1 min read
Multiwavelength View of Supernova 1987A

Astronomers combined observations from three different observatories to produce this colorful, multiwavelength image of the intricate remains of Supernova 1987A. The red color shows newly formed dust in the center of the supernova remnant, taken at submillimeter wavelengths by the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope in Chile. The green and blue hues reveal where the expanding shock wave from the exploded star is colliding with a ring of material around the supernova. The green represents the glow of visible light, captured by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The blue color reveals the hottest gas and is based on data from NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. The ring was initially made to glow by the flash of light from the original explosion. Over subsequent years the ring material has brightened considerably as the explosion’s shock wave slams in it. Supernova 1987A resides 163,000 light-years away in the Large Magellanic Cloud, where a firestorm of star birth is taking place. The ALMA, Hubble, and Chandra images at the bottom of the graphic were used to make up the multiwavelength view.
Image: NASA, ESA, and A. Angelich (NRAO/AUI/NSF)
Hubble data: NASA, ESA, and R. Kirshner (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics and Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation)
Chandra data: NASA/CXC/Penn State/K. Frank et al.
ALMA data: ALMA (ESO/NAOJ/NRAO) and R. Indebetouw (NRAO/AUI/NSF)
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.05h 35m 28.03s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-69° 16' 11".8
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Dorado
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.Approximately 163,000 light-years (50 kiloparsecs) away
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.SN 1987A
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Remnant
- Release DateFebruary 24, 2017
- Science ReleaseThe Dawn of a New Era for Supernova 1987A
- CreditNASA, ESA, A. Angelich (NRAO, AUI, NSF), Robert Kirshner (CfA, Moore Foundation), Kari Frank (PSU), R. Indebetouw (NRAO, AUI, NSF)
Related Images & Videos

Hubble Captures Wide View of Supernova 1987A
This Hubble Space Telescope image shows Supernova 1987A within the Large Magellanic Cloud, a neighboring galaxy to our Milky Way. Distant stars serve as a backdrop for Supernova 1987A, located in the center of the image. The bright ring around the central region of the exploded...

A Multiwavelength View of Supernova 1987A
Astronomers combined observations from three different observatories to produce this colorful, multiwavelength image of the intricate remains of Supernova 1987A. The red color shows newly formed dust in the center of the supernova remnant, taken at submillimeter wavelengths by...

An ALMA View of Supernova 1987A
This is an image of the intricate remains of Supernova 1987A taken in submillimeter wavelengths by the Atacama Large Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA) telescope in Chile. The red color shows newly formed dust in the center of the supernova remnant. Image Credit: NASA, ESA,...

A Hubble View of Supernova 1987A
This is an image of the intricate remains of Supernova 1987A taken by NASA’s Hubble Space Telescope. The green hue reveals where the expanding shock wave from the exploded star is colliding with a ring of material around the supernova. The green represents the glow of visible...

A Chandra View of Supernova 1987A
This is an image of the intricate remains of Supernova 1987A taken by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory. The blue hue reveals where the expanding shock wave from the exploded star is colliding with a ring of material around the supernova. The blue color reveals the hottest gas....

Scale and Compass for SN 1987A
Image of Supernova Remnant SN 1987A, with compass arrows, scale bar, and color key for reference. The north and east compass arrows show the orientation of the image on the sky. Note that the relationship between north and east on the sky (as seen from below) is flipped relative...
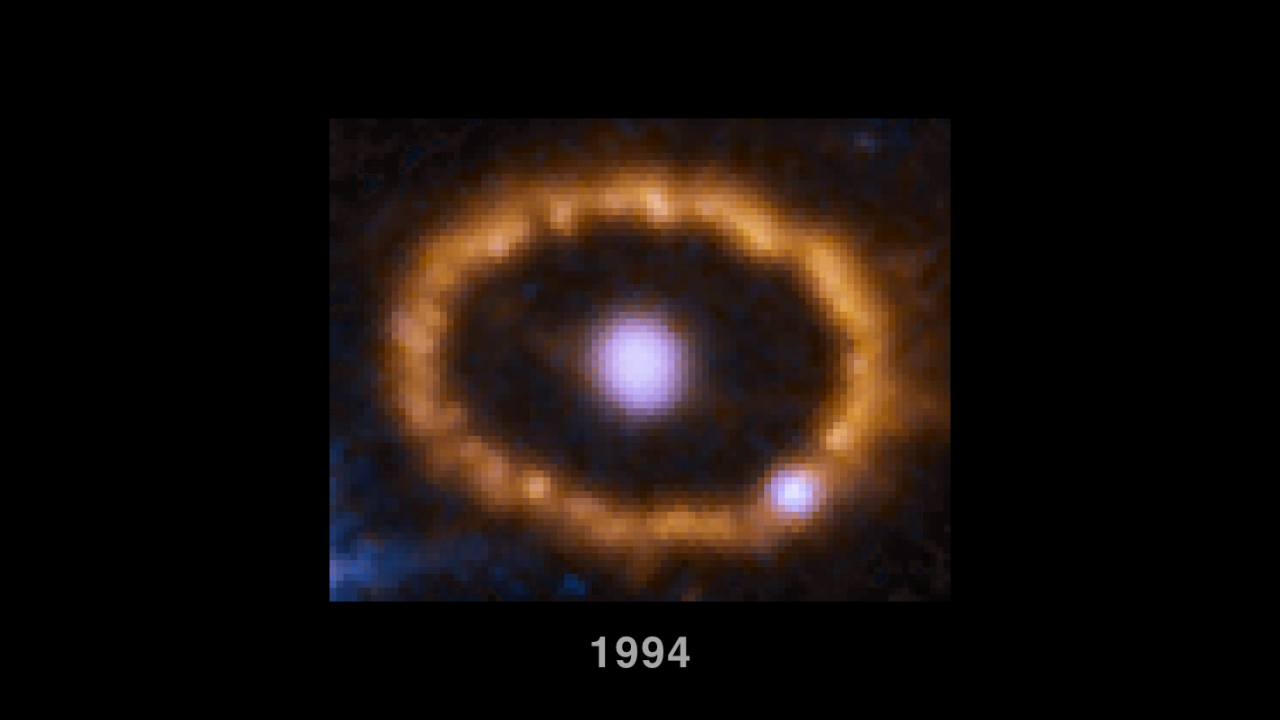

Hubble Chronicles Brightening of Ring around an Exploded Star (Annotated)
This time-lapse video sequence of Hubble Space Telescope images reveals dramatic changes in a ring of material around the exploded star Supernova 1987A. The images, taken from 1994 to 2016, show the effects of a shock wave from the supernova blast smashing into the ring. The...
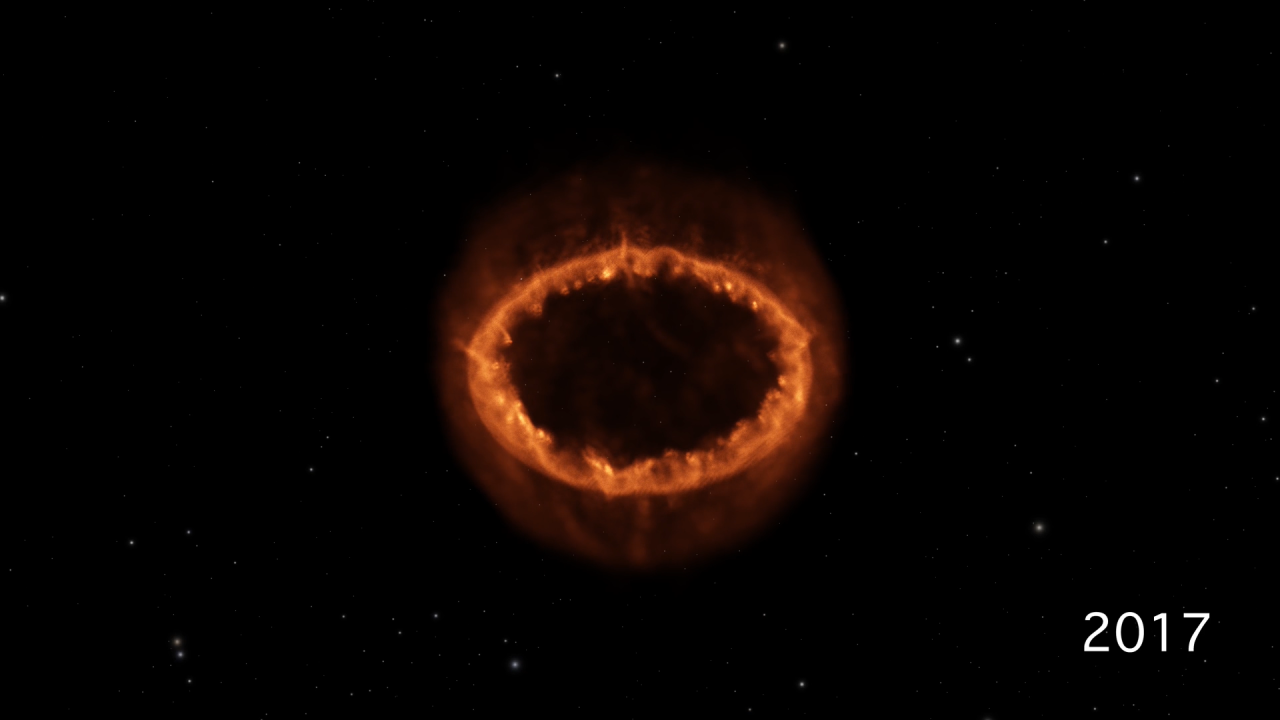
The Development of Supernova 1987A
This scientific visualization shows the development of Supernova 1987A, from the initial blast observed three decades ago to the luminous ring of material we see today. The sequence, using data from a computer simulation, begins with the star before it exploded. A ring of...
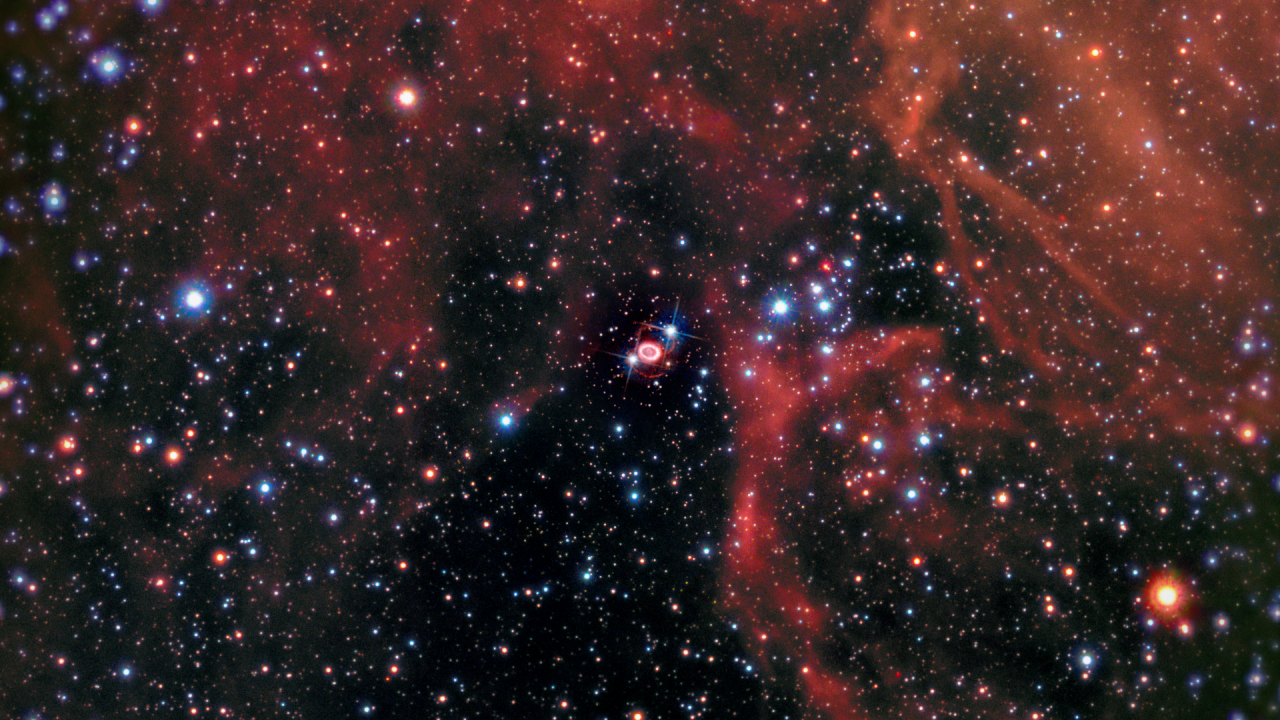

A Zoom into Supernova 1987A
The video begins with a nighttime view of the Small and Large Magellanic clouds, satellite galaxies of our Milky Way. It then zooms into a rich star-birth region in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Nestled between mountains of red-colored gas is the odd-looking structure of Supernova...

Interview with Astronomer Robert Kirshner
Harvard astronomer and chief program officer of science at the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, Robert Kirshner discusses key events in the 30 years of observing Supernova 1987A, the nearest supernova explosion seen in hundreds of years. The Hubble Space Telescope was among...
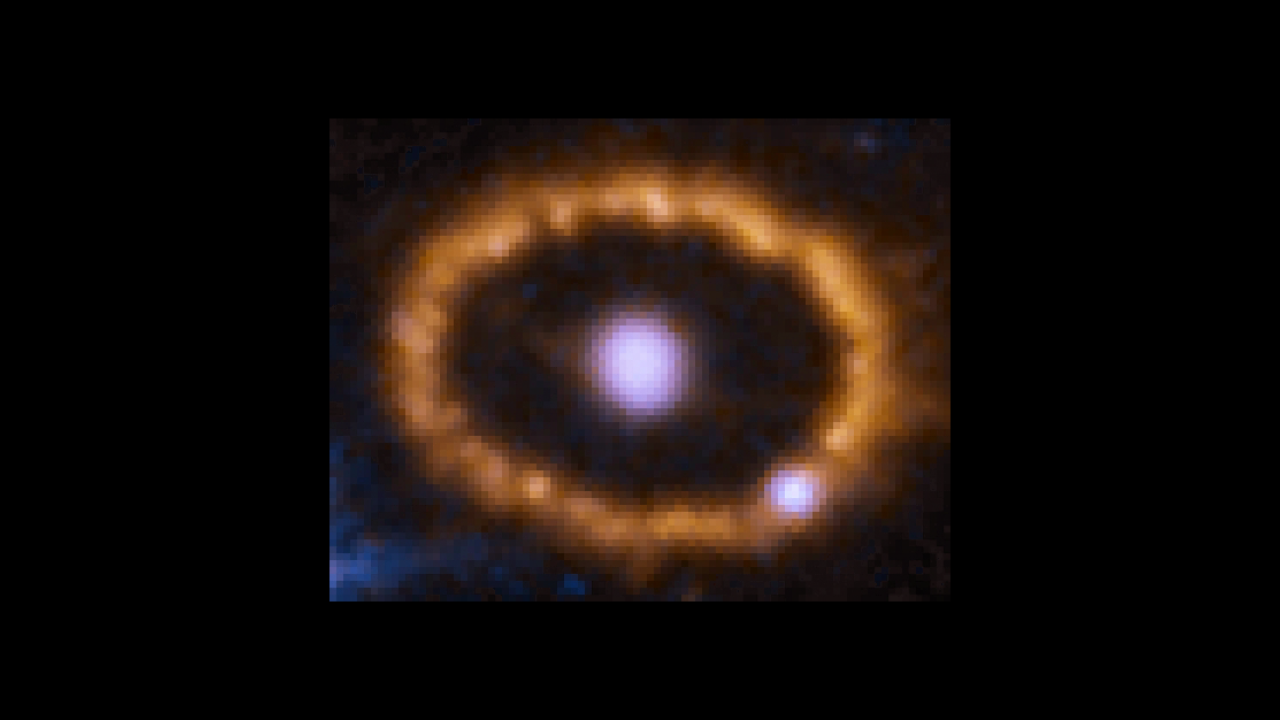

Hubble Chronicles Brightening of Ring around an Exploded Star
This time-lapse video sequence of Hubble Space Telescope images reveals dramatic changes in a ring of material around the exploded star Supernova 1987A. The images, taken from 1994 to 2016, show the effects of a shock wave from the supernova blast smashing into the ring. The...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov

































