1 min read
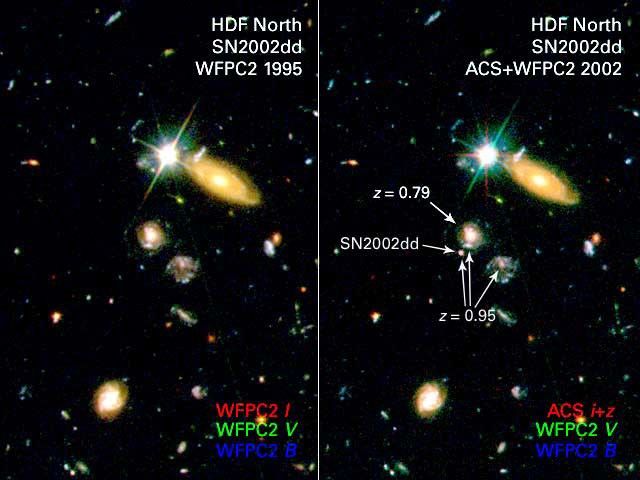
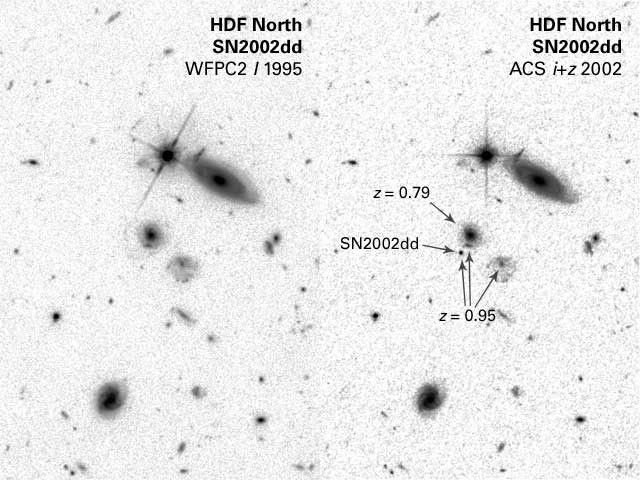
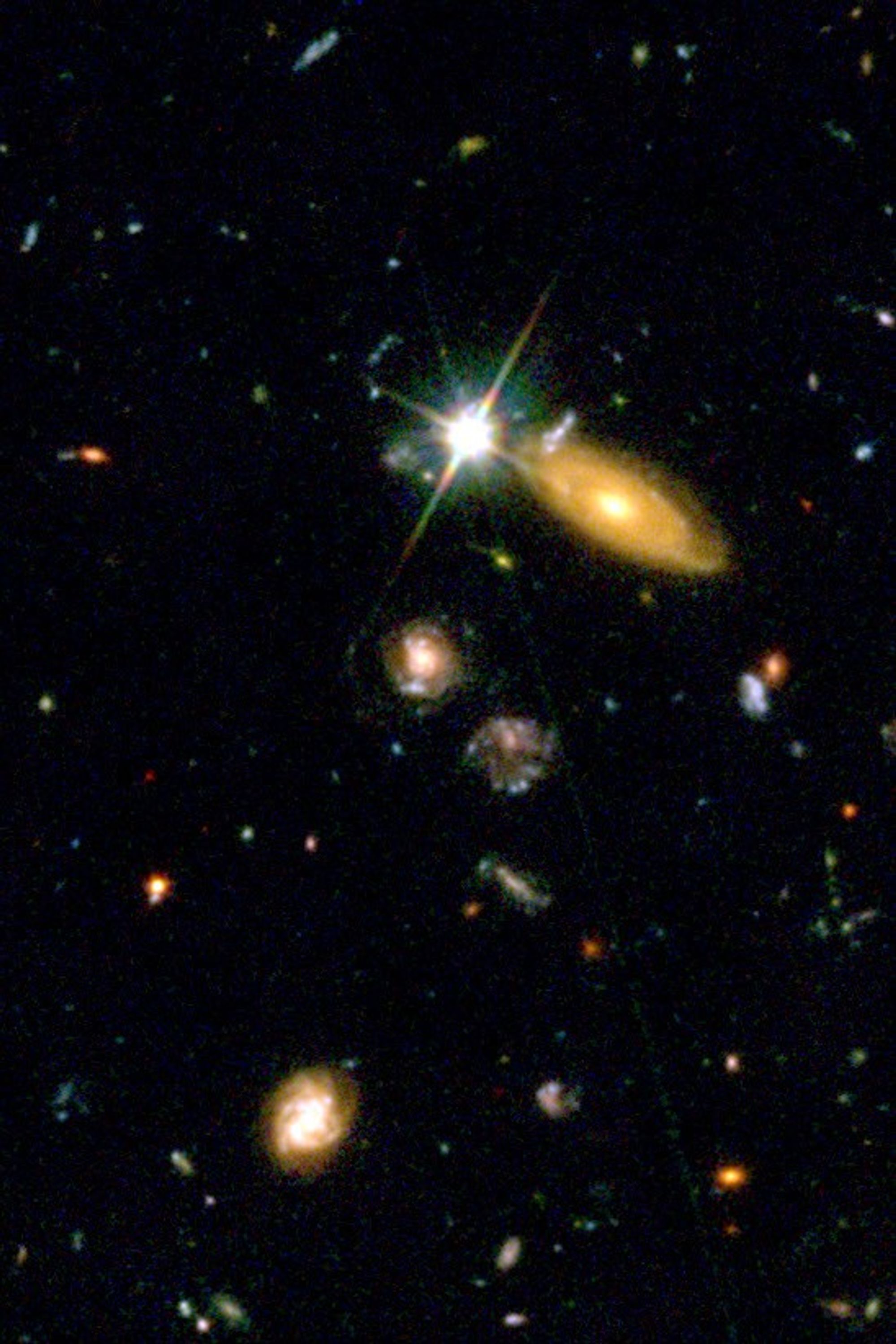
Supernova (SN 2002dd) in the Hubble Deep Field — 1995

About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h 36m 55.36s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+62° 12' 46.1"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Major
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.2.4 billion parsecs (8 billion light-years)
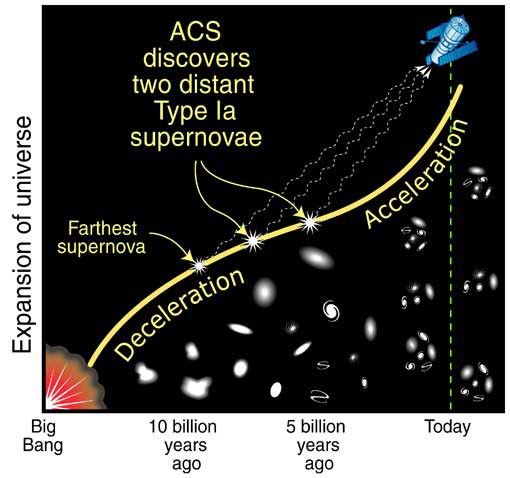
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Redshift: z = 0.95
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.These observations are from the HST proposals 9301 (H. Ford and collaborators) and 9352 (A. Riess (STScI) and collaborators). The science team for the SN2002dd results include: J.P. Blakeslee (JHU), Z.I. Tsvetanov (JHU), A. Riess (STScI), H.C. Ford (JHU), G.D. Illingworth (UCO/Lick Obs.), D. Magee (Lick Obs./UCSC), J. Tonry (IfA/Univ. Hawaii), N. Benitez (JHU), M. Clampin (STScI), G.F. Hartig (STScI), G.R. Meurer (JHU), M. Sirianni (JHU), D.R. Ardila (JHU), F. Bartko (Bartko Science & Technology), R.J. Bouwens (UCO/Lick Obs.), T.J. Broadhurst (Racah Institute of Physics, The Hebrew University), N.J.G. Cross (JHU), P.D. Feldman (JHU), M. Franx (Leiden Observatory), D.A.Golimowski (JHU), C. Gronwall (PSU), R.A. Kimble (NASA GSFC), J.E. Krist (STScI), A.R. Martel (JHU), F. Menanteau (JHU), G.K. Miley (Leiden Obs.), M. Postman (STScI), P. Rosati (ESO), W.B. Sparks (STScI), L.-G. Strologer (STScI), H.D. Tran (JHU), R.L. White (STScI/JHU), and W. Zheng (JHU). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFPC2
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.1995
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F300W, F450W (B), F606W (V), and F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.HDF
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Supernova Type Ia in Hubble Deep Field North
- Release DateApril 10, 2003
- Science ReleaseFar-Flung Supernovae Shed Light on Dark Universe
- CreditNASA and J. Blakeslee (JHU)

Color Info
Color InfoA brief description of the methods used to convert telescope data into the color image being presented.
Blue: F450W (B) Green: F606W (V) Red: F814W (I)
Related Images & Videos
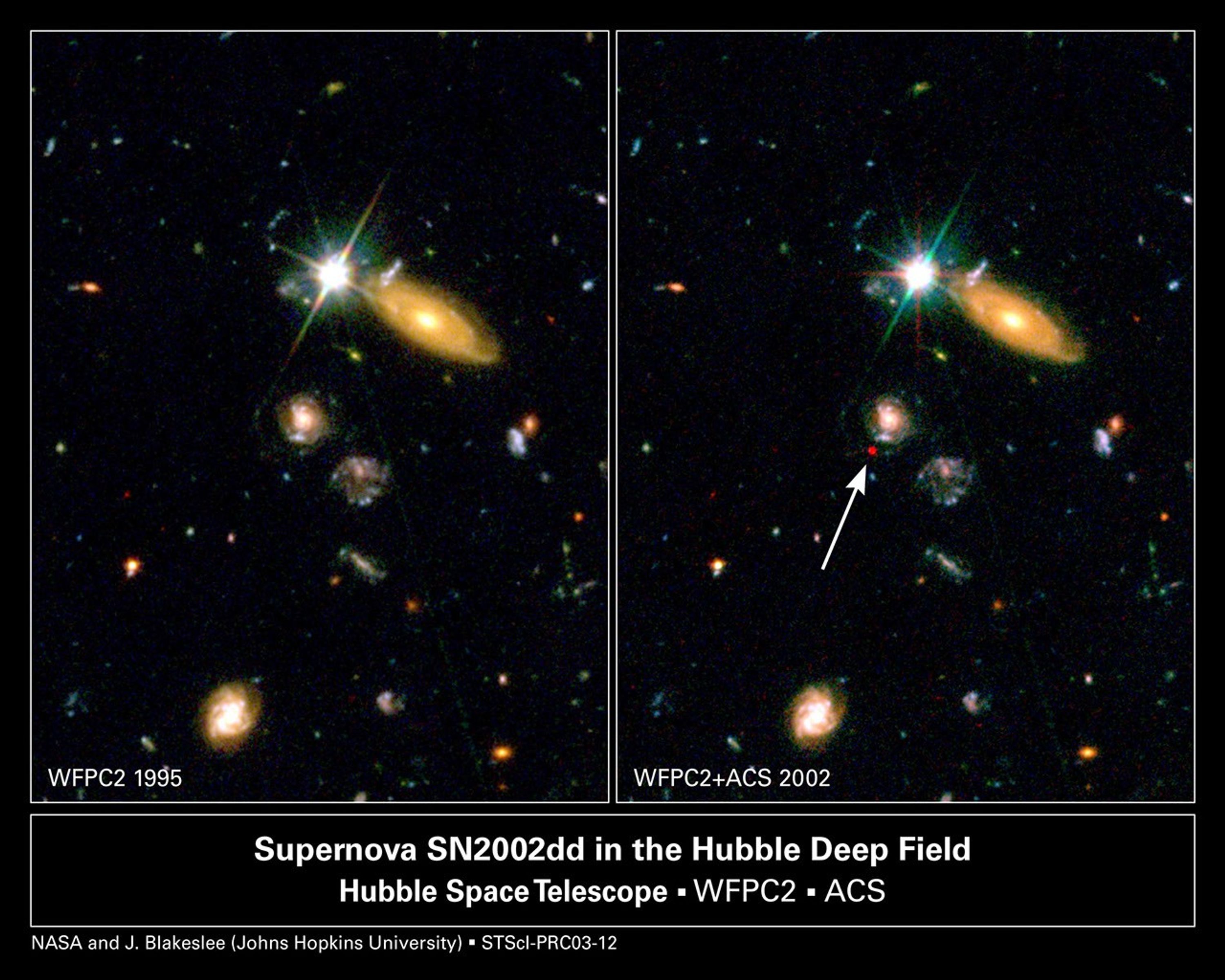

Far-Flung Supernova Sheds Light on Dark Universe
[Left] - A Hubble Space Telescope image of a portion of the Hubble Deep Field North as originally photographed in 1995 with the Wide Field Planetary Camera 2. [Right] - A composite image of the same field as imaged by Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys (ACS), combined with the...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov