1 min read
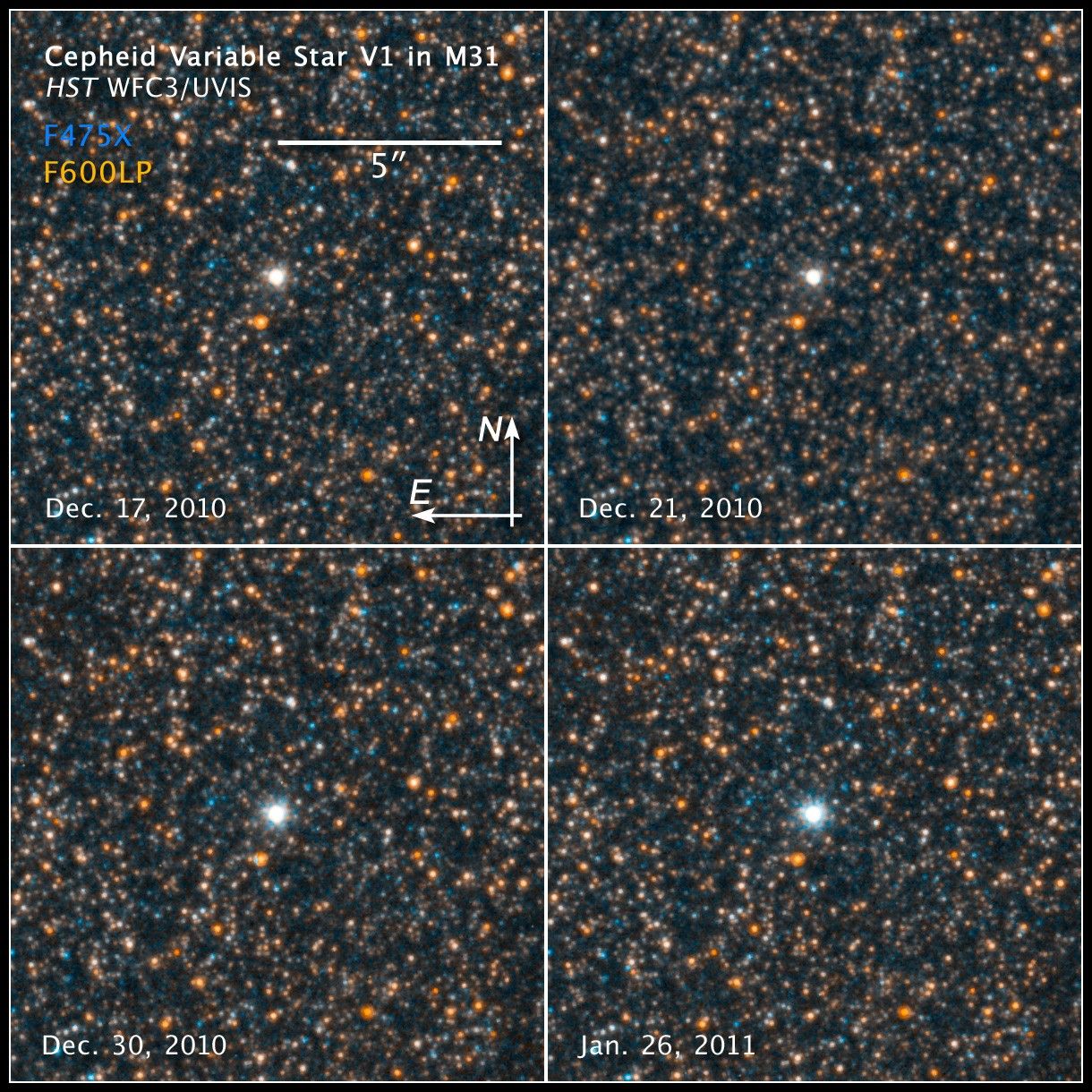
Star Field in M31 Imaged by Hubble WFC3

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.00h 41m 26.99s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.41° 10' 6.0"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Andromeda
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 2.5 million light-years (0.8 megaparsecs)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 12326: K. Noll (PI), Z. Levay, M. Mutchler, T. Borders, L. Frattare, M. Livio, C. Christian, D. Soderblom, and H. Bond (Hubble Heritage Team/STScI). Note:The Hubble Space Telescope observations of Hubble's Variable M31-V1 were made possible from ground-based data provided by the American Association of Variable Star Observers (AAVSO). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.December 2010 - January 2011, Exposure Time: 1.7 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F475X (Wide Blue) and F600LP (Long Pass)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.M31-V1
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Cepheid Variable Star V1 in M31
- Release DateMay 23, 2011
- Science ReleaseHubble Views the Star that Changed the Universe
- CreditNASA, ESA, and the Hubble Heritage Team (STScI/AURA)

This image is a composite of separate exposures acquired by the WFC3 instrument on HST. Several filters were used to sample broad wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic (grayscale) image associated with an individual filter. In this case, the assigned colors are: Cyan: F475X (Wide Blue) Orange: F600LP (Long Pass)
Related Images & Videos
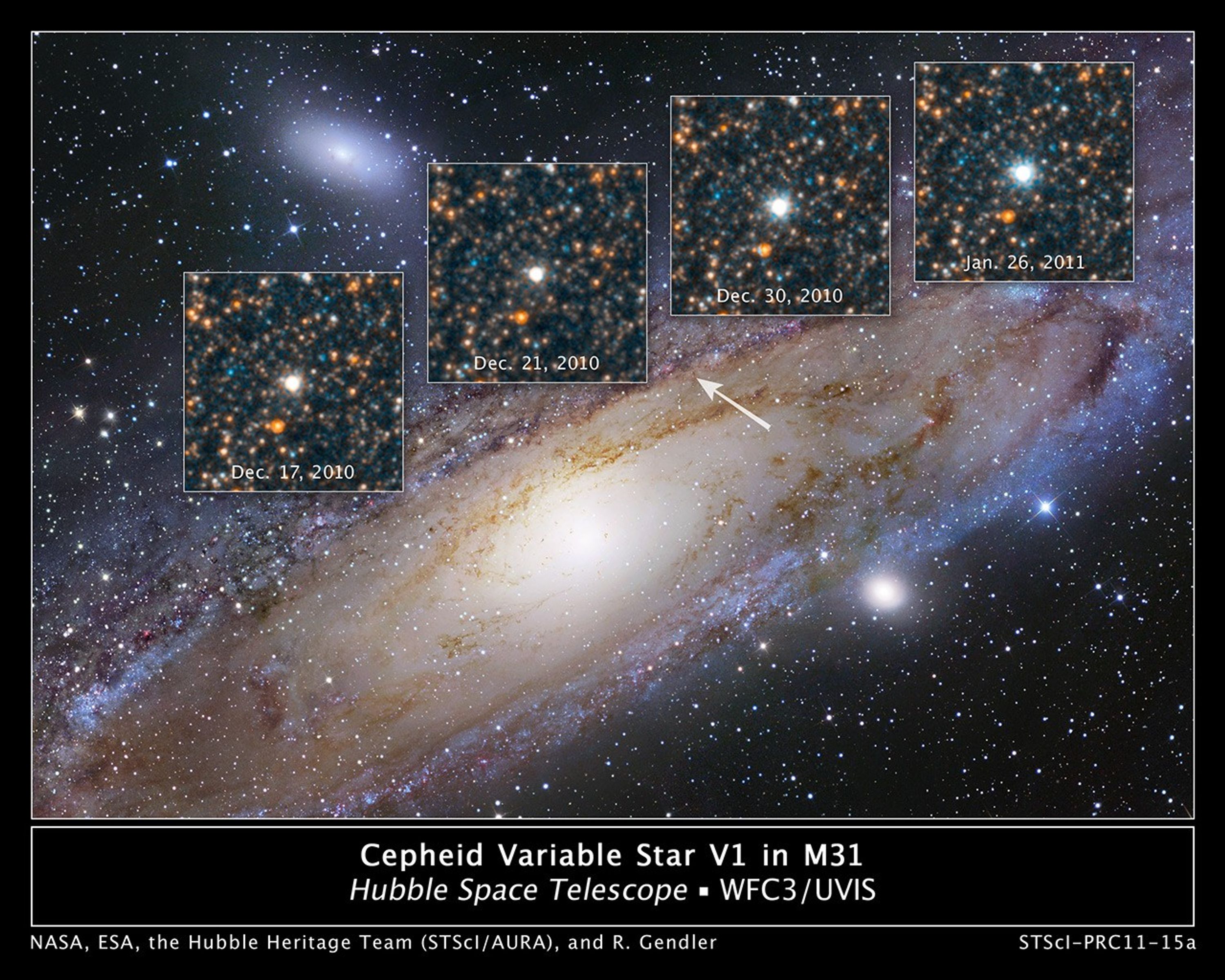

Hubble Views the Star that Changed the Universe
Though the universe is filled with billions upon billions of stars, NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has been trained on a single variable star that in 1923 altered the course of modern astronomy. And, at least one famous astronomer of the time lamented that the discovery had...
