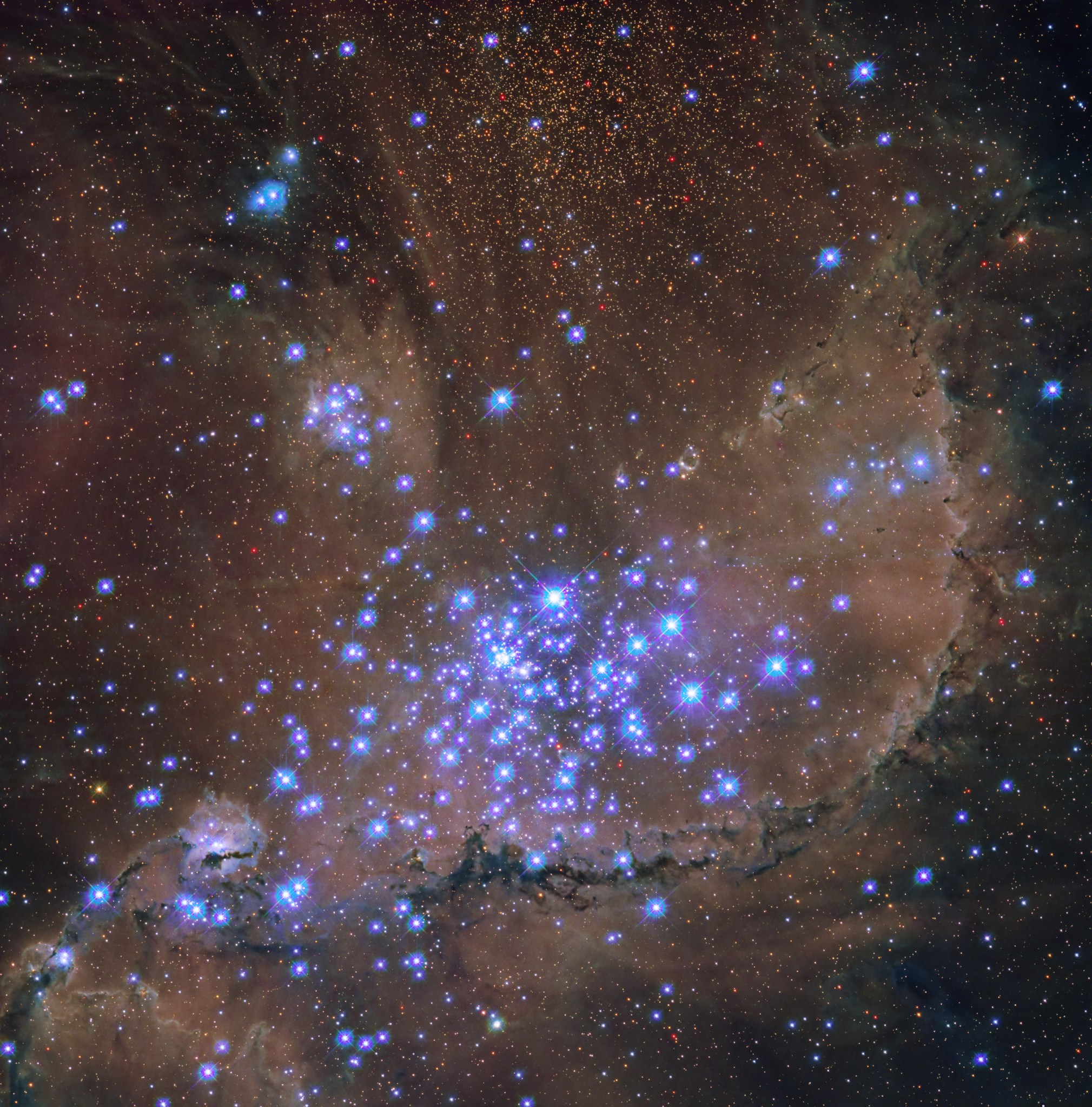
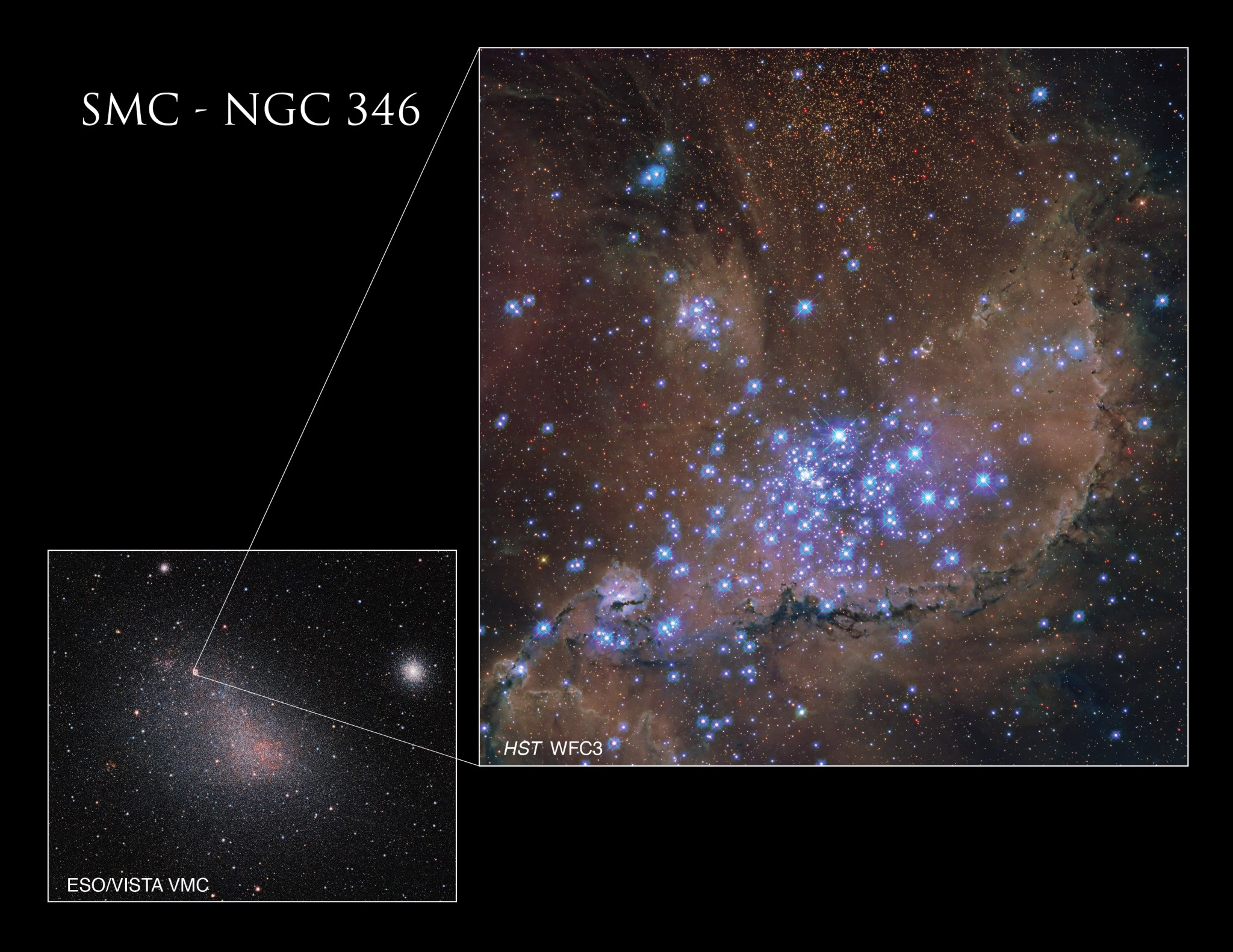
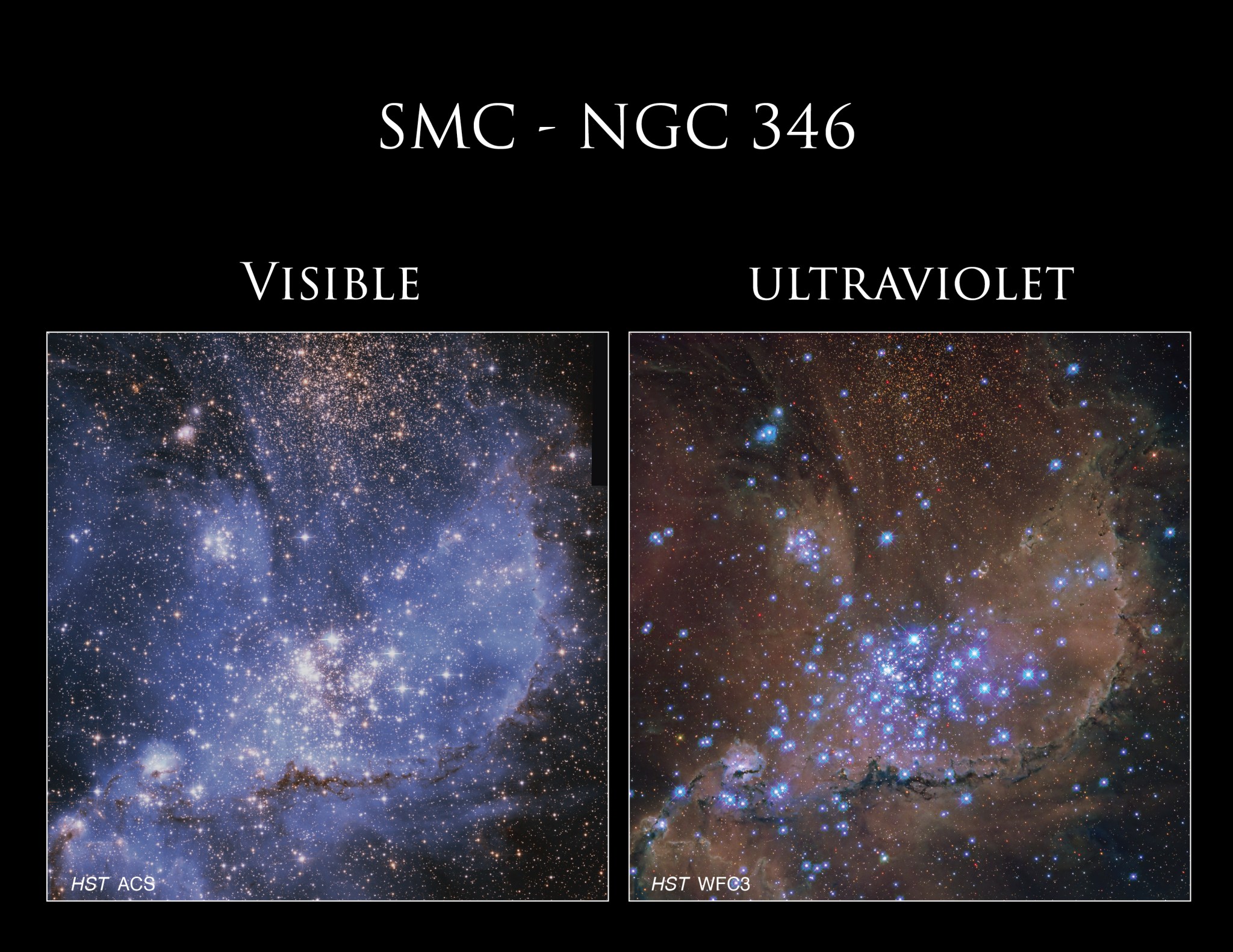
Roughly 210,000 light-years away, the Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) is one of our Milky Way galaxy’s closest neighbors. In fact, this small galaxy is one of the Milky Way’s “satellite” galaxies, which orbit our home spiral galaxy.
Nested within the SMC is this spectacular star cluster, known as NGC 346. Its hot stars unleash a torrent of radiation and energetic outflows, which erode the denser portions of gas and dust in the surrounding nebula, N66. Dozens of hot, blue, and high-mass stars shine within NGC 346, and astronomers believe this cluster contains more than half of the known high-mass stars in the whole SMC.
The NASA/ESA Hubble Space Telescope has observed this cluster before, but its new view shows NGC 346 in ultraviolet light, along with some visible-light data. Ultraviolet light helps scientists understand more about star formation and evolution, and Hubble – with its combined sharp resolution and position above our UV-blocking atmosphere – is the only telescope with the ability to make sensitive, ultraviolet observations.
These specific observations were gathered to learn more about how star formation shapes the interstellar medium, which is the gas distributed throughout seemingly empty space, in a low-metallicity galaxy like the SMC. Astronomers call elements heavier than hydrogen and helium “metals,” and the SMC contains fewer metals when compared to most parts of our Milky Way. This condition helps make it an excellent example of a galaxy similar to those that existed in our early universe, when very few heavy elements were around to incorporate.
Explore More
Media Contact:
Claire Andreoli
NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center, Greenbelt, MD
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov