1 min read
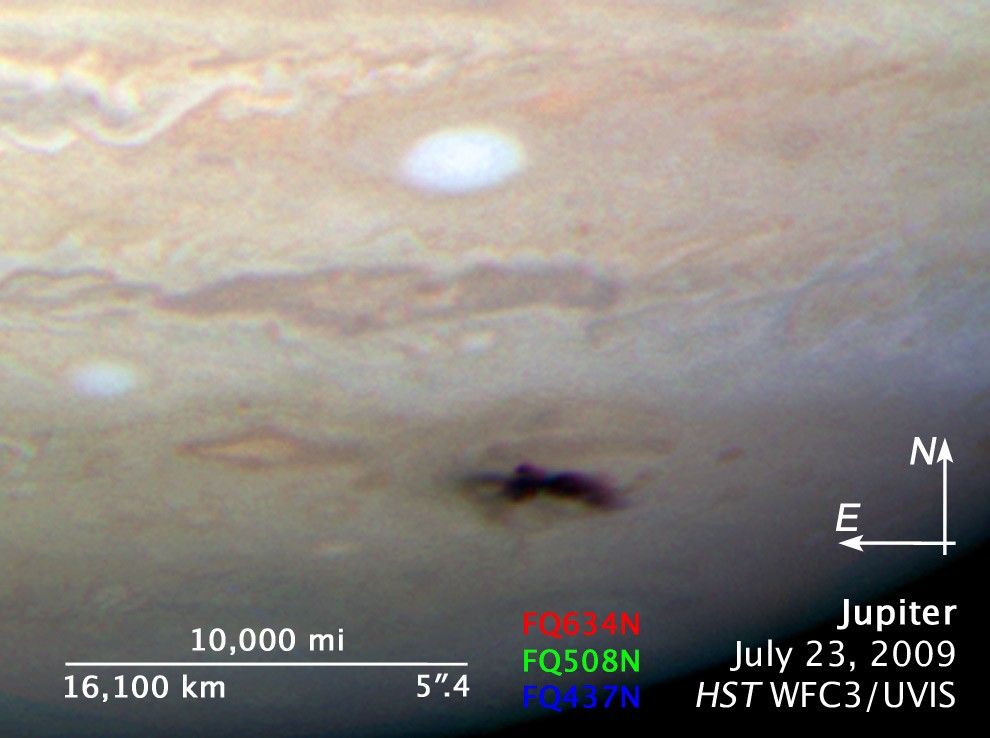
Closeup of New Dark Spot on Jupiter

Closeup view of the new dark spot on Jupiter taken with Hubble's Wide Field Camera 3 on July 23, 2009.
About the Object
- DistanceDistanceThe physical distance from Earth to the astronomical object. Distances within our solar system are usually measured in Astronomical Units (AU). Distances between stars are usually measured in light-years. Interstellar distances can also be measured in parsecs.The semi-major axis of Jupiter's orbit about the sun is 5.2 astronomical units (483 million miles or 778 million km). On July 23, 2009 Jupiter was 381 million miles from Earth.
- DimensionsDimensionsThe physical size of the object or the apparent angle it subtends on the sky.The planet has a diameter of roughly 88,789 miles (142,984 km) at the equator.
About the Data
- Data DescriptionData DescriptionProposal: A description of the observations, their scientific justification, and the links to the data available in the science archive.
Science Team: The astronomers who planned the observations and analyzed the data. "PI" refers to the Principal Investigator.The image was created from Hubble data from proposal 12003: H. Hammel (Space Science Institute), A. Simon-Miller (NASA Goddard Space Flight Center), J. Clarke (Boston University), I. de Pater (University of California, Berkeley), K. Noll (STScI), G. Orton (Jet Propulsion Laboratory), A. Sanchez-Lavega (University of the Basque Country, Spain), and M. Wong (STScI). - InstrumentInstrumentThe science instrument used to produce the data.HST>WFC3/UVIS
- Exposure DatesExposure DatesThe date(s) that the telescope made its observations and the total exposure time.July 23, 2009 19:00 UT
- FiltersFiltersThe camera filters that were used in the science observations.F225W (225 nm), F275W (275 nm), FQ378N (378 nm), FQ437N (437 nm), FQ508N (508nm), FQ634N (634 nm), FQ727N (727 nm), FQ889N (889 nm), FQ906N (906 nm), and FQ924N (924 nm)
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.Jupiter
- Object DescriptionObject DescriptionThe type of astronomical object.Planet
- Release DateJuly 24, 2009
- Science ReleaseHubble Captures Rare Jupiter Collision
- Credit

Color Info
Color InfoA brief description of the methods used to convert telescope data into the color image being presented.
The image is a composite of separate exposures made by the WFC3 instrument on the Hubble Space Telescope. Three filters were used to sample narrow wavelength ranges. The color results from assigning different hues (colors) to each monochromatic image. In this case, the assigned colors are: Blue: FQ437N (437 nm) Green: FQ508N (508nm) Red: FQ634N (634 nm)
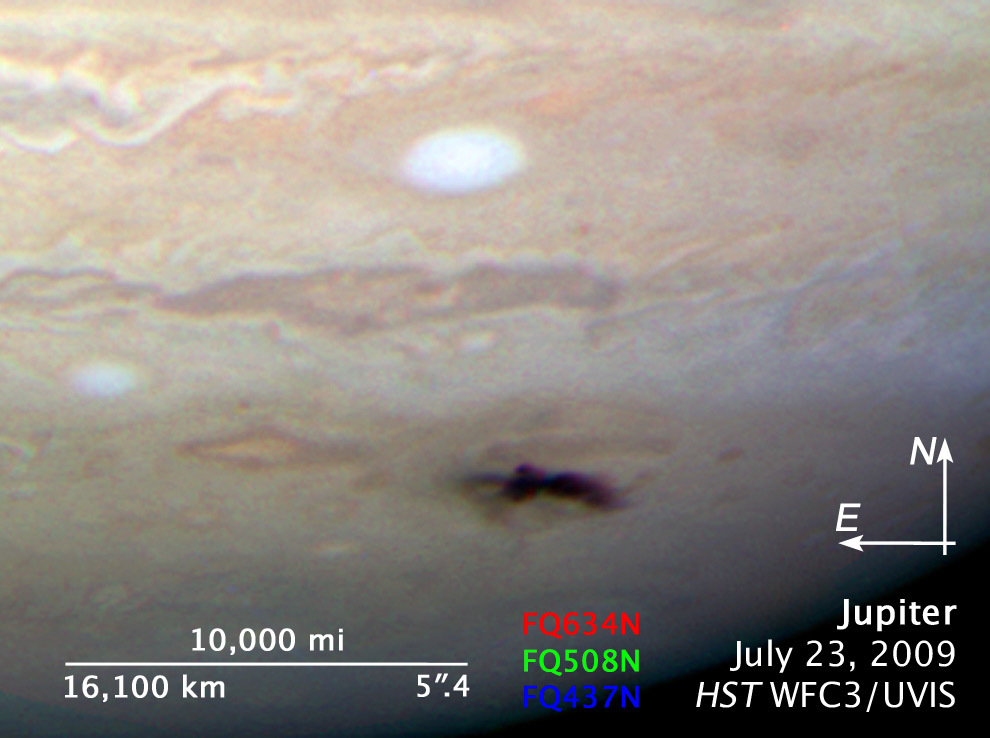

Compass and Scale
Compass and ScaleAn astronomical image with a scale that shows how large an object is on the sky, a compass that shows how the object is oriented on the sky, and the filters with which the image was made.
Related Images & Videos
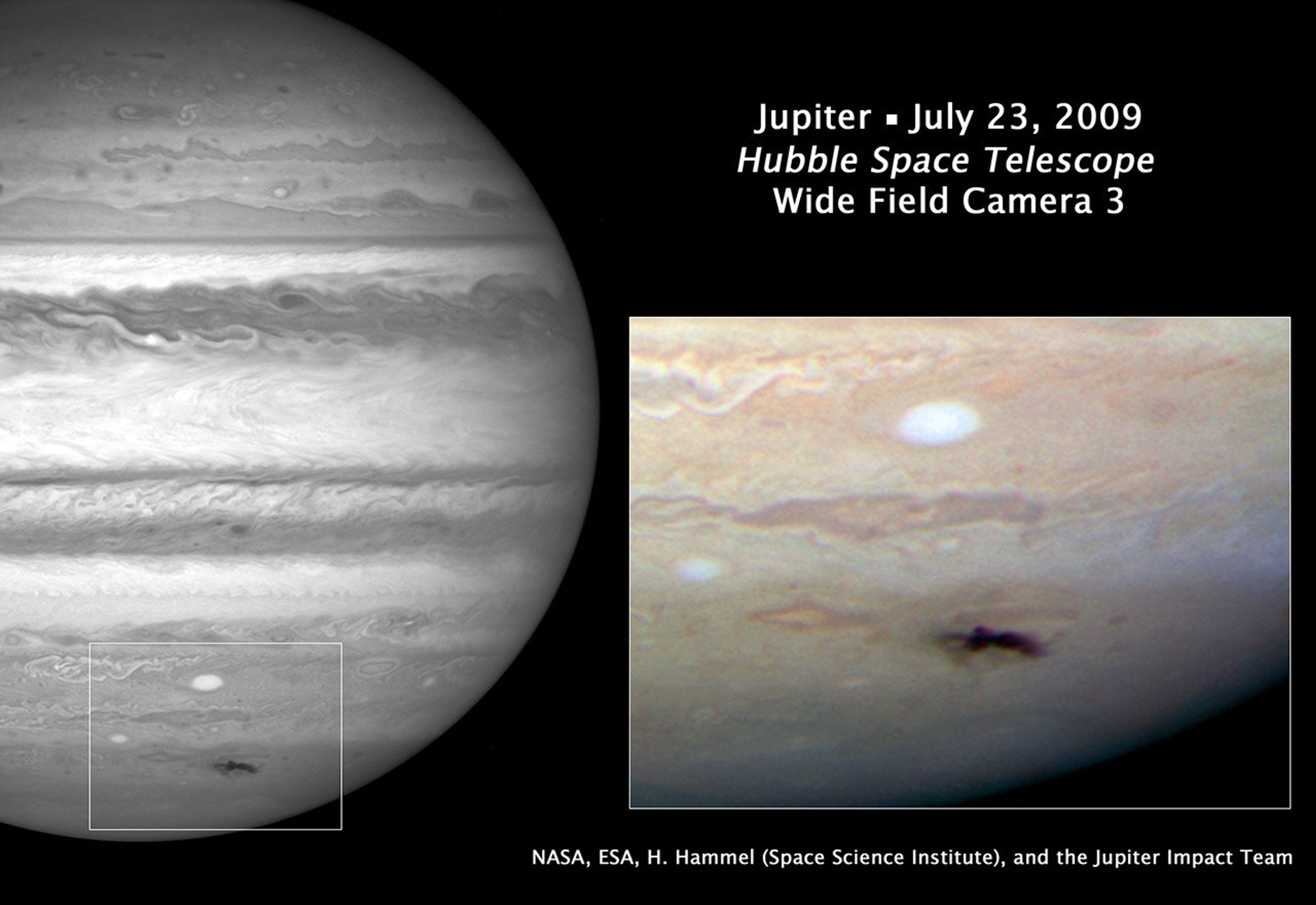
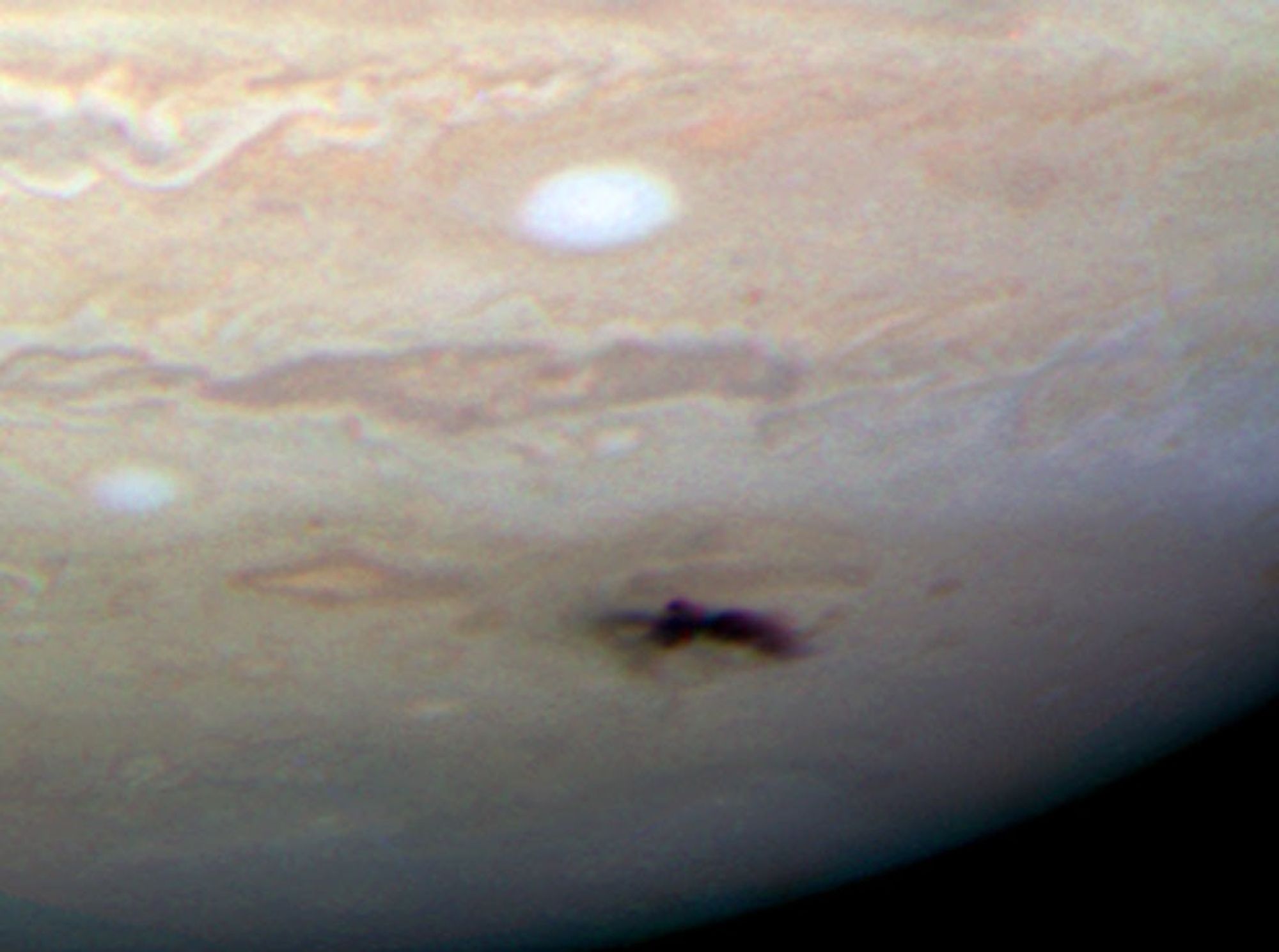
Hubble Views New Dark Spot on Jupiter
This Hubble picture, taken on July 23, is the sharpest visible-light picture taken of the impact feature. The observations were made with Hubble's new camera, the Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3). The combination of the Hubble data with mid-infrared images from ground-based telescopes...
Share
Details
Last Updated
Aug 17, 2025
Contact
Media
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov






























