1 min read
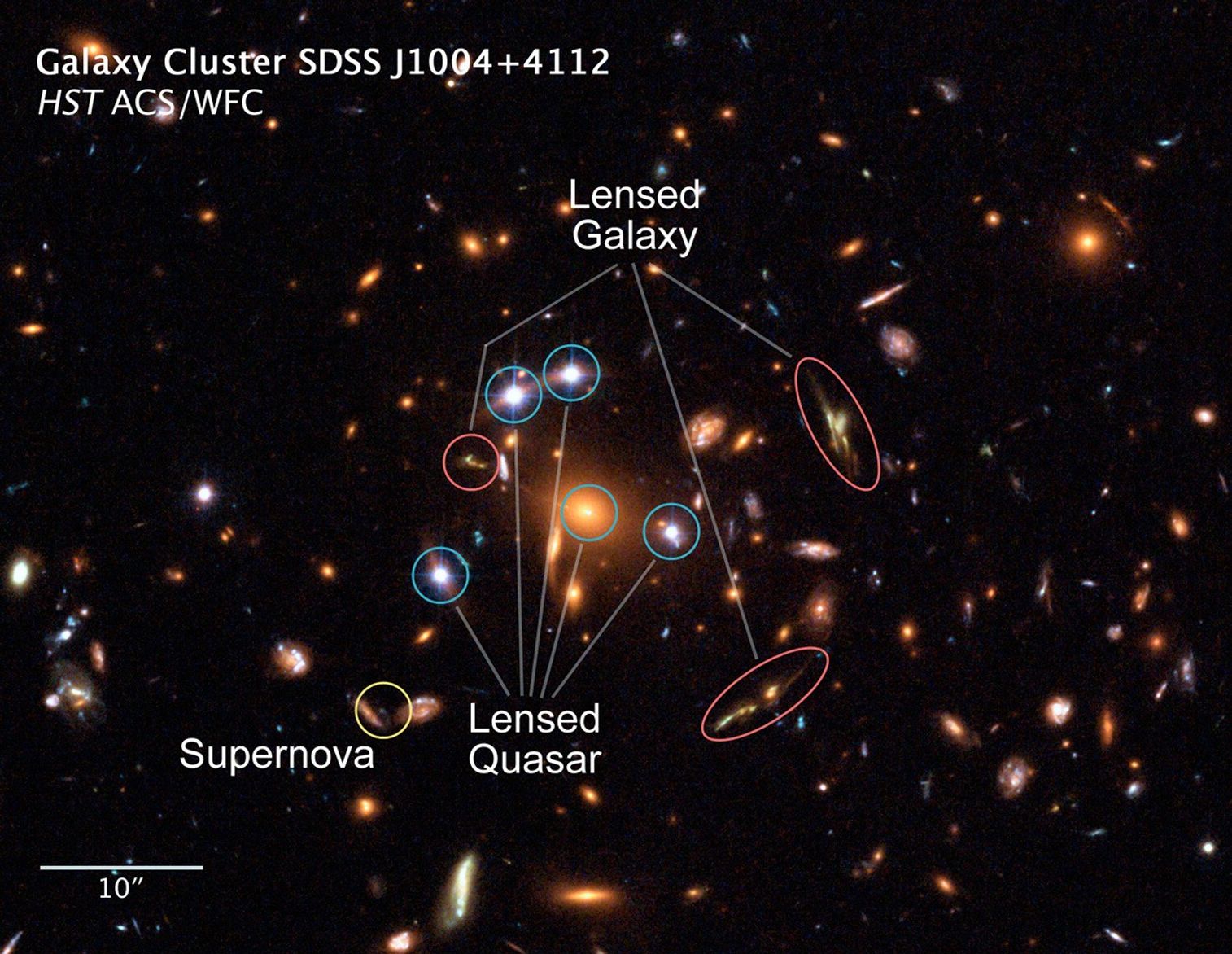
Gravitational Lens SDSS J1004+4112 – Annotated
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.10h 4m 11.83s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.41° 12' 50.4"
- ConstellationConstellationOne of 88 recognized regions of the celestial sphere in which the object appears.Leo Minor
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The distance to the galaxy cluster gravitational lens is roughly 7 billion light-years (2.1 Gigaparsecs). The distance to the quasar being lensed is roughly 10 billion light-years (3 Gigaparsecs). The distance to the farthest galaxy being lensed into an arc is 12 billion light-years (3.7 Gigaparsecs).
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.1.9 arcminutes wide
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.This image was created from HST data from proposals: 9744: C. Kochanek (Smithsonian Institution Astrophysical Observatory), S. Myers (Associated Universities, Inc. ), I. Browne (University of Manchester), R. Blandford (California Institute of Technology), N. Jackson (University of Manchester), C. Keeton (University of Chicago), J. Munoz (Universidad de Valencia, Observatorio Astronomico), J. Lovell (CSIRO, Australia Telescope National Facility), L. Wisotzki (Astrophysikalisches Institut Potsdam), M. Gregg (University of California, Davis), D. Eisenstein (University of Arizona), D. Johnston (University of Chicago), N. Inada (University of Tokyo, Institute of Cosmic Ray Research), B. Pindor (Princeton University), S. Burles (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), G. Richards (Princeton University), E. Falco and B. Mcleod (Smithsonian Institution Astrophysical Observatory), P. Schechter (Massachusetts Institute of Technology), D. Rusin and J. Winn (Smithsonian Institution Astrophysical Observatory), L. Koopmans (Space Telescope Science Institute), C. Fassnacht (University of California, Davis), C. Impey (University of Arizona), H.-W. Rix (Max-Planck-Institut fur Astronomie, Heidelberg), and C. Peng (University of Arizona) 10509: C. Kochanek (The Ohio State University Research Foundation), M. Oguri (Princeton University), E. Ofek, K. Sharon, D. Maoz, and T. Broadhurst (Tel Aviv University - Wise Observatory), and N. Inada and Y. Suto (University of Tokyo, Institute of Astronomy). The science team studying this gravitational lens includes: K. Sharon (Tel Aviv University), E. Ofek (Tel Aviv University/Caltech), G. Smith (Caltech), T. Broadhurst and D. Maoz (Tel Aviv University), C. Kochanek (Ohio State University), M. Oguri (University of Tokyo/Princeton University), Y. Suto and N. Inada (University of Tokyo), and E. Falco (Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>ACS/WFC
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.April 28, 2004, January 2, 2005, and December 12-13, 2005, Exposure Time: 16 hours
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F435W (B), F555W (V), F814W (I)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.SDSS J1004+4112
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Galaxy cluster gravitational lens
- Release DateMay 23, 2006
- Science ReleaseHubble Captures a “Five-Star” Rated Gravitational Lens
- Credit

Compass and Scale
Compass and ScaleAn astronomical image with a scale that shows how large an object is on the sky, a compass that shows how the object is oriented on the sky, and the filters with which the image was made.
Related Images & Videos

Hubble Captures a "Five-Star" Rated Gravitational Lens
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope has captured the first-ever picture of a group of five star-like images of a single distant quasar. The multiple-image effect seen in the Hubble picture is produced by a process called gravitational lensing, in which the gravitational field of a...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov