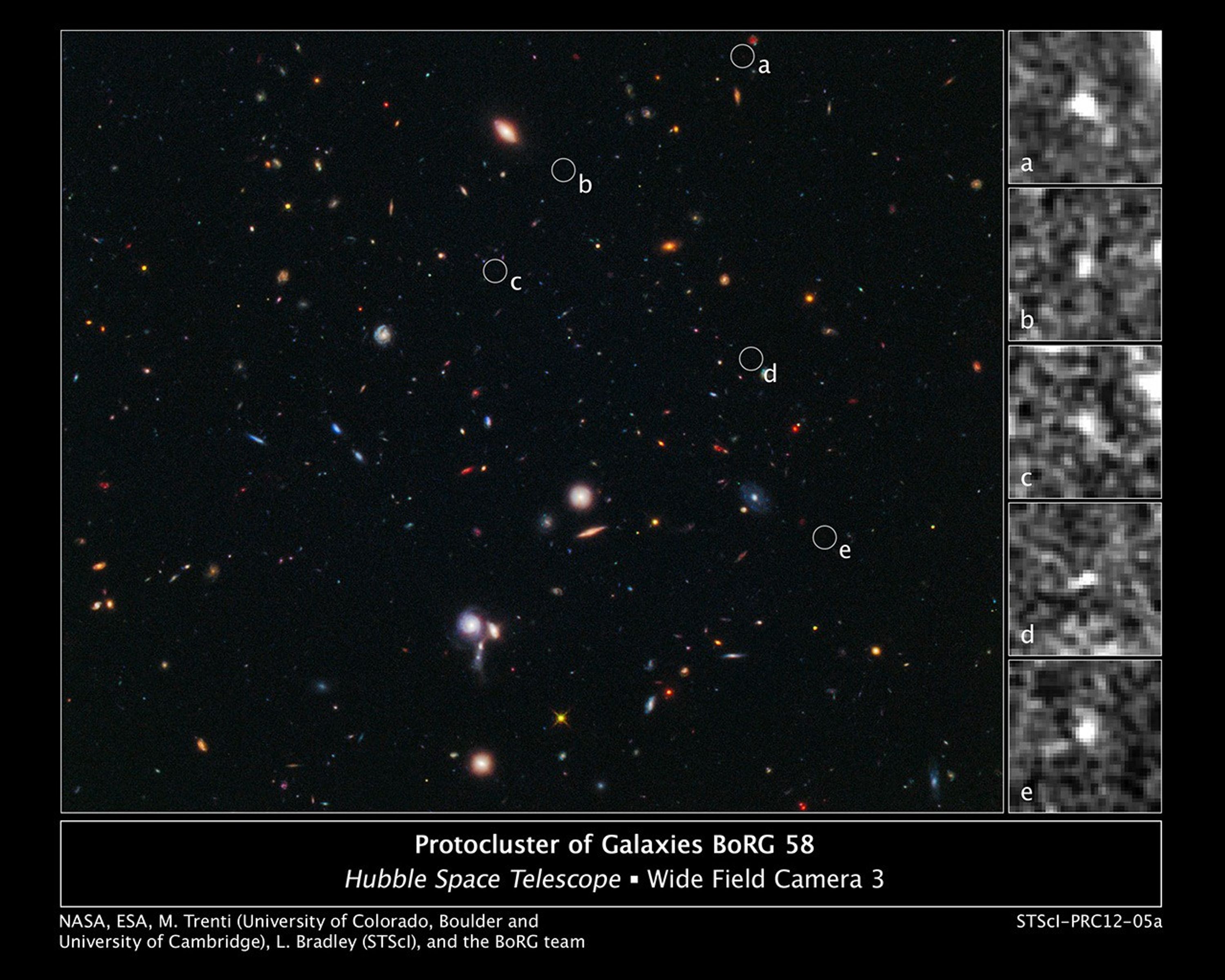

Hubble Spies Building Blocks of Most Distant Galaxy Cluster
The composite image at left, taken in visible and near-infrared light, reveals the location of five tiny galaxies clustered together 13.1 billion light-years away. The circles pinpoint the galaxies. The sharp-eyed Wide Field Camera 3 aboard NASA's Hubble Space Telescope spied...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov