1 min read
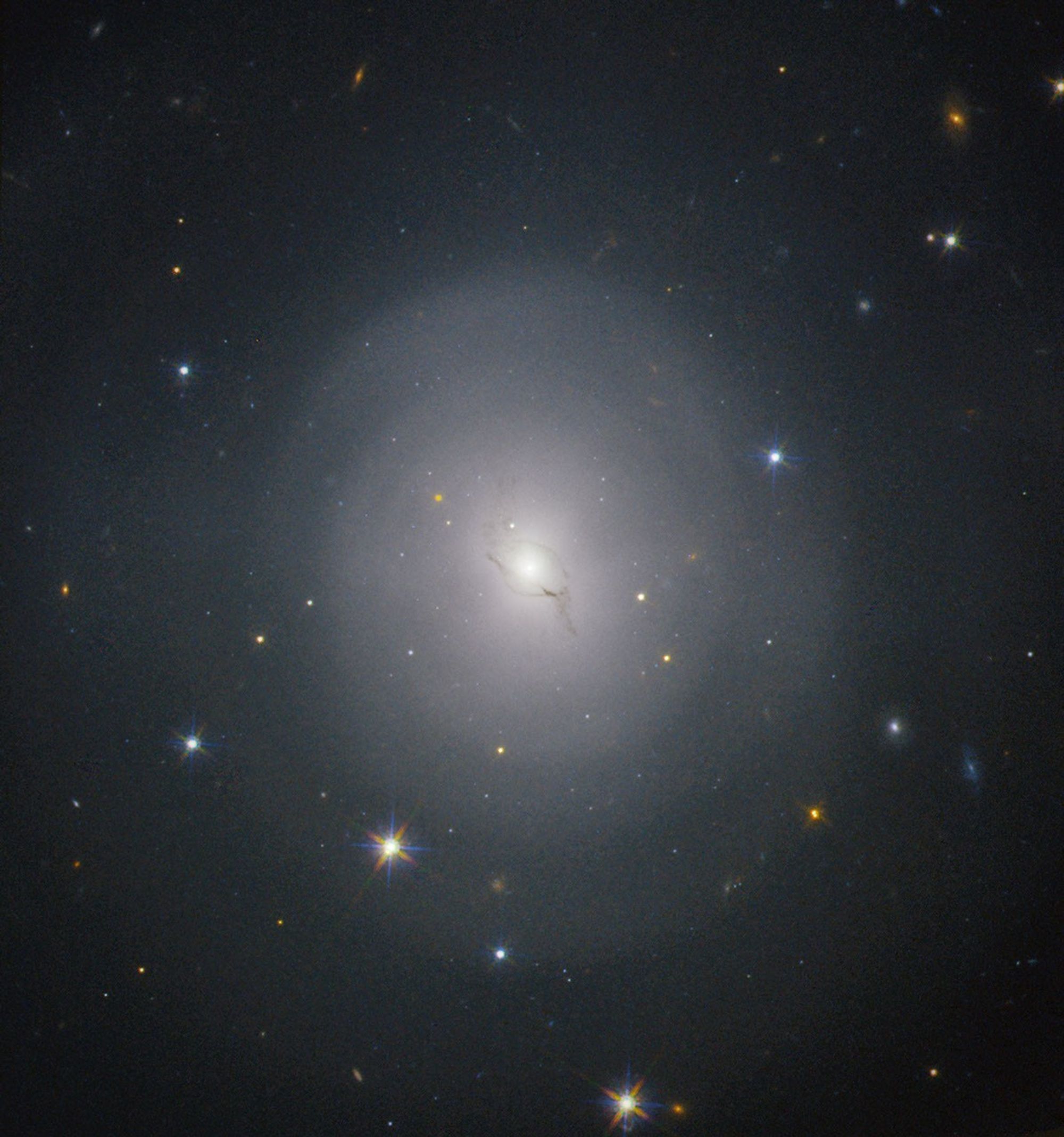
NGC 4993

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.13 09 48.080
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.-23 22 53.20
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Hydra
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.130 million light-years (to NGC 4993)
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is about 1.6 arcmin across, about 60,500 light-years at the distance of NGC 4993.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator. - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.WFC3/UVIS, WFC3/IR
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.April 28, and August 22, 2017
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.WFC3/UVIS F606W, WFC3/IR F110W, F160W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.NGC 4993
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Elliptical Galaxy
- Release DateOctober 16, 2017
- Science ReleaseNASA Missions Catch First Light from a Gravitational-Wave Event
- Credit

This image is a composite of separate exposures made by the WFC3 instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope using two different cameras and filters isolating the light of specific elements or of specific broad wavelength ranges. The color arises by assigning different hues (colors), to each monochromatic image. In this case, the colors are: blue WFC3/UVIS F606W, green WFC3/IR F110W, orange/red: WFC3/IR F160W.

Related Images & Videos

Gravitational Wave Source in NGC 4993
On August 17, 2017, the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory detected gravitational waves from a neutron star collision. Within 12 hours, observatories had identified the source of the event within the galaxy NGC 4993, shown in this Hubble Space Telescope image,...

Neutron Star Collision Creates Kilonova
Panel 1: A pair of neutron stars in a binary system spiral together. Orbital momentum is dissipated through the release of gravitational waves, which are tiny ripples in the fabric of space-time. Panel 2: In the final milliseconds, the two objects merge and produce a gamma-ray...
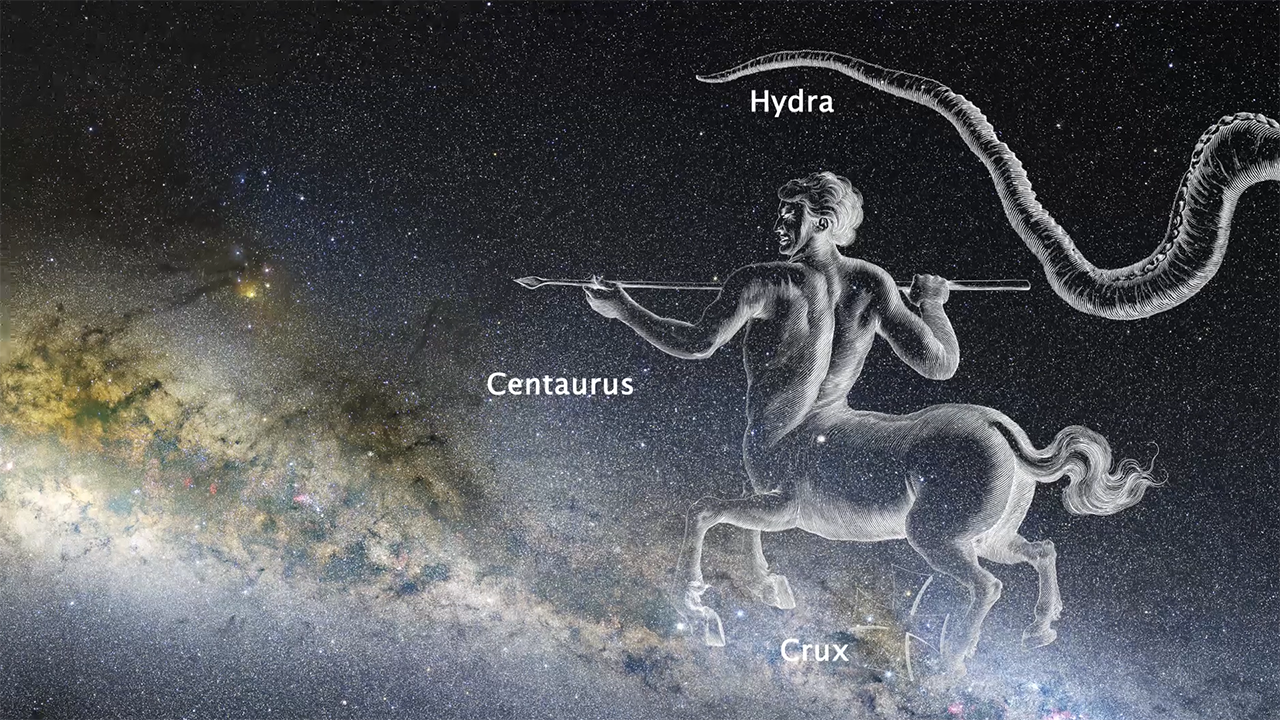
Narrated Zoom into GRB170817A in NGC 4993
This narrated movie zooms into the constellation Hydra to focus on the galaxy NGC 4993. Within this galaxy, a neutron star collision generated gravitational waves and an associated gamma-ray burst (GRB). It also resulted in a glow called a kilonova that was visible to telescopes...
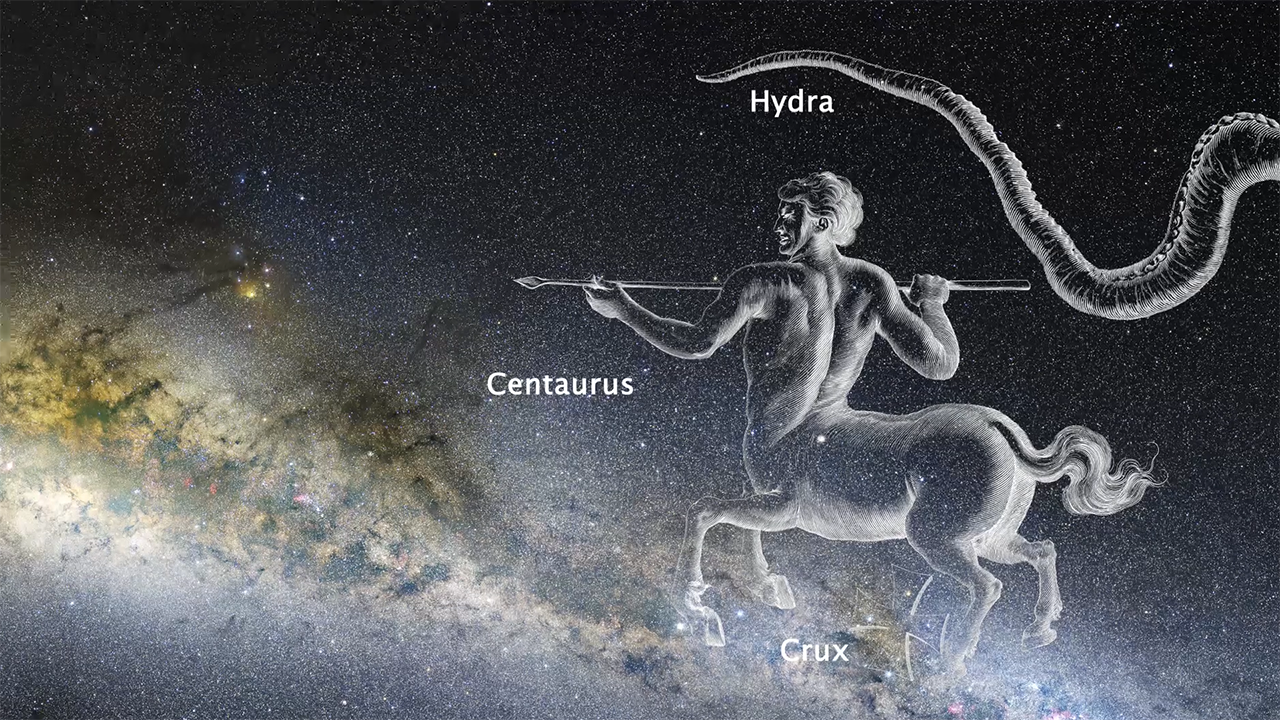
Zoom into GRB170817A in NGC 4993
This movie zooms into the constellation Hydra to focus on the galaxy NGC 4993. Within this galaxy, a neutron star collision generated gravitational waves and an associated gamma-ray burst (GRB). It also resulted in a glow called a kilonova that was visible to telescopes...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov






