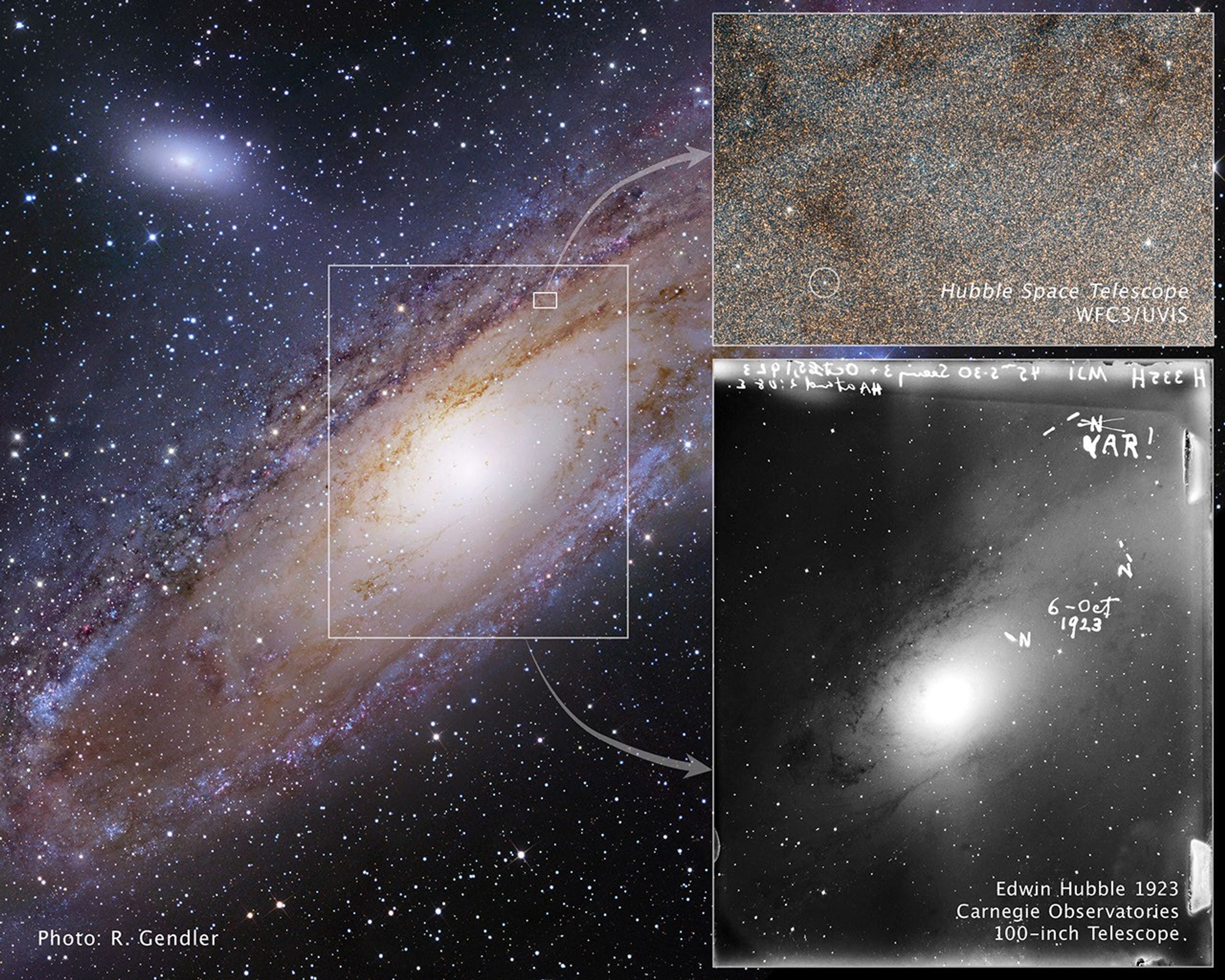

Snapshots of the Star that Changed the Universe
Views of a famous pulsating star taken nearly 90 years apart and a portrait of its galactic home are shown in this image collection. The pancake-shaped disk of stars, gas, and dust that make up the Andromeda galaxy, or M31, is shown in the image at left. Andromeda is a Milky Way...
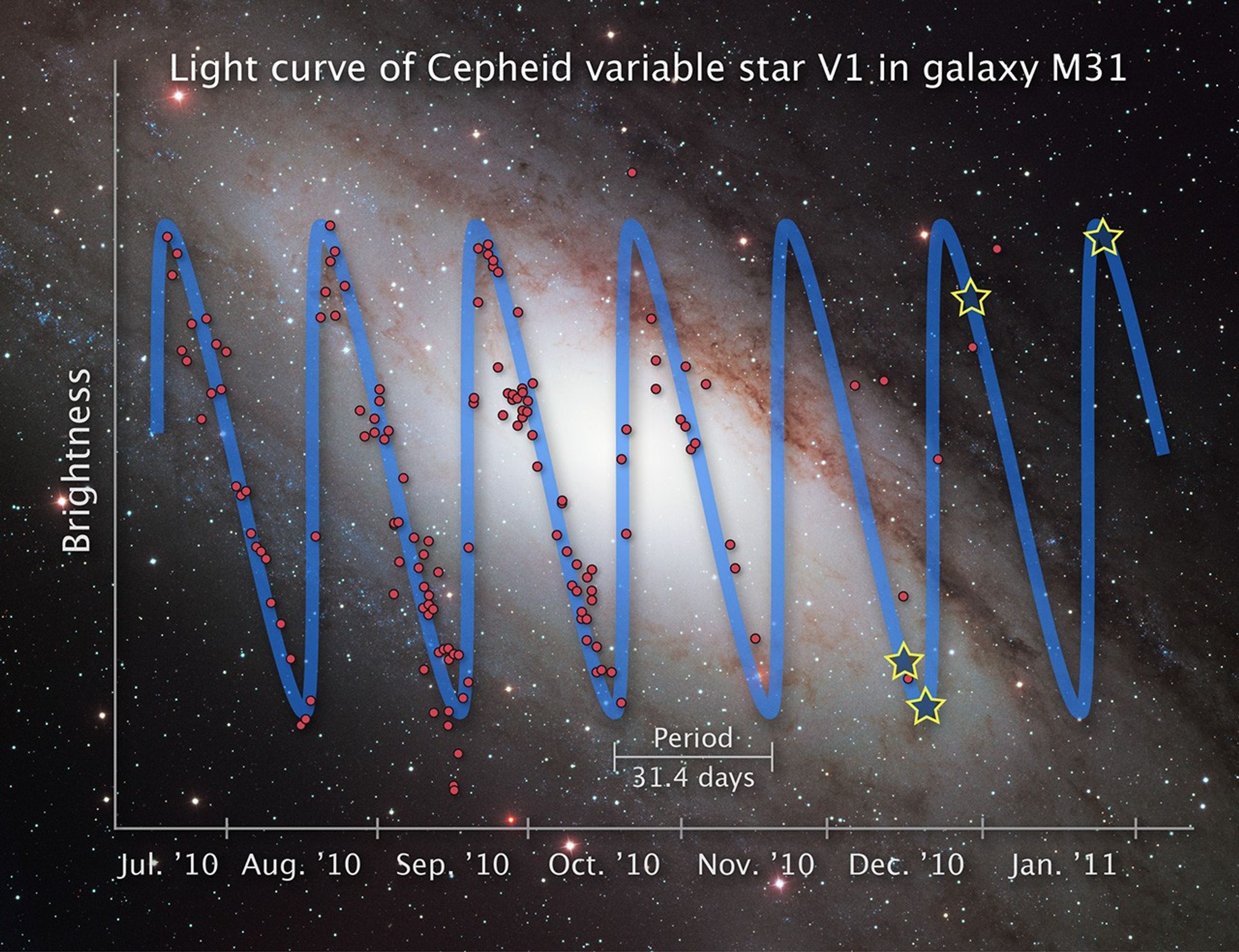
Light Curve of Cepheid Variable Star V1
This illustration shows the rhythmic rise and fall of starlight from the Cepheid variable star V1 over a seven-month period. Cepheid variables are pulsating stars that brighten and fade in a predictable pattern. The illustrated graph shows that V1 completes a pulsation cycle...

Hubble Space Telescope Returns to Namesake's Discovery (Narrated)
Less than a century ago, the bright arc of our Milky Way was thought to contain all the stars in the universe. But, astronomers were perplexed by a cigar-shaped object in the autumn sky called the Andromeda nebula. Some astronomers thought it was another galaxy like our Milky...

Hubble Space Telescope Returns to Namesake's Discovery (Unnarrated)
Less than a century ago, the bright arc of our Milky Way was thought to contain all the stars in the universe. But, astronomers were perplexed by a cigar-shaped object in the autumn sky called the Andromeda nebula. Some astronomers thought it was another galaxy like our Milky...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov