-
Active Orbiting Heliophysics Missions
Each mission is positioned at a critical, well-thought out vantage point to observe and understand the flow of energy and particles throughout the solar system—all helping us untangle the effects of the star we live with. Orbiting missions, with spacecraft orbiting an object in space, i.e. Earth, the Sun, the Moon, or other planets and moons, are just one type of NASA mission. Other missions include sounding rockets, which follow a parabolic trajectory, typically reaching altitudes of 50–200 km before returning to Earth, and cube satellites, or CubeSats, which are small, standardized satellite, typically about the size of a Rubik's cube. Sounding rockets and CubeSats, not listed here, are quicker and less expensive methods for gathering data than missions that require rocket launches. Retired and future heliophysics missions are also not listed here.
ACE
Advanced Composition Explorer
Designed to collect and analyze particles from near and far, ranging from solar wind ions to galactic cosmic ray nuclei, ACE far exceeded its expected life span of five years and continues to provide data on space weather, and give advance warning of geomagnetic storms.
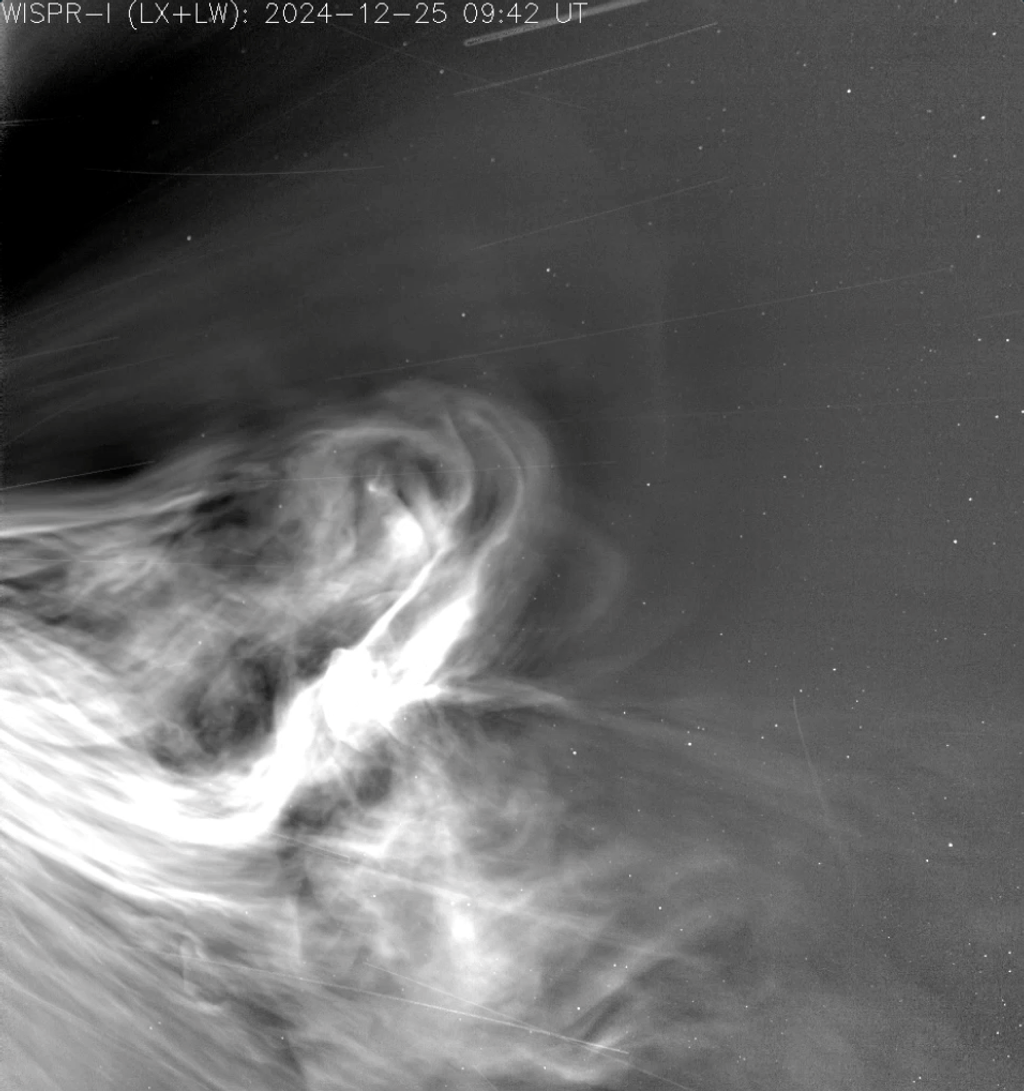
ARTEMIS (THEMIS)
Acceleration, Reconnection, Turbulence and Electrodynamics of Moon's Interaction with the Sun
Launched in 2007, THEMIS studies how mass and energy move through the near-Earth space environment to determine the physical processes initiating auroras. In 2010, two of its five spacecraft were repurposed as ARTEMIS and moved to a new location to study similar processes closer to the Moon.

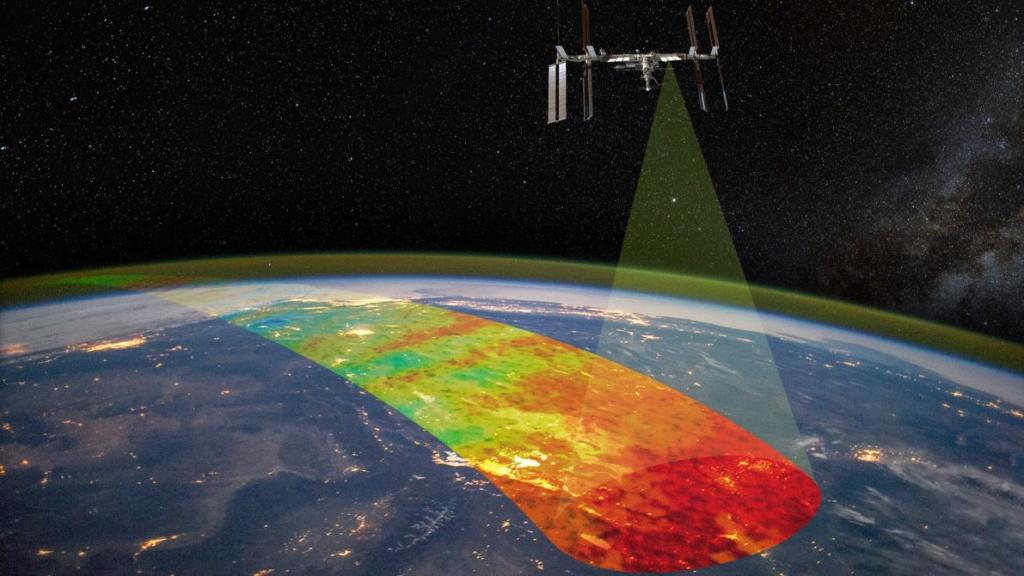
AWE
Atmospheric Waves Experiment
The Atmospheric Waves Experiment (AWE) is attached to the exterior of the Earth-orbiting International Space Station. From its space station perch, AWE focuses on colorful bands of light in Earth’s atmosphere, called airglow, to determine what combination of forces drive space weather in the upper atmosphere.
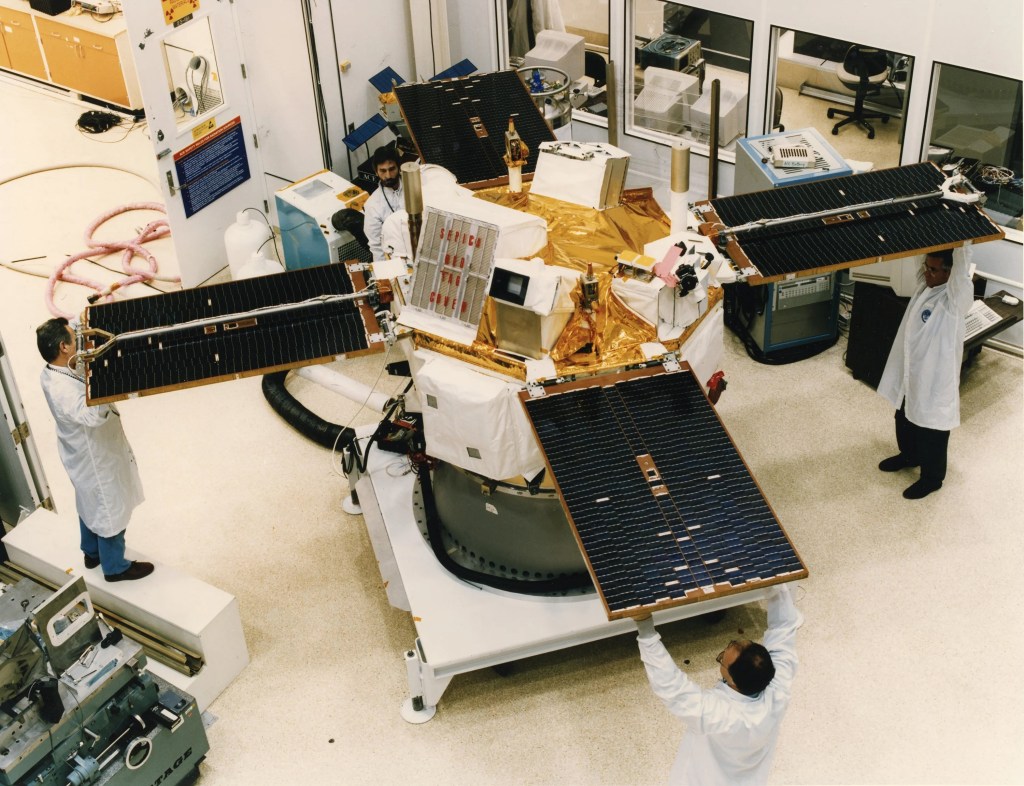
DSCOVR
Deep Space Climate Observatory
DSCOVR is a space weather station that monitors changes in the solar wind, providing space weather alerts and forecasts for geomagnetic storms that could disrupt power grids, satellites, telecommunications, aviation and GPS.
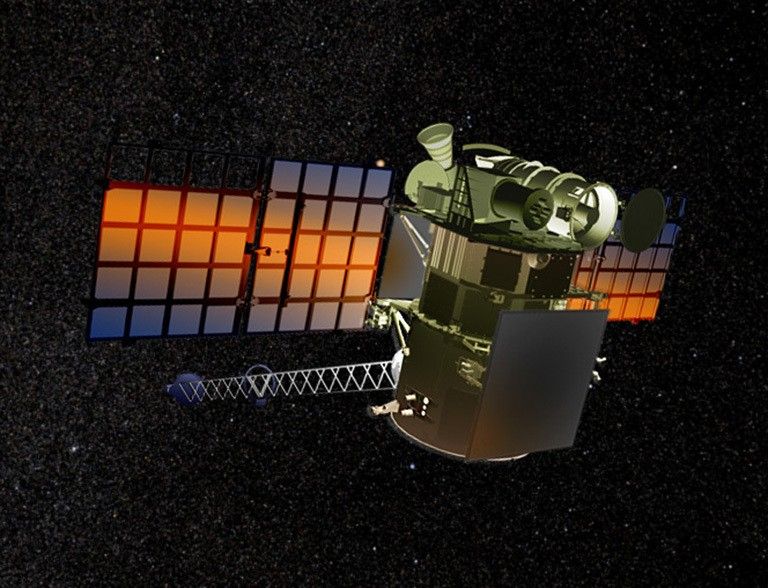

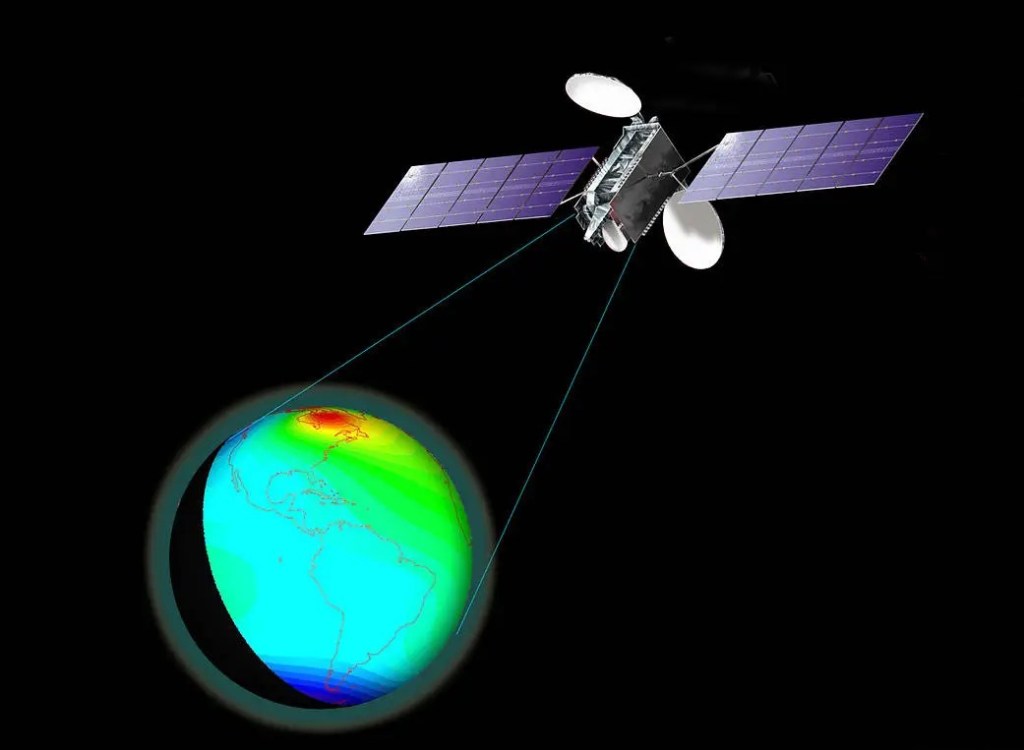
GOLD
Global-scale Observations of the Limb and Disk
GOLD measures densities and temperatures in Earth’s thermosphere and ionosphere. GOLD makes these measurements, in unprecedented detail, with an ultraviolet (UV) imaging spectrograph on a geostationary satellite.
The goal of the investigation is to provide answers to key elements of an overarching question for Heliophysics science: What is the global-scale response of the thermosphere and ionosphere to forcing in the integrated Sun-Earth system?
IBEX
Interstellar Boundary Explorer
IBEX is a NASA spacecraft studying how our heliosphere, the magnetic bubble surrounding our Sun and planets, interacts with interstellar space. IBEX created the first maps showing the interactions at that border, and how they change over time.
IRIS
Interface Region Imaging Spectrograph
IRIS observes how solar material moves, gathers energy, and heats up as it travels through a little-understood region in the Sun's lower atmosphere.
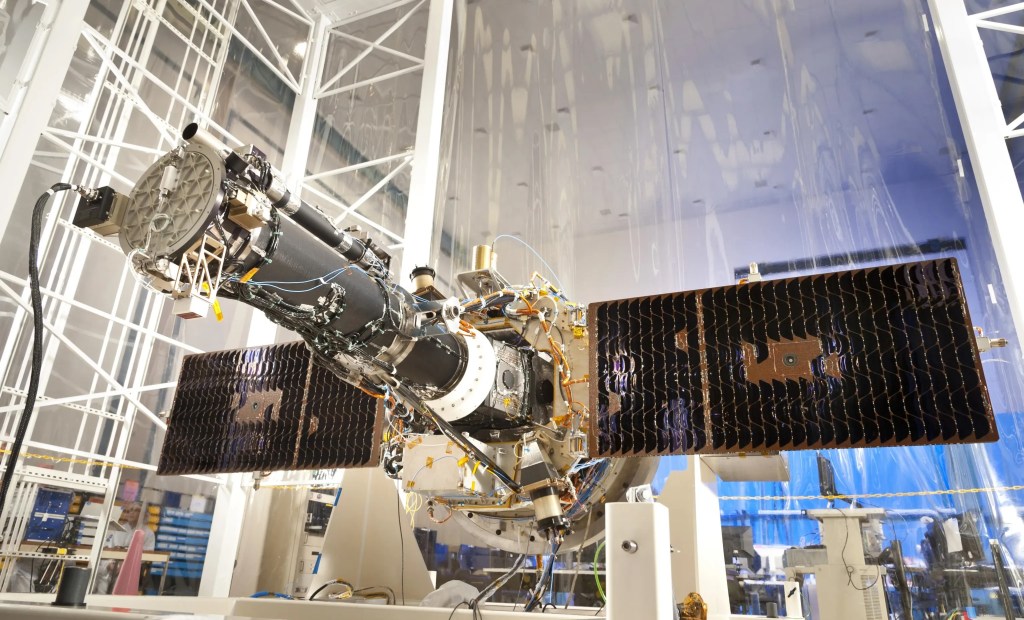

MMS
Magnetospheric Multiscale
MMS investigates how the Sun's and Earth's magnetic fields connect and disconnect, explosively transferring energy from one to the other. This process occurs throughout the universe and is known as magnetic reconnection.
Parker Solar Probe
Parker Solar Probe is collecting measurements and images to expand our knowledge of the origin and evolution of solar wind.
On a mission to “touch the Sun,” NASA's Parker Solar Probe became the first spacecraft to fly through the corona – the Sun’s upper atmosphere – in 2021. NASA's Parker Solar Probe will revolutionize our understanding of the Sun and makes critical contributions to forecasting changes in the space environment that affect life and technology on Earth.

SDO
Solar Dynamics Observatory
SDO studies how solar activity is created and drives space weather, by monitoring the Sun’s interior, atmosphere, magnetic field, and energy output.
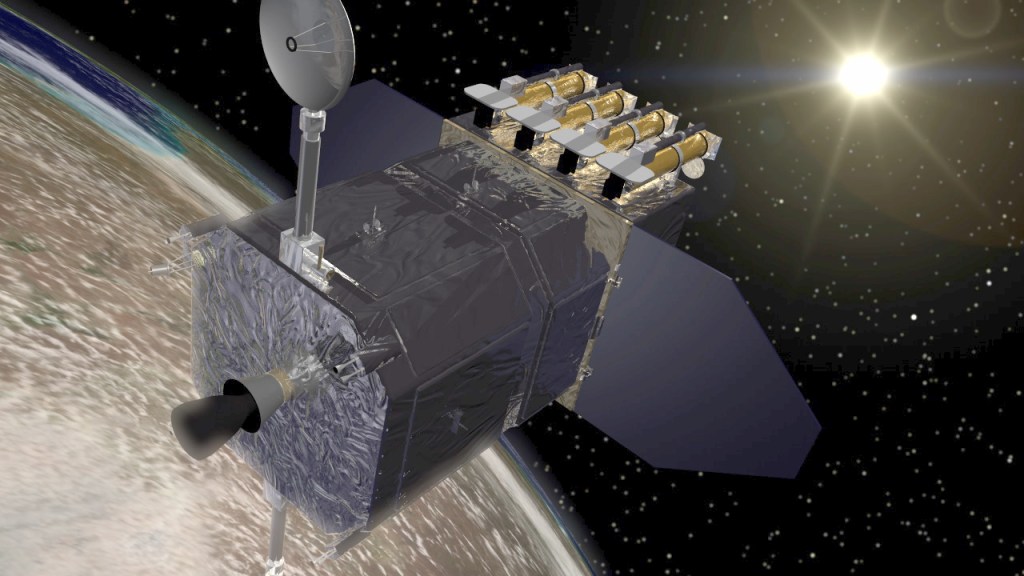

SOHO
Solar and Heliospheric Observatory
Launched in December 1995, the joint NASA-ESA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory mission (SOHO), was designed to study the Sun inside out. Though its mission was scheduled to run until only 1998, it has continued collecting data, adding to scientists' understanding of our closest star, and making many new discoveries, including more than 5,000 comets.

Solar Orbiter
An international cooperative mission between the European Space Agency (ESA) and NASA.
Solar Orbiter is a Sun-observing satellite with 10 science instruments, all designed to provide unprecedented insight into how our local star 'works.'
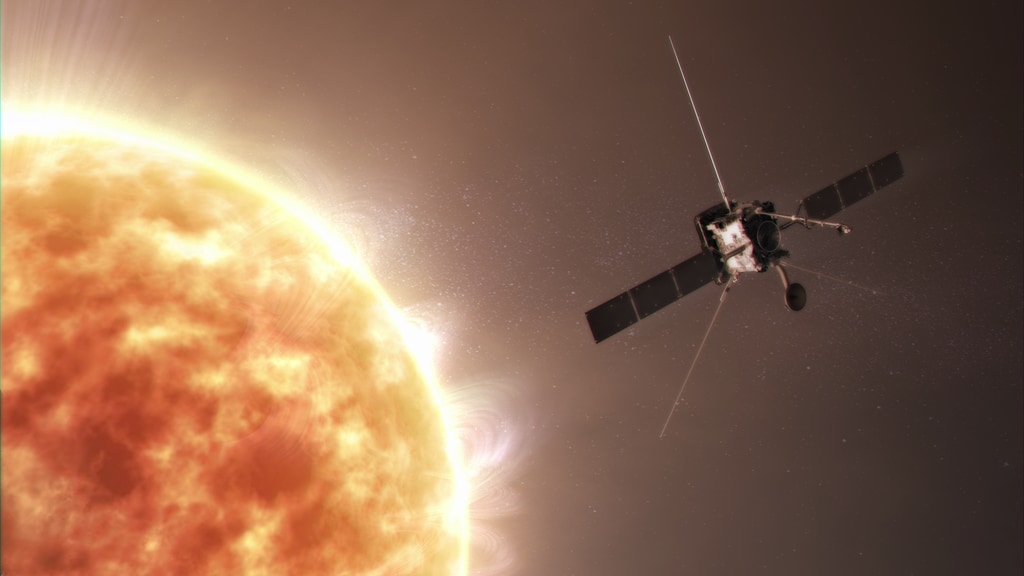

STEREO A & B
Solar TErrestrial RElations Observatory
Providing a revolutionary view of the Sun-Earth system, STEREO launched with two nearly identical observatories – one ahead of Earth in its orbit, the other trailing behind – to capture stereoscopic images revealing the 3D structure of the Sun’s coronal mass ejections. The STEREO A spacecraft continues to study the Sun today.
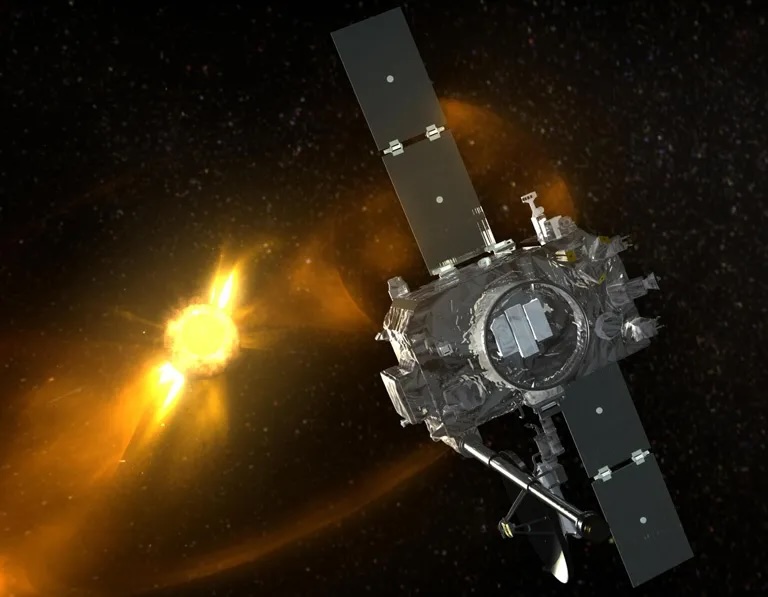

TIMED
Thermosphere Ionosphere Mesosphere Energetics and Dynamics
The TIMED mission is studying the influence of the Sun and humans on the least explored and understood region of Earth's atmosphere – the mesosphere and lower thermosphere / ionosphere. This region is a gateway between Earth and space, where the Sun's energy is first deposited into Earth's environment.
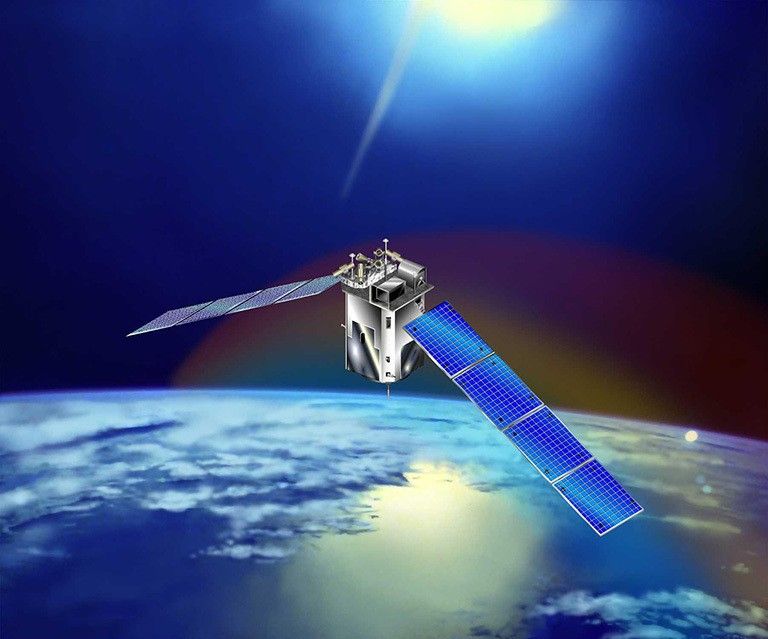

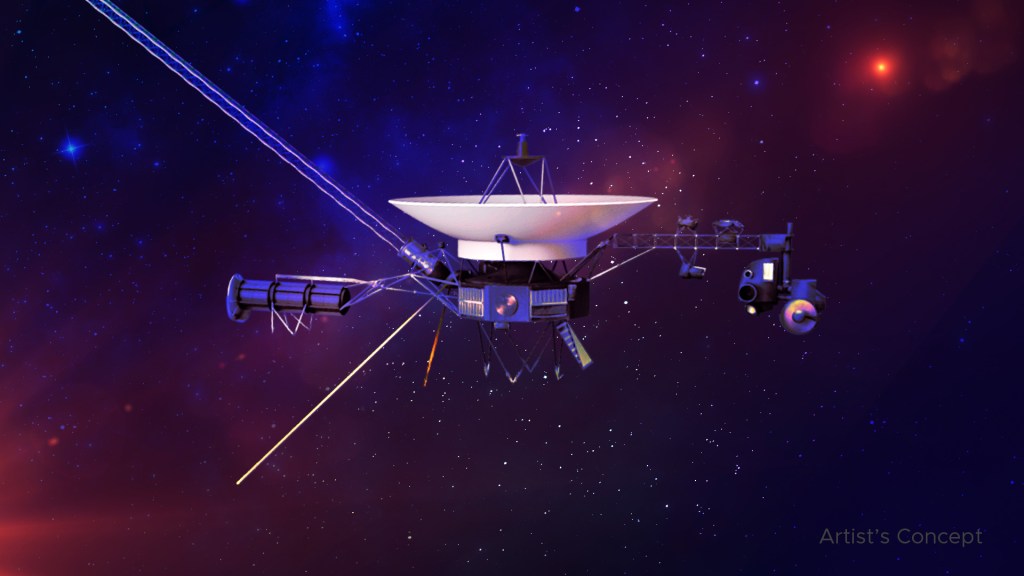
Voyager 1 & 2
Interstellar Messengers
Voyager 1 and its twin Voyager 2 are the only spacecraft ever to operate outside the heliosphere, the protective bubble of particles and magnetic fields generated by the Sun. Voyager 1 reached the interstellar boundary in 2012, while Voyager 2 (traveling slower and in a different direction than its twin) reached it in 2018.

Wind
Wind measures the incoming solar wind.
Wind is a spin-stabilized spacecraft that observes the solar wind that is about to impact the magnetosphere of Earth.
Heliophysics Missions Learning Resources
Explore these resources from the Heliophysics Resource Database to teach learners about NASA heliophysics missions.
NASA Helio Club
Explore multiple heliophysics missions and other NASA program missions with a set of lessons and activities for out-of-school time environments or the classroom.
Level: Intermediate, Advanced
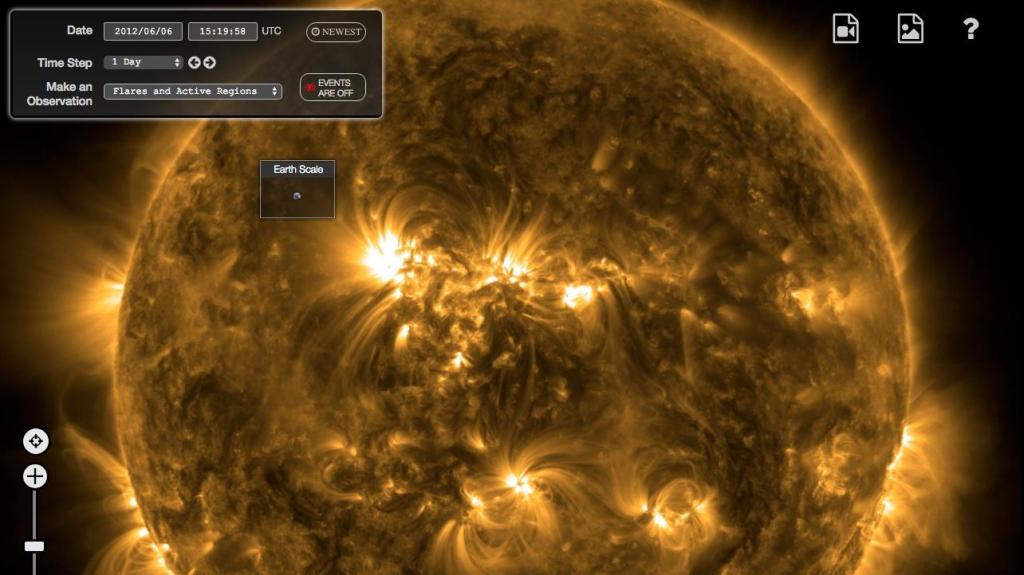
Student Helioviewer
A student-friendly interactive with accessible NASA data, collected by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory, the joint ESA/NASA Solar and Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO) and others, about the Sun and its features, including solar flares, magnetic fields, sunspots, and CMEs.
Level: Intermediate, Advanced
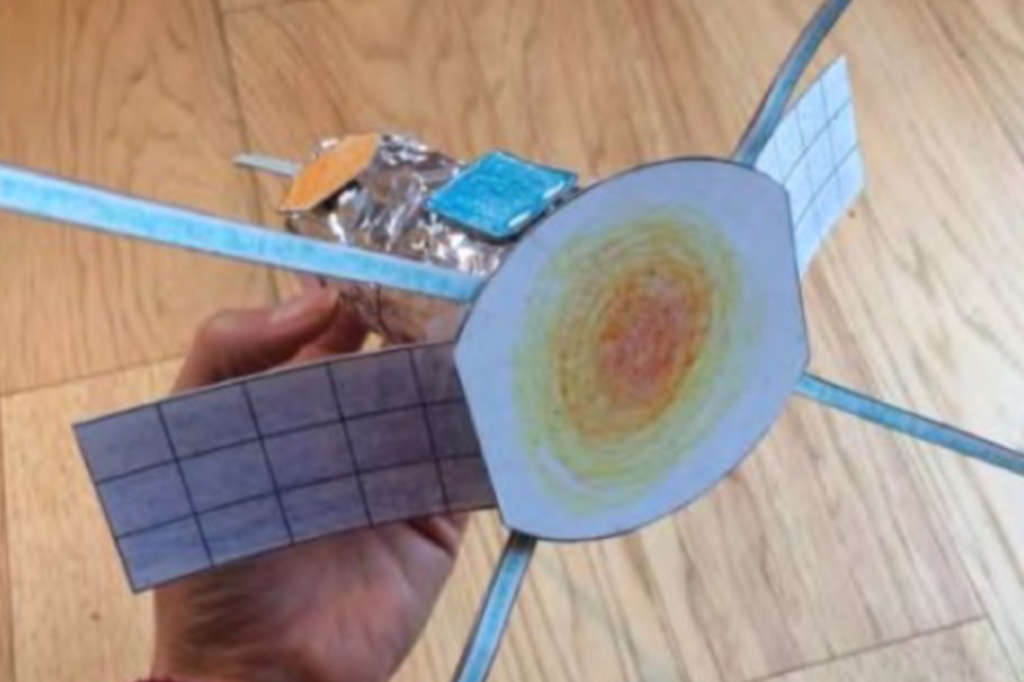
Build a Model Solar Probe
Discover the Parker Solar Probe and embark on a mission to the Sun with this easy-to-build spacecraft model.
Level: Beginner, Intermediate

IBEX Mission Heliosphere Infographic and Activity
Model the parts of the heliosphere with this infographic, created with real data from the IBEX mission. Level: Intermediate, Advanced

Exploring the Sun with Solar Orbiter
Watch a conversation about the Solar Orbiter mission with NASA scientist Dr. Teresa Nieves-Chinchilla (17 min video).
Level: Beginner, Intermediate

Estimate the Speed of a Lunar Shadow with DSCOVR Mission Data
5 math problems created by a NASA scientist, using DSCOVR data collected during the 2017 eclipse across the US.
Level: Intermediate
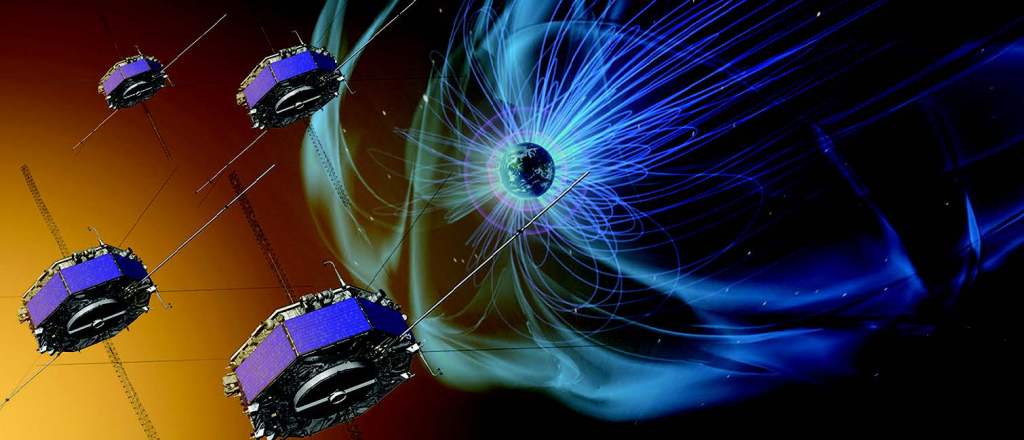

Energy of a Magnetic Field and Solar Flares (MMS Data)
This activity helps students consider the energy stored in the magnetic field produced by different configurations of magnets and apply their findings to explain the release of energy from solar flares.
Level: Advanced
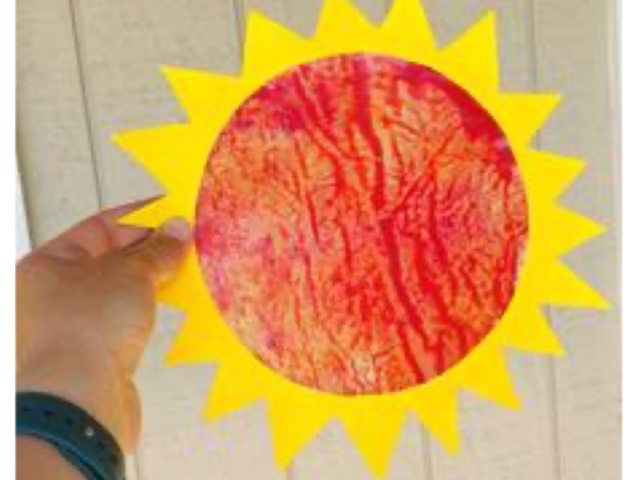

Make a Suncatcher with SDO Images
Make a suncatcher, inspired by images of the Sun captured by NASA's Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO).
Level: Beginner, Intermediate

Parker Solar Probe Videos
These four short videos (approximately 4 minutes each) examine the challenges of NASA's Parker Solar Probe Mission to touch the Sun.
Level: Intermediate, Advanced
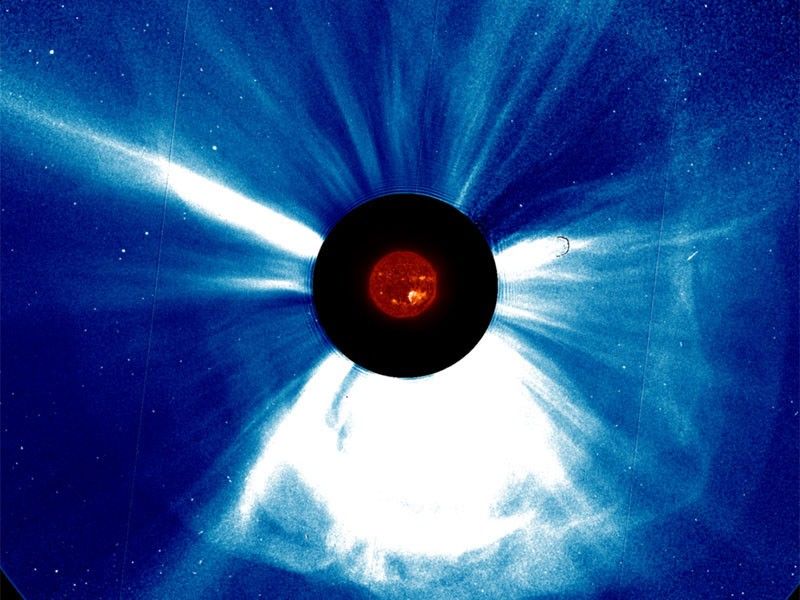

Coronal Mass Ejection Science "Digi Kit" (SOHO Data)
This web-based interactive lab blends physics and space science as students analyze authentic data from the NASA SOHO space observatory to measure the speed of a coronal mass ejection (CME). Level: Advanced
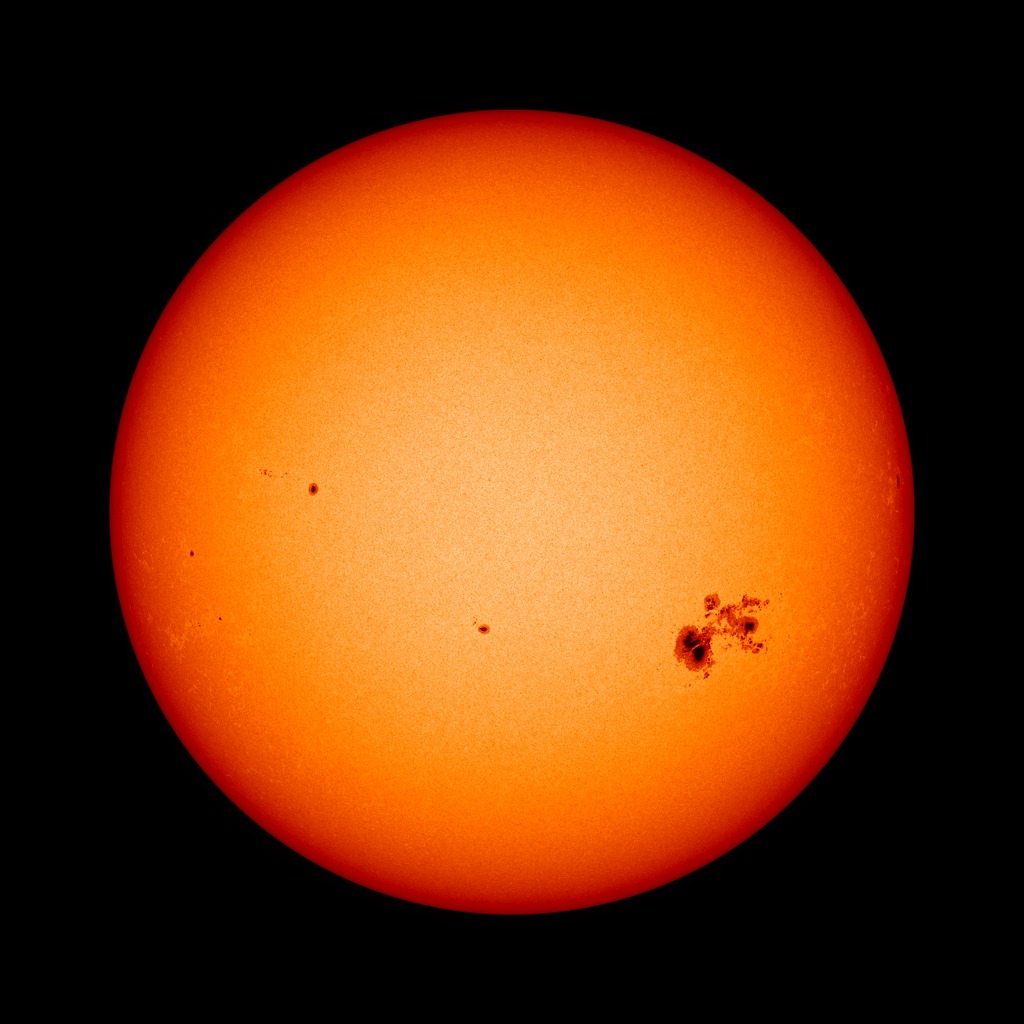

Sunspot Science "Digi Kit" (SOHO Data)
This web-based interactive lab uses authentic data from NASA's Solar Heliospheric Observatory (SOHO), to have students explore sunspot images to make meaning of the terms "frequency" and "period" within the context of a natural phenomenon occurring on the sun.
Level: Advanced

Space Weather Math
Educator guide containing hands-on activities, with embedded math problems, that explore the causes and effects of space weather. Includes data from SDO, Hinode, and other heliophysics missions.
Level: Beginner, Intermediate, Advanced
Heliophysics Resource Database
Find more heliophysics resources at each level in the Heliophysics Resource Database.
Resource Database