1 min read
Cloud 9, Starless Gas Cloud
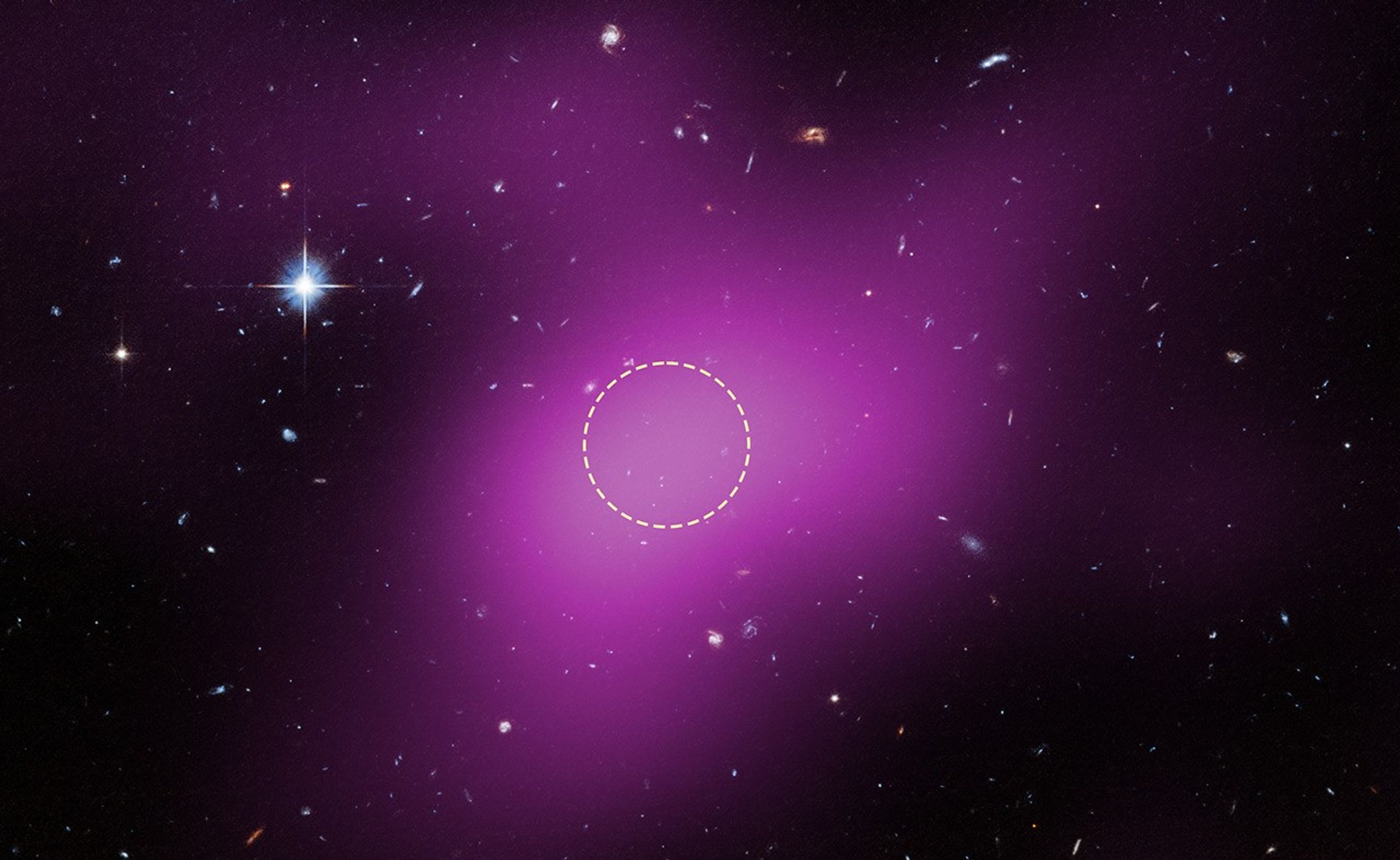

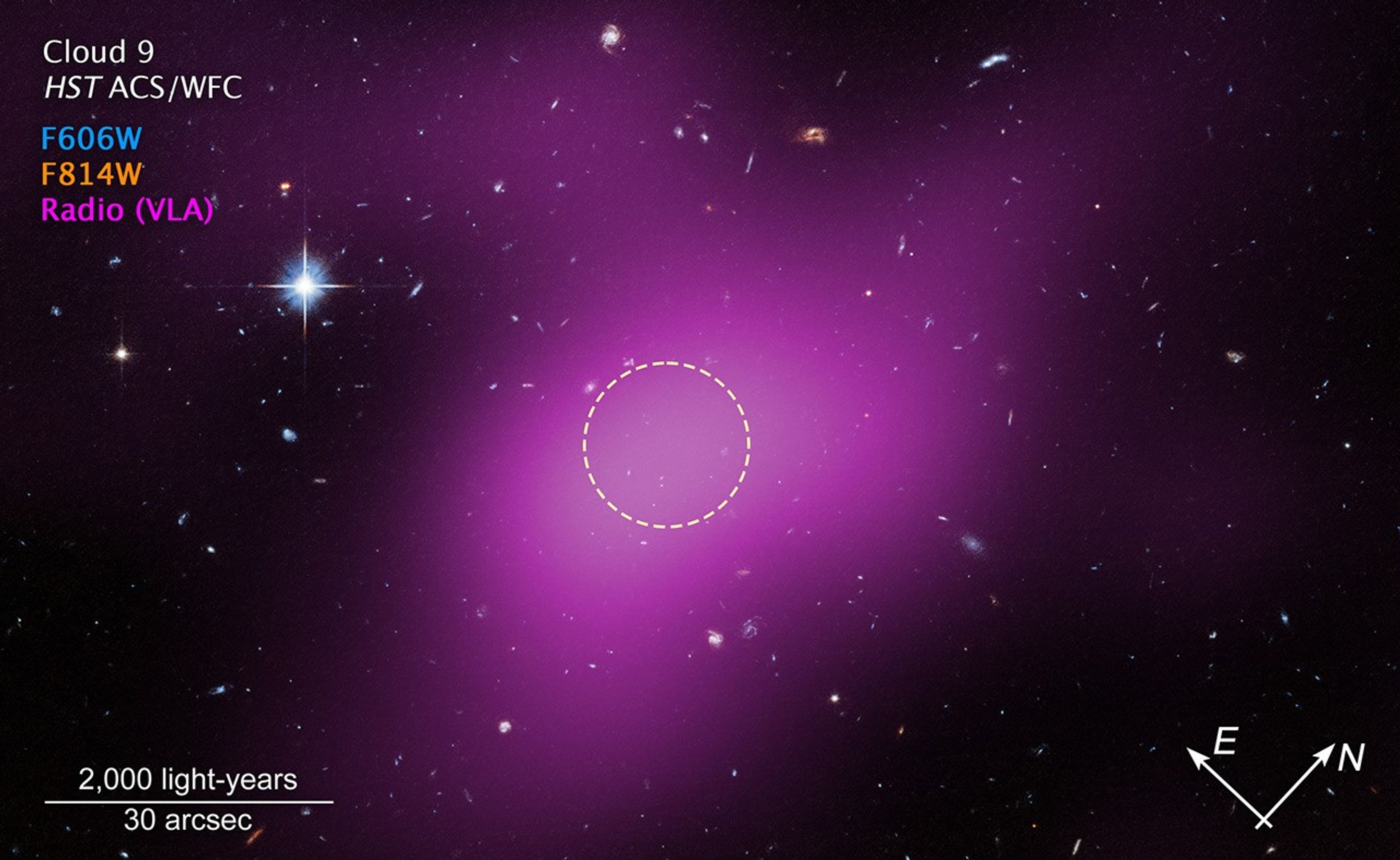
This image shows the location of Cloud-9, which is 14 million light-years from Earth. The diffuse magenta is radio data from the ground-based Very Large Array (VLA) showing the presence of the cloud. The dashed circle marks the peak of radio emission, which is where researchers focused their search for stars. Follow-up observations by the Hubble Space Telescope’s Advanced Camera for Surveys found no stars within the cloud. The few objects that appear within its boundaries are background galaxies. Before the Hubble observations, scientists could argue that Cloud-9 is a faint dwarf galaxy whose stars could not be seen with ground-based telescopes due to the lack of sensitivity. Hubble’s Advanced Camera for Surveys shows that, in reality, the failed galaxy contains no stars.
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12:51:51.33
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.+40:18:05.46
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Ursa Major
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.About 14 million light-years
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.Image is 2.4 arcmin across (about 10,000 light-years)
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The Hubble observations include those from program 17712 (A. Benitez-Llambay)
- InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.February 17-19, 2025
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F606W, F814W
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Cloud-9
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Starless gas cloud
- Release DateJanuary 5, 2026
- Science ReleaseNASA’s Hubble Examines Cloud-9, First of New Type of Object
- CreditScience: NASA, ESA, VLA, Gagandeep Anand (STScI), Alejandro Benitez-Llambay (University of Milano-Bicocca); Image Processing: Joseph DePasquale (STScI)
Downloads

These images were acquired by the ACS Instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to a monochromatic (grayscale) image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Cyan: F606W, Orange: F814W
Related Images & Videos
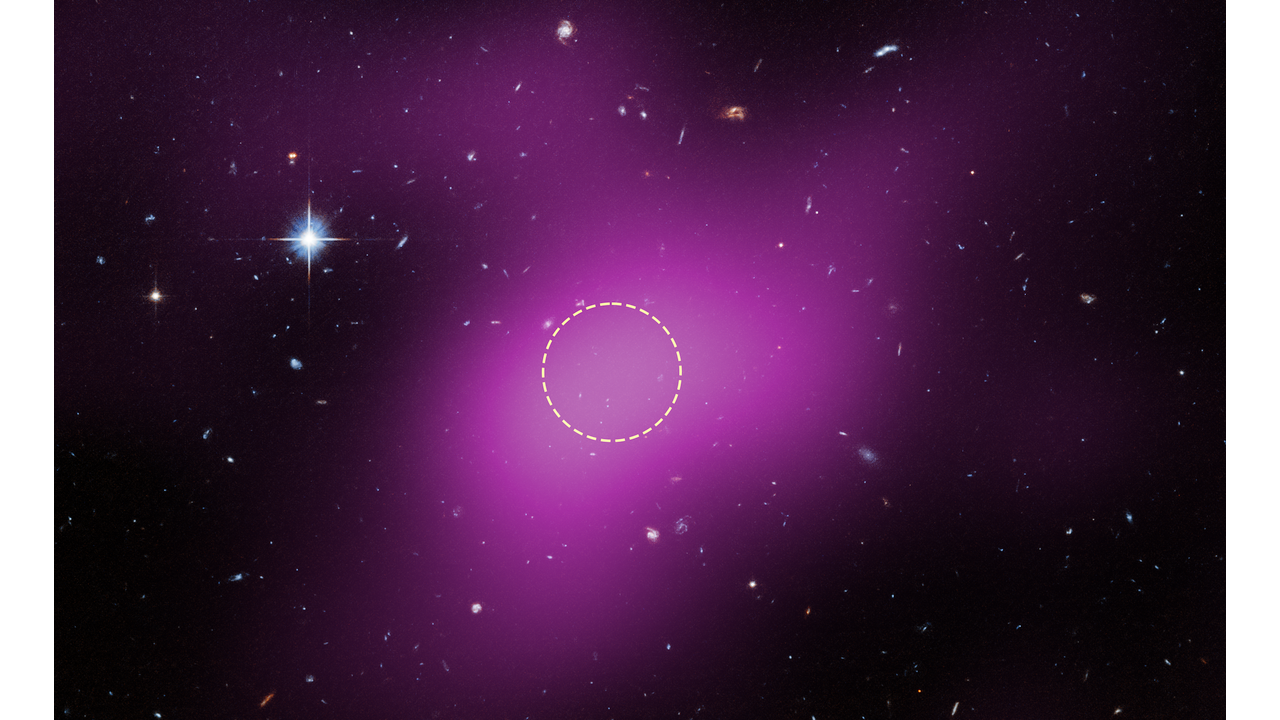

Cloud 9, Starless Gas Cloud Video
This annotated video shows the location of Cloud-9 on the sky. As the video zooms into this gas-rich, dark-matter cloud, it becomes evident that there are no stars within it. Only background galaxies appear behind Cloud-9, which has survived since the universe’s early days....
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov