Between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter lies a large concentration of asteroids, which are conglomerates of rock and ice that hold clues to the formation of our solar system. This ‘Asteroid Belt’ is the rubble left over from the construction of our solar system, and Hubble’s observations have helped shape our understanding of their interactions and compositions.
-
A Fragmented Asteroid
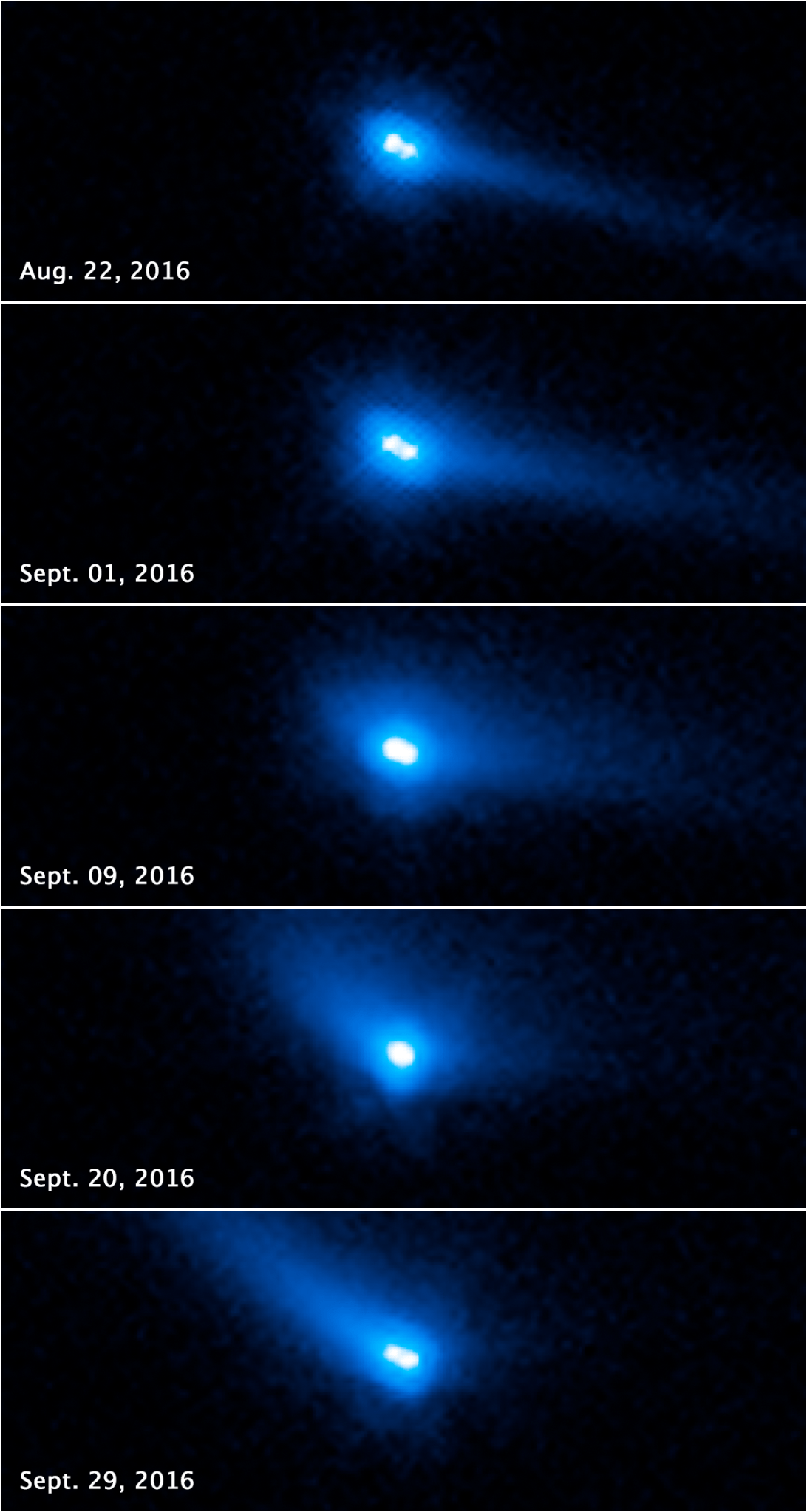
Hubble watched the slow disintegration of asteroid P/2013 R3 into 10 smaller pieces. The Hubble data revealed that the fragments are drifting away from each other at a leisurely one mile per hour — slower than the speed of a strolling human — which suggests the breakup is not the result of a collision.
NASA’s Hubble Witnesses Asteroid’s Mysterious Disintegration
 P/2013 R3 on November 15, 2013.NASA, ESA, and D. Jewitt (UCLA)
P/2013 R3 on November 15, 2013.NASA, ESA, and D. Jewitt (UCLA)
-
Asteroid Collisions
Astronomers using Hubble witnessed the impact of two asteroids in the asteroid belt. Hubble observations showed a bizarre, X-shaped pattern of filamentary structures near the point-like core of an object with trailing streamers of dust. This complex structure suggested the small body was the product of a head-on collision between two asteroids traveling five times faster than a rifle bullet. The observation helped support the idea that the asteroid belt is slowly eroding through collisions.
Suspected Asteroid Collision Leaves Odd X-Pattern of Trailing Debris
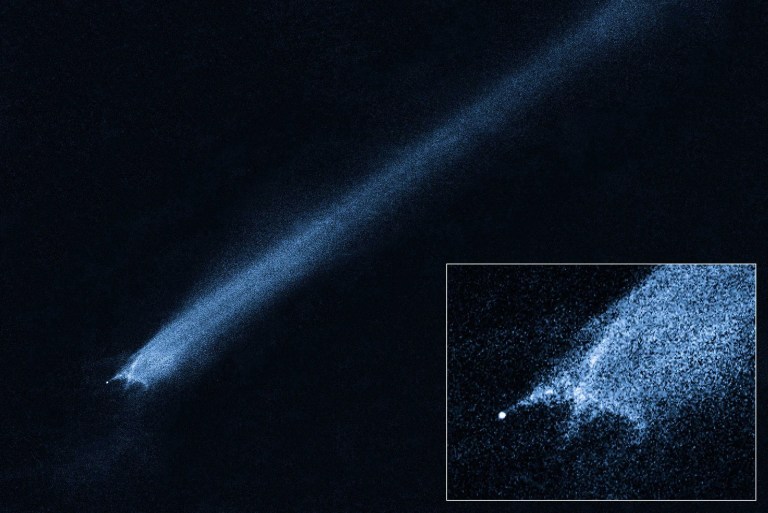 An odd, X-shaped debris field trailing dusty streamers is likely the remnants of an asteroid collision. Scientists think that a small, fast-moving asteroid blasted into a larger and slower-moving one.NASA, ESA, and D. Jewitt (UCLA)
An odd, X-shaped debris field trailing dusty streamers is likely the remnants of an asteroid collision. Scientists think that a small, fast-moving asteroid blasted into a larger and slower-moving one.NASA, ESA, and D. Jewitt (UCLA) -
Asteroid or Comet?
In 2013, Hubble observed an asteroid with six comet-like tails of dust radiating from it like spokes on a wheel. Unlike all other known asteroids, which appear simply as tiny points of light, this asteroid resembles a rotating lawn sprinkler. Computer models of the object suggest the tails may have formed through a series of dust-ejection events.
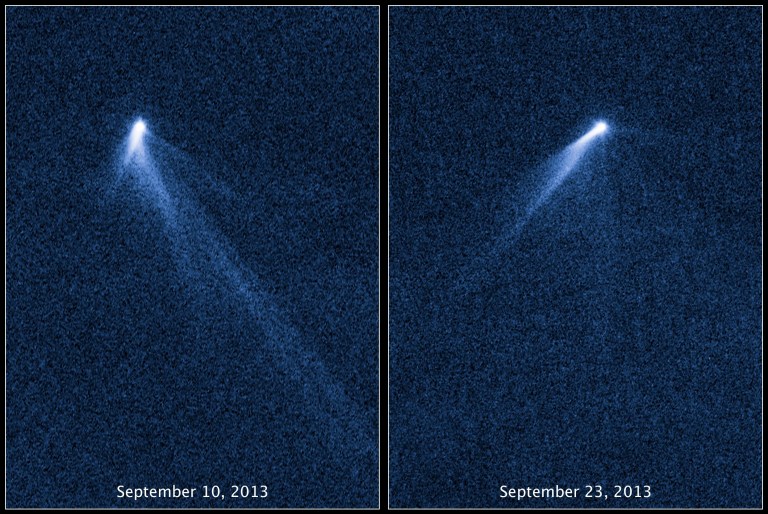 Images of asteroid P/2013 P5 revealed its unique dust trails radiating in multiple directions and changing in appearance with time.NASA, ESA, and D. Jewitt (UCLA)
Images of asteroid P/2013 P5 revealed its unique dust trails radiating in multiple directions and changing in appearance with time.NASA, ESA, and D. Jewitt (UCLA)
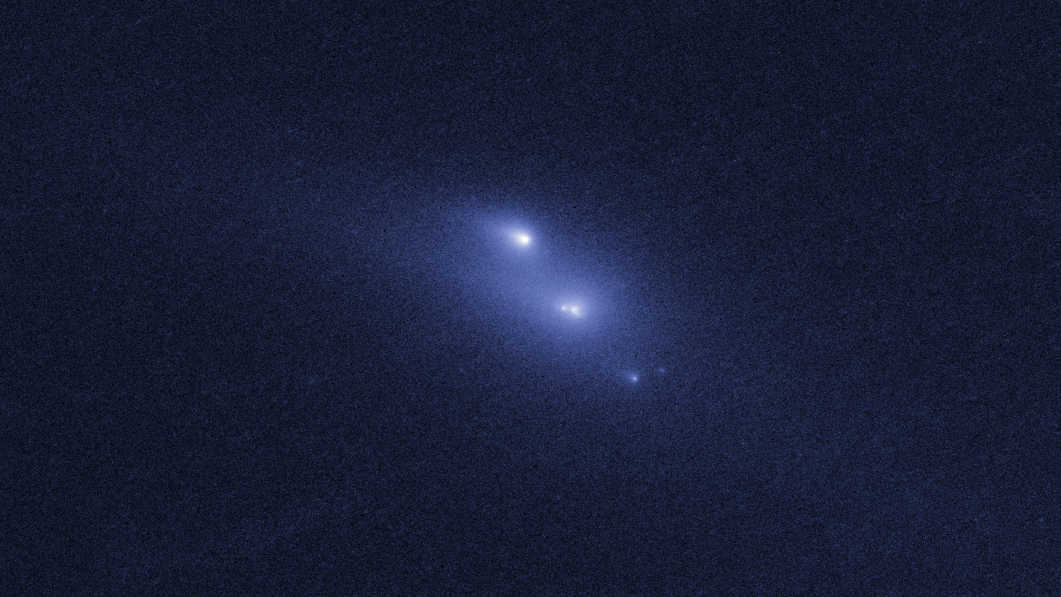
A Binary Asteroid
Hubble also observed the first known binary asteroid that also looks like a comet. The asteroid duo orbits each other and has a tail of dust like a comet. The asteroid, called 300163 (2006 VW139), likely broke into two pieces some 5,000 years ago due to its fast rotation.

Asteroid Vesta and Dwarf Planet Ceres
Hubble captured images of the two most massive objects in the Asteroid Belt, Ceres and Vesta, to help NASA better plan the Dawn spacecraft's visit to these two worlds.
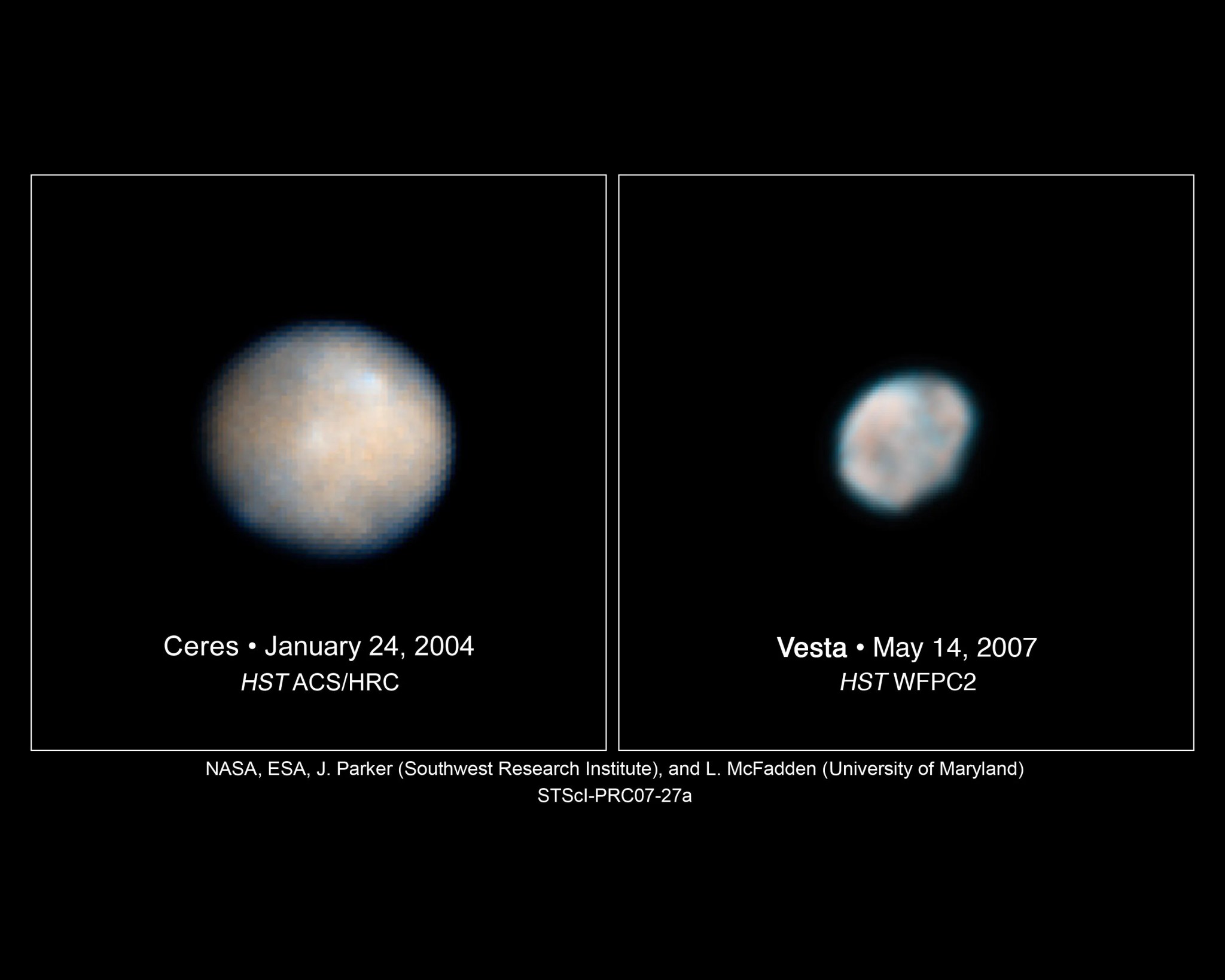
Ceres image: NASA; ESA; J. Parker (Southwest Research Institute); P. Thomas (Cornell University); L. McFadden (University of Maryland, College Park); and M. Mutchler and Z. Levay (Space Telescope Science Institute)
Hubble's observations of Ceres revealed bright and dark regions on the asteroid's surface that could be topographic features, such as craters, and/or areas containing different surface material. Large impacts may have caused some of these features and potentially added new material to the landscape.
Hubble images of Vesta allowed researchers to map its southern hemisphere, a region dominated by a giant impact basin formed billions of years ago. Hubble discovered the basin and its central peak through observations made in 1997. NASA's Dawn Mission later confirmed that the basin is actually two colossal impact craters—the 310 mile (500 km) wide Rheasilvia basin, and the older 250 mi (400 km) wide Veneneia crater. Rheasilvia’s width is 95% of the mean diameter of Vesta and about 12 miles (19 km) deep. Its central peak, which Hubble first detected in its 1997 observations, rises 12-16 miles (19-26 km) and is more than 100 miles (160 km) wide. If Earth had a crater of proportional size, it would fill the Pacific Ocean basin.
The impact broke off chunks of Vesta, propelling about one-percent of the asteroid into space. This produced more than 50 smaller asteroids that astronomers have nicknamed "vestoids," along with many more smaller fragments in the asteroid belt and ejected into the solar system. Roughly 6 percent of all meteorites we find on Earth are likely the result of this ancient impact in deep space.
Hubble's sharp "eye" saw features as small as about 37 miles (60 kilometers) across on Vesta. The image above shows the difference in brightness and color on the asteroid's surface.
Hubble's view also revealed global features stretching from the northern to the southern hemisphere. The image above shows widespread differences in brightness in the east and west, which probably reflects a difference in composition. The size of these different regions varies. Some are hundreds of miles across.
Learn More

Hubble Reveals Huge Crater on the Surface of the Asteroid Vesta
Astronomers have used Hubble to discover a giant impact crater on the asteroid Vesta. The crater is a link in a chain of events thought responsible for forming a distinctive class of tiny asteroids as well as some meteorites that reached Earth.
Hubble Science Highlights
Discover the breadth and depth of Hubble's exciting discoveries!
Studying the Planets and Moons
Hubble’s systematic observations chart the ever-changing environments of our solar system's planets and their moons.
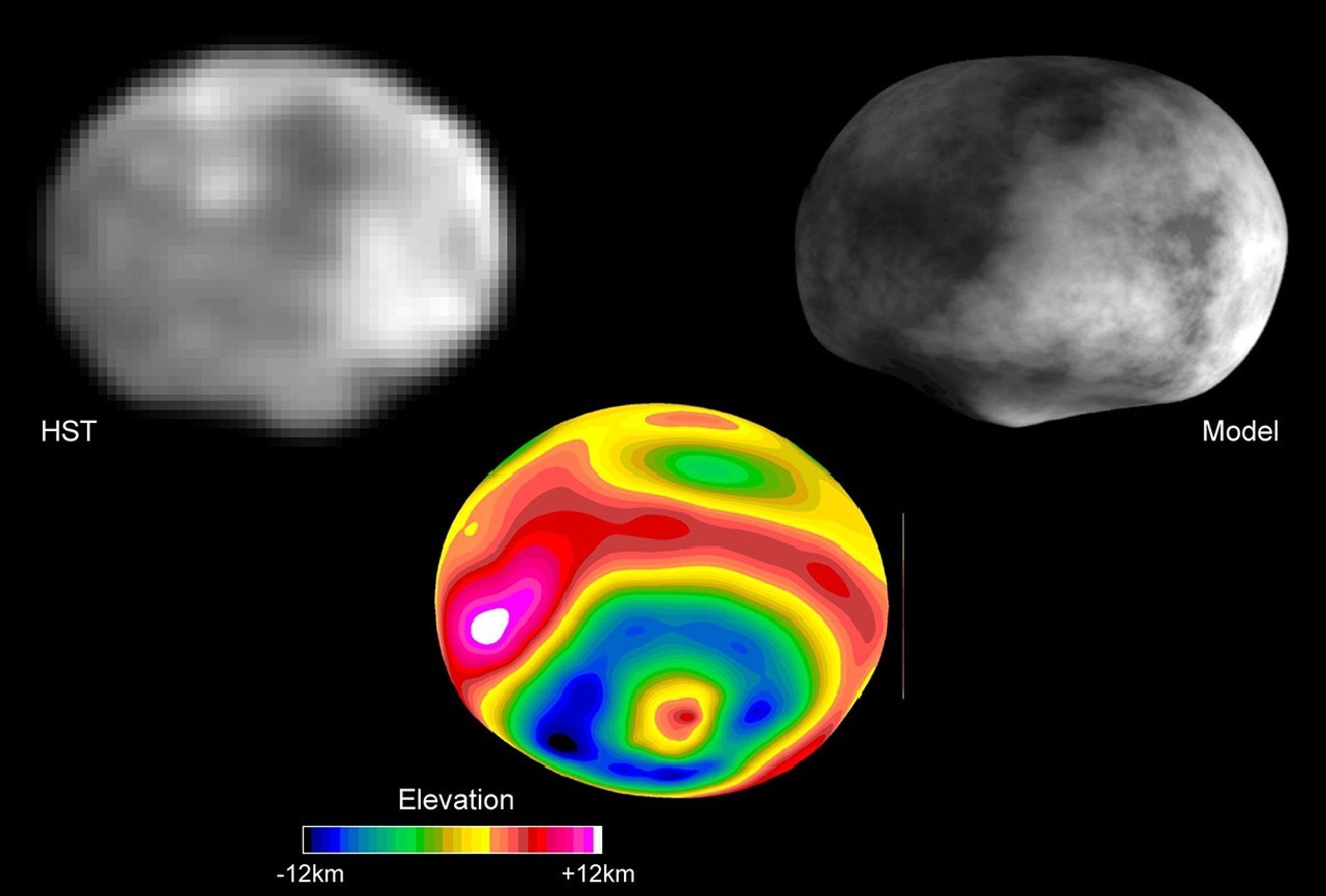
Uncovering Icy Objects in the Kuiper Belt
Hubble’s discoveries helped NASA plan the New Horizon spacecraft’s flyby of Pluto and beyond.
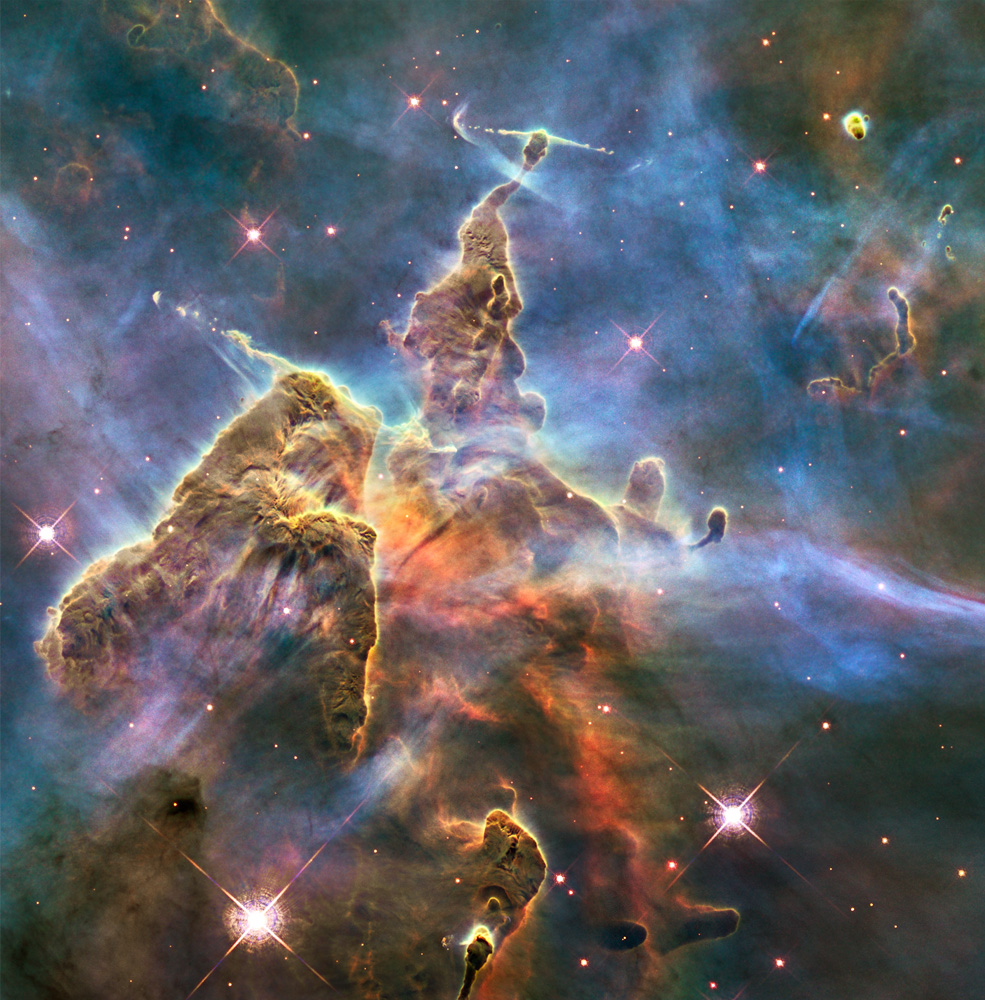

Exploring the Birth of Stars
Seeing ultraviolet, visible, and near-infrared light helps Hubble uncover the mysteries of star formation.
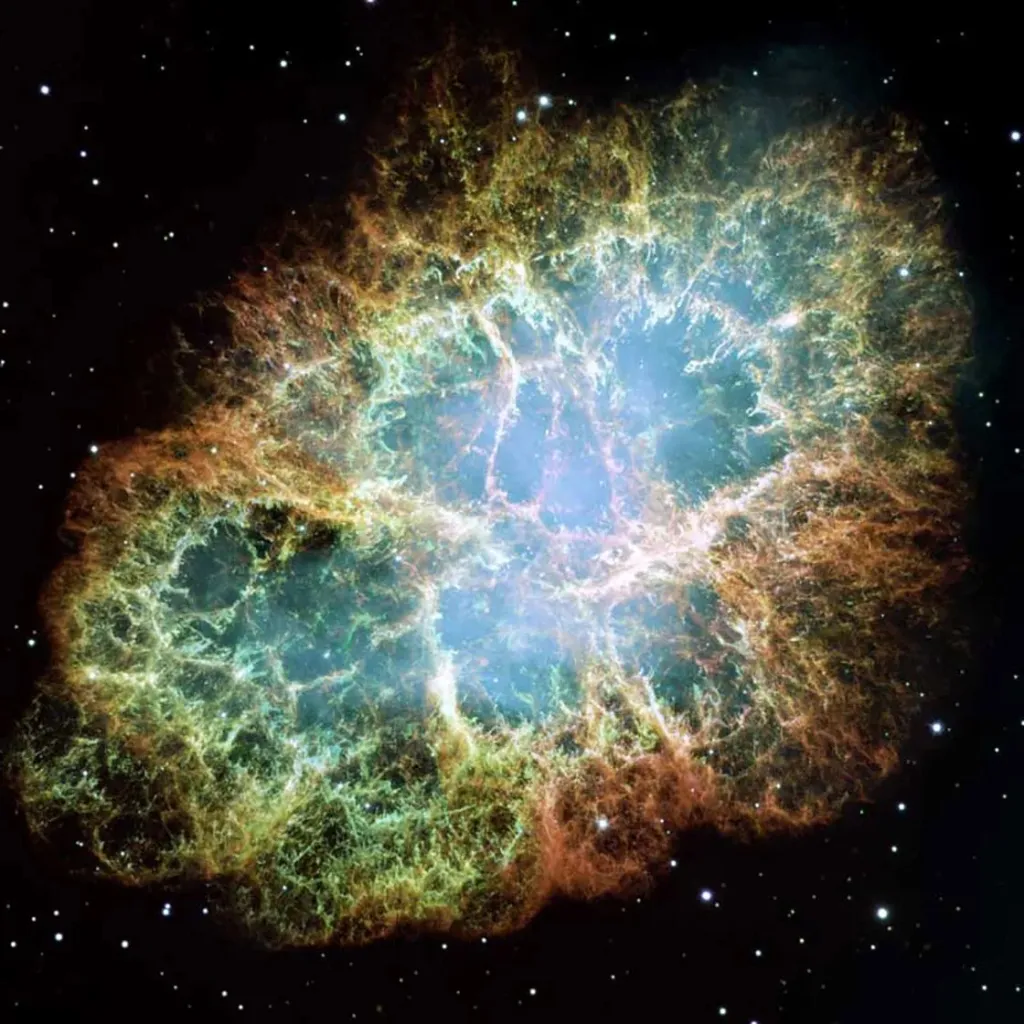

The Death Throes of Stars
When stars die, they throw off their outer layers, creating the clouds that birth new stars.
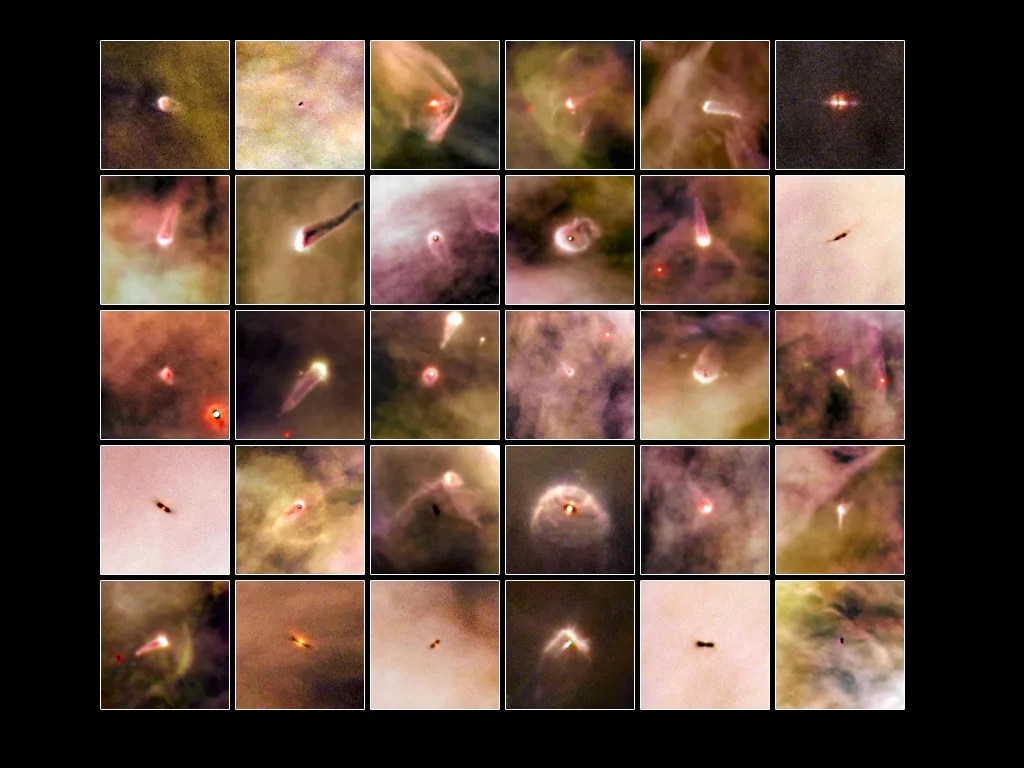

Finding Planetary Construction Zones
Hubble’s sensitivity uncovers the seeds of planets in enormous disks of gas and dust around stars.
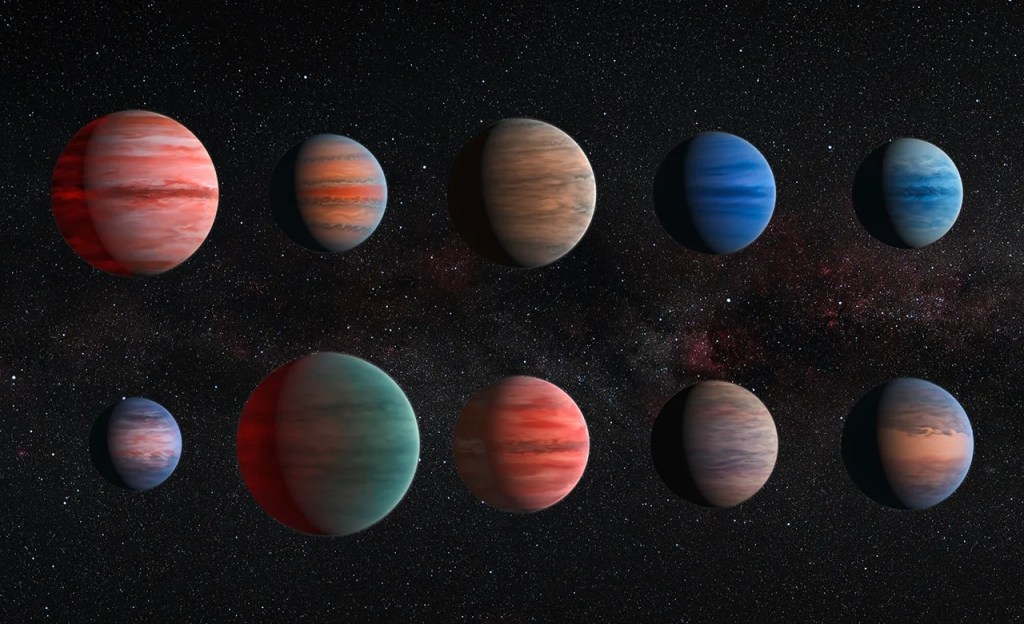

Recognizing Worlds Beyond Our Sun
Hubble can detect and measure the basic organic components for life on planets orbiting other stars
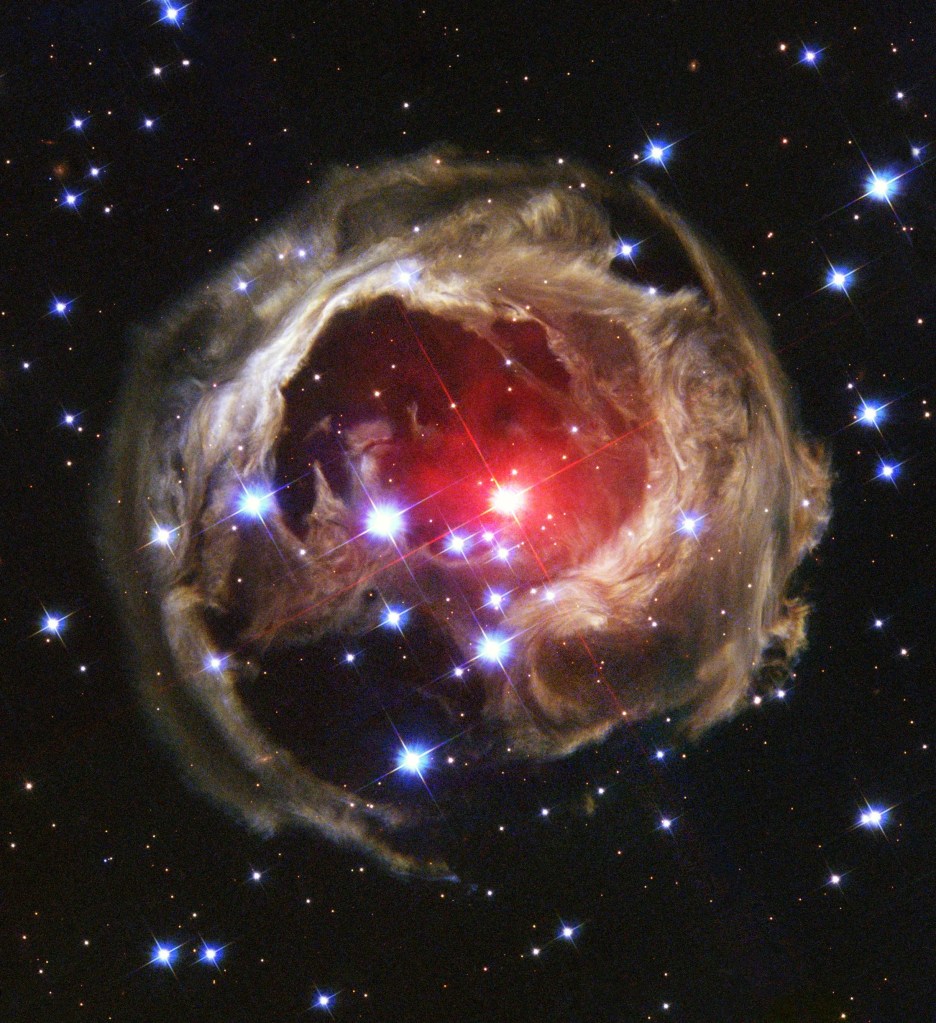

Seeing Light Echoes
Like ripples on a pond, pulses of light reverberate through cosmic clouds forming echoes of light.
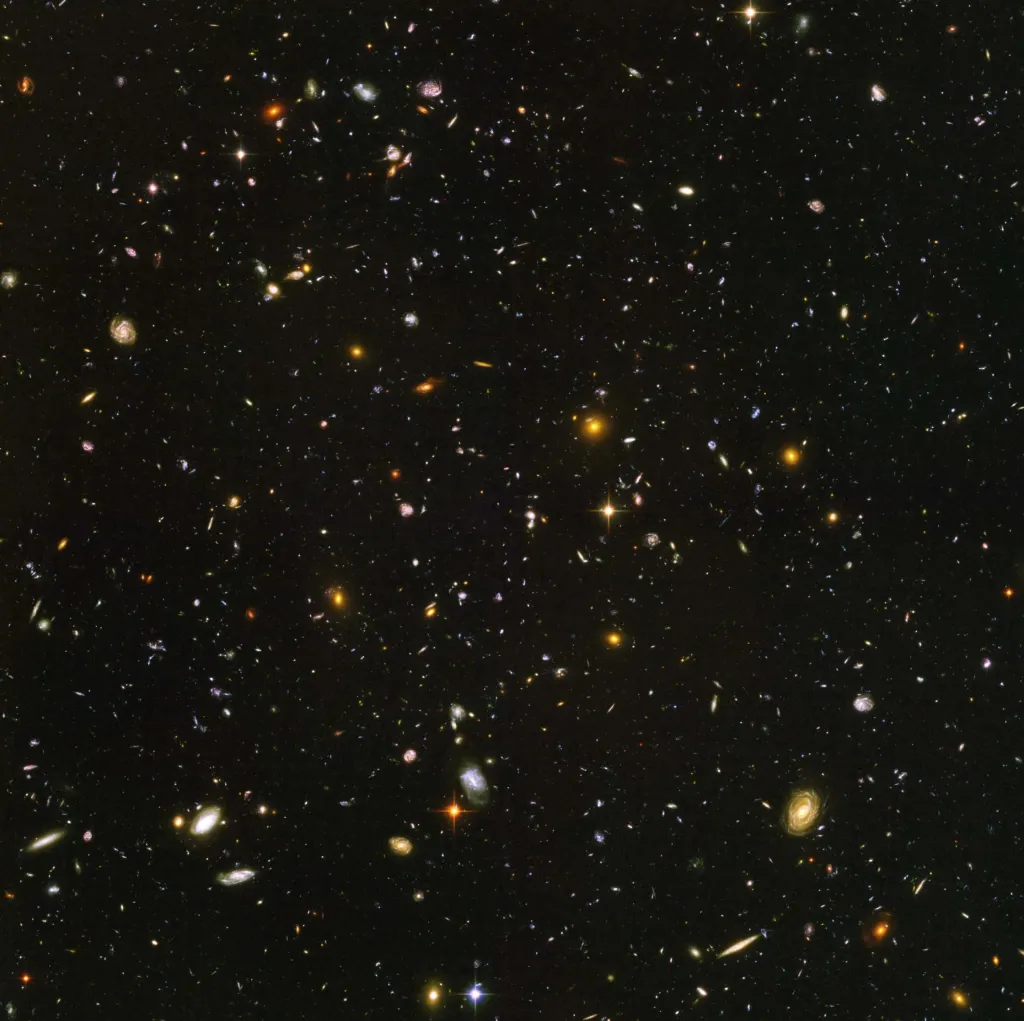

Tracing the Growth of Galaxies
Hubble's Deep Field observations are instrumental in tracing the growth of galaxies.
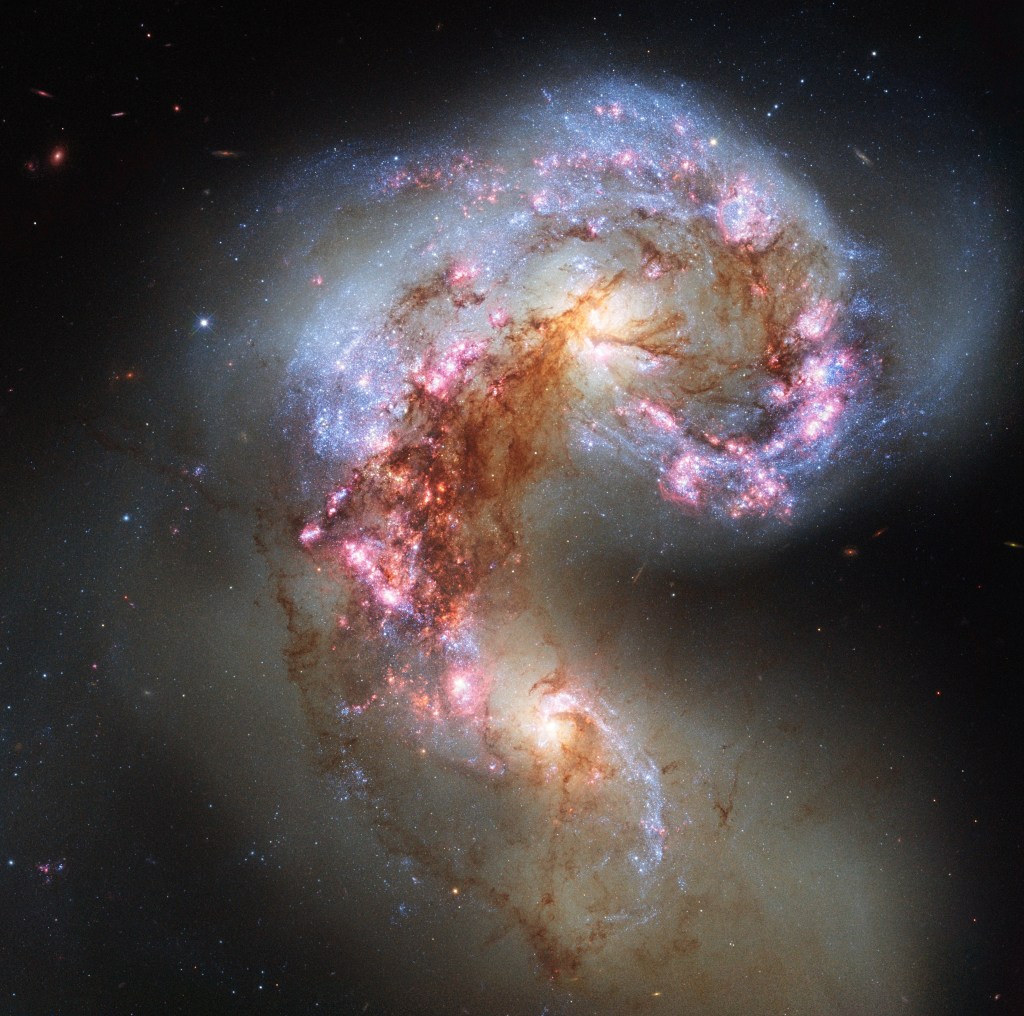

Galaxy Details and Mergers
Galaxies evolve through gravitational interaction with their neighbors, creating a menagerie of forms.
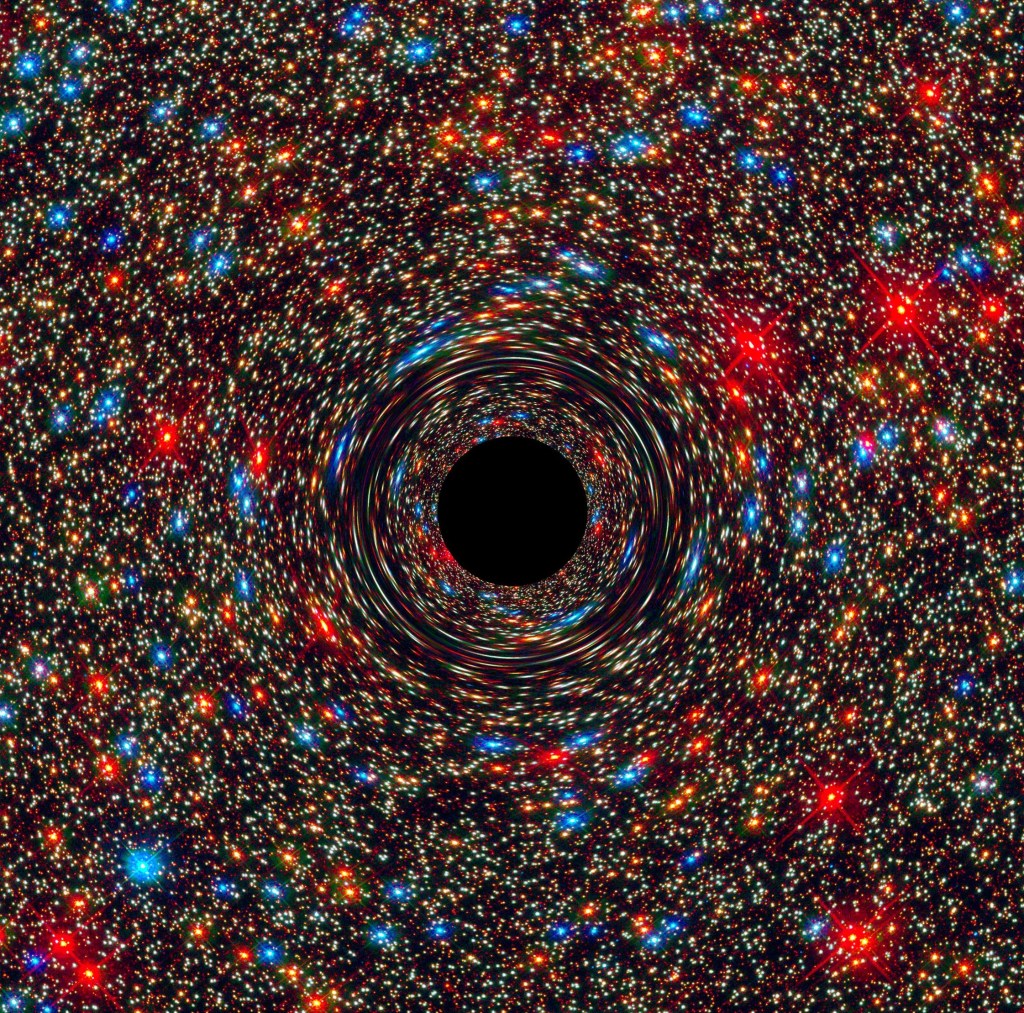

Monster Black Holes are Everywhere
Supermassive black holes lie at the heart of nearly every galaxy.
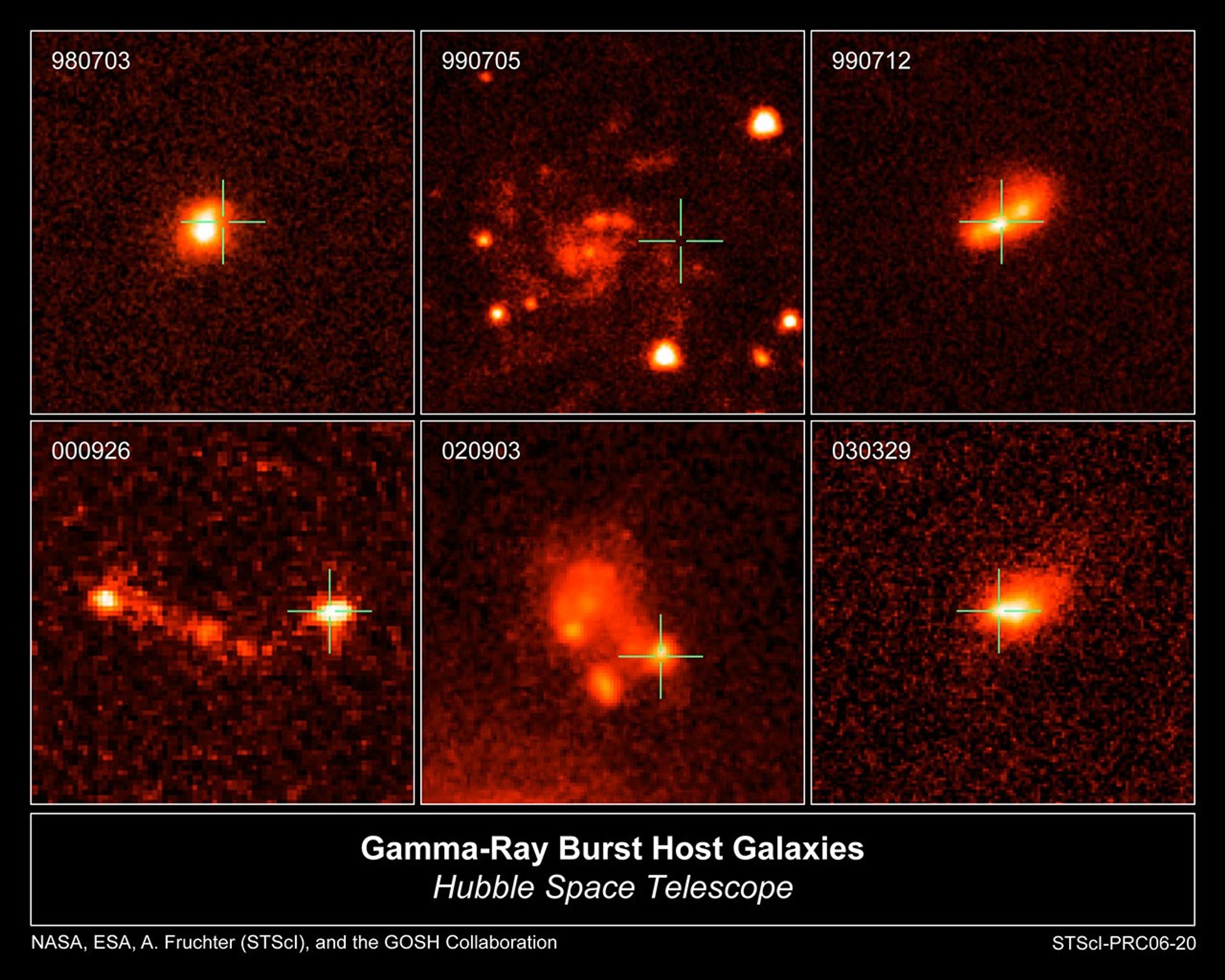
Homing in on Cosmic Explosions
Hubble helps astronomers better understand and define some of the largest explosions in the universe.
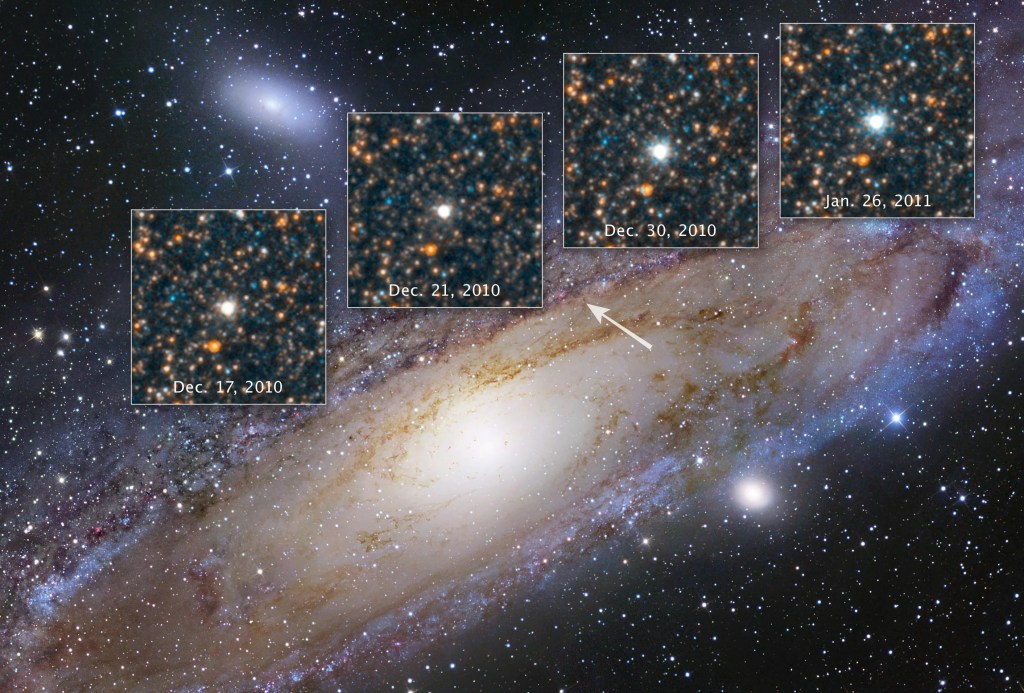

Discovering the Runaway Universe
Our cosmos is growing, and that expansion rate is accelerating.
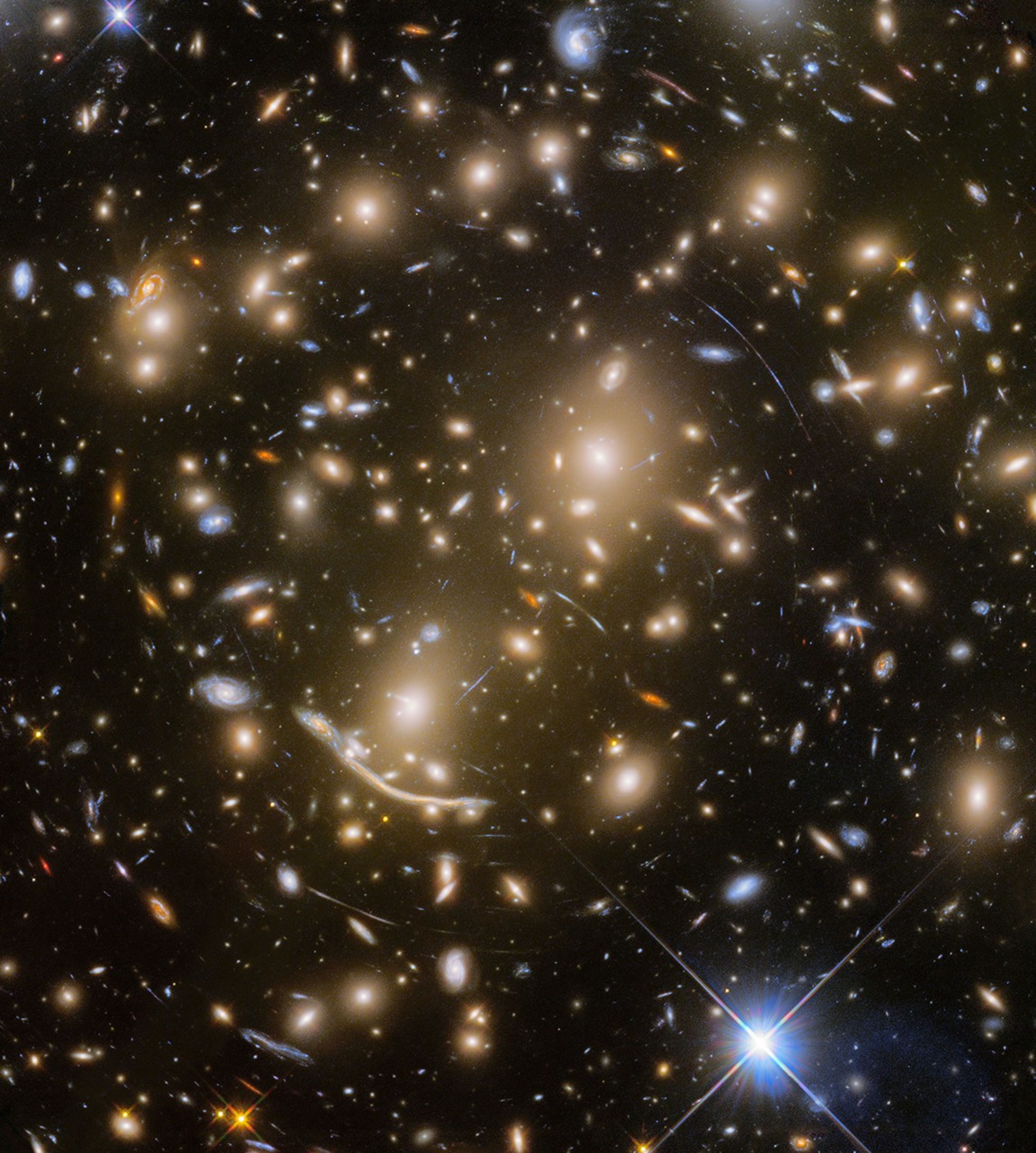

Focusing in on Gravitational Lenses
Gravitational lenses are 'Nature's Boost', expanding our view deeper into space and farther back in time.
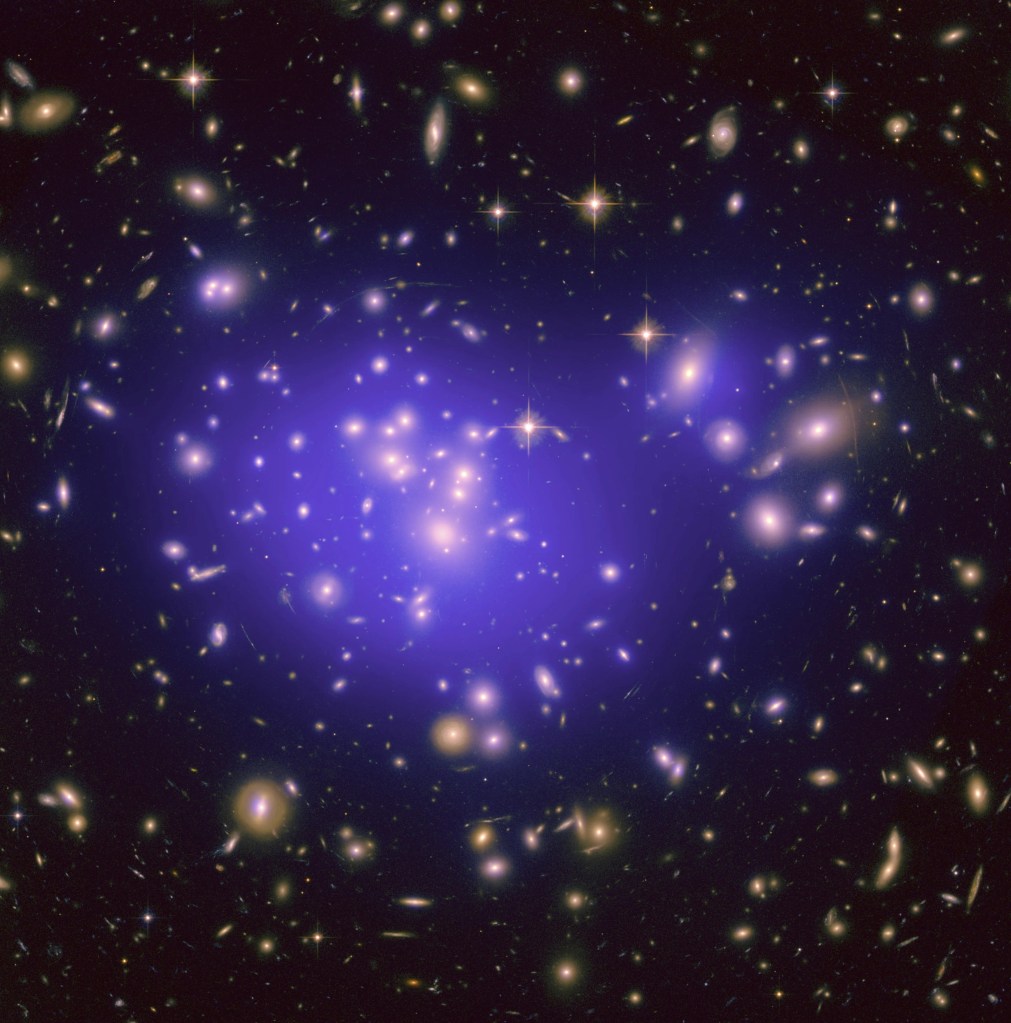

Shining a Light on Dark Matter
The gravitational pull of dark matter guides the formation of everything we can see in the universe.

Mapping the Cosmic Web
Filaments and sheets of matter create an interconnected web that forms the large-scale structure of the universe.