1 min read
Spiral Gas Disk in Active Galaxy M87
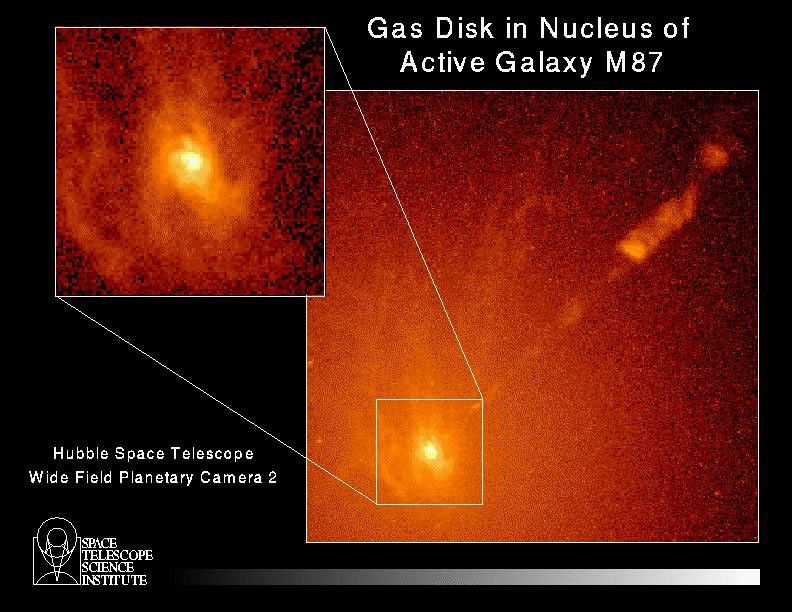
A NASA Hubble Space Telescope image of a spiral-shaped disk of hot gas in the core of active galaxy M87. HST measurements show the disk is rotating so rapidly it contains a massive black hole at its hub.
A black hole is an object that is so massive yet compact nothing can escape its gravitational pull, not even light. The object at the center of M87 fits that description. It weights as much as three billion suns, but is concentrated into a space no larger than our solar system.
Now that astronomers have seen the signature of the tremendous gravitational field at the center of M87, it is clear that the region contains only a fraction of the number of stars that would be necessary to create such a powerful attraction.
The giant elliptical galaxy M87 is located 50 million light-years away in the constellation Virgo. Earlier observations suggested the black hole was present, but were not decisive. A brilliant jet of high- speed electrons that emits from the nucleus (diagonal line across image) is believed to be produced by the black hole "engine."
The image was taken with HST's Wide Field Planetary Camera 2
About the Object
- R.A. PositionR.A. PositionRight ascension – analogous to longitude – is one component of an object's position.12h 30m 49.42s
- Dec. PositionDec. PositionDeclination – analogous to latitude – is one component of an object's position.12° 23' 27.99"
- Object NameObject NameA name or catalog number that astronomers use to identify an astronomical object.M87, NGC 4486
- Release DateMay 25, 1994
- Science ReleaseHubble Confirms Existence of Massive Black Hole at Heart of Active Galaxy
- CreditHolland Ford, Space Telescope Science Institute/Johns Hopkins University; Richard Harms, Applied Research Corp.; Zlatan Tsvetanov, Arthur Davidsen, and Gerard Kriss at Johns Hopkins; Ralph Bohlin and George Hartig at Space Telescope Science Institute; Linda Dressel and Ajay K. Kochhar at Applied Research Corp. in Landover, Md.; and Bruce Margon from the University of Washington in Seattle.; NASA
Related Images & Videos
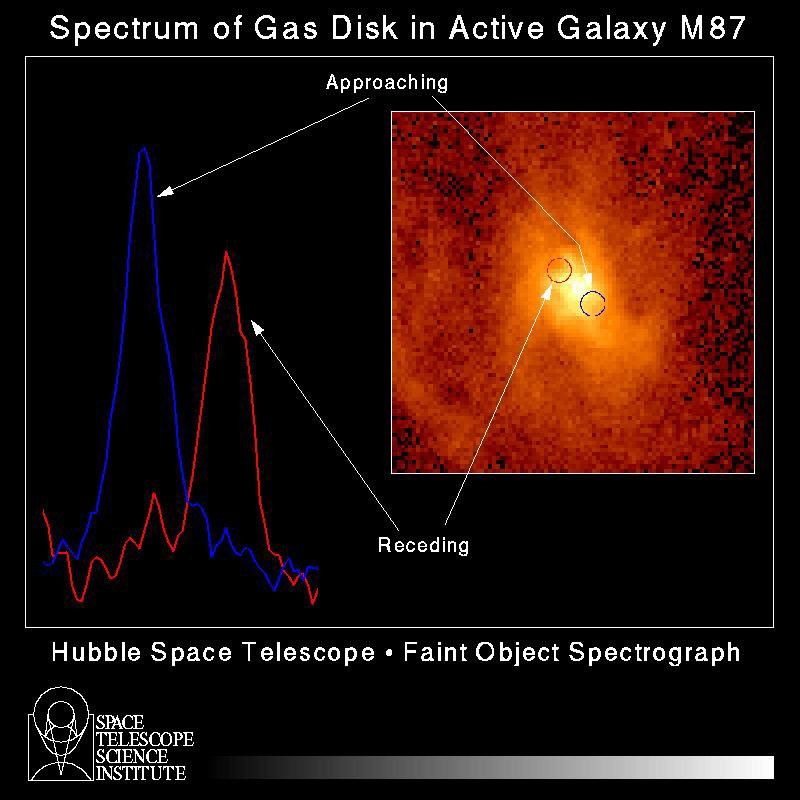
Hubble Measures Velocity of Gas Orbiting Black Hole
A schematic diagram of velocity measurements of a rotating disk of hot gas in the core of active galaxy M87. The measurement was made by studying how the light from the disk is redshifted and blueshifted – as part of the swirling disk spins in earth's direction and the other...
Share
Details
Claire Andreoli
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Greenbelt, Maryland
claire.andreoli@nasa.gov

































